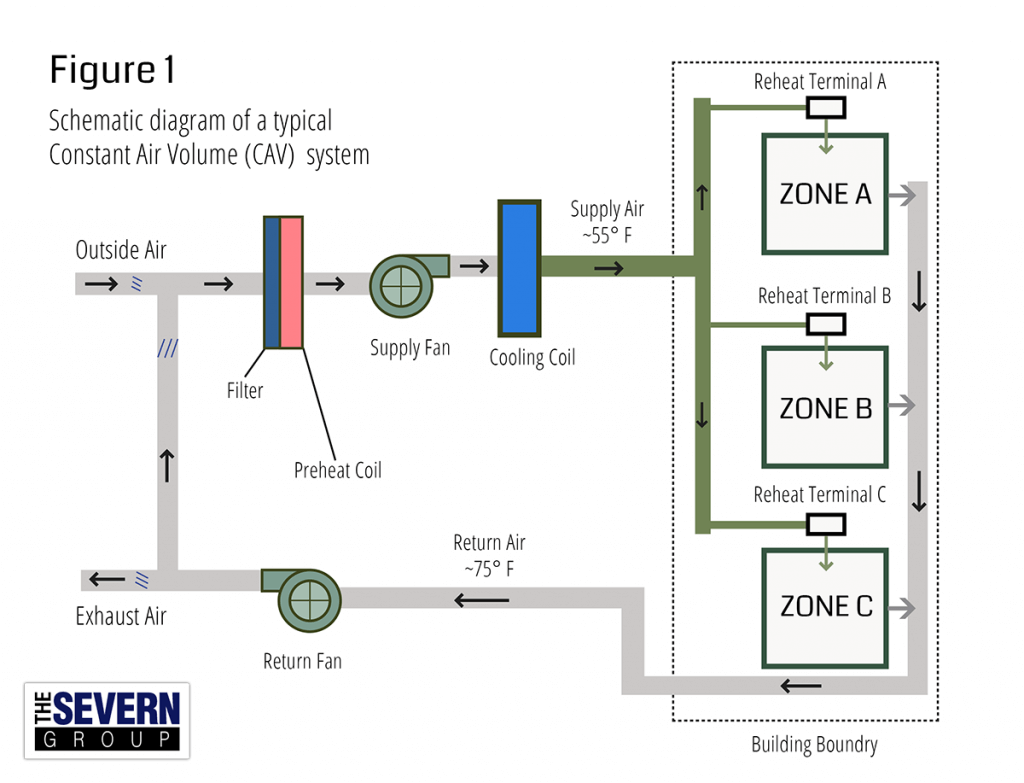
CAV and VAV are types of ventilation systems that supply air to each building region (or "zone") and help regulate internal air temperatures. CAV is the older of the two options, leveraging a centralized duct system and compressor to supply constant air flow to different zones. The VAV (variable air volume) system is one of the most energy efficient ways for building air-handling system. Offers more precise temperature control as the fan speed varies depending on the temperature in the space. The compressor regulates the refrigerant flow to maintain a constant air temperature.
CAV vs VAV HVAC Systems The Severn Group
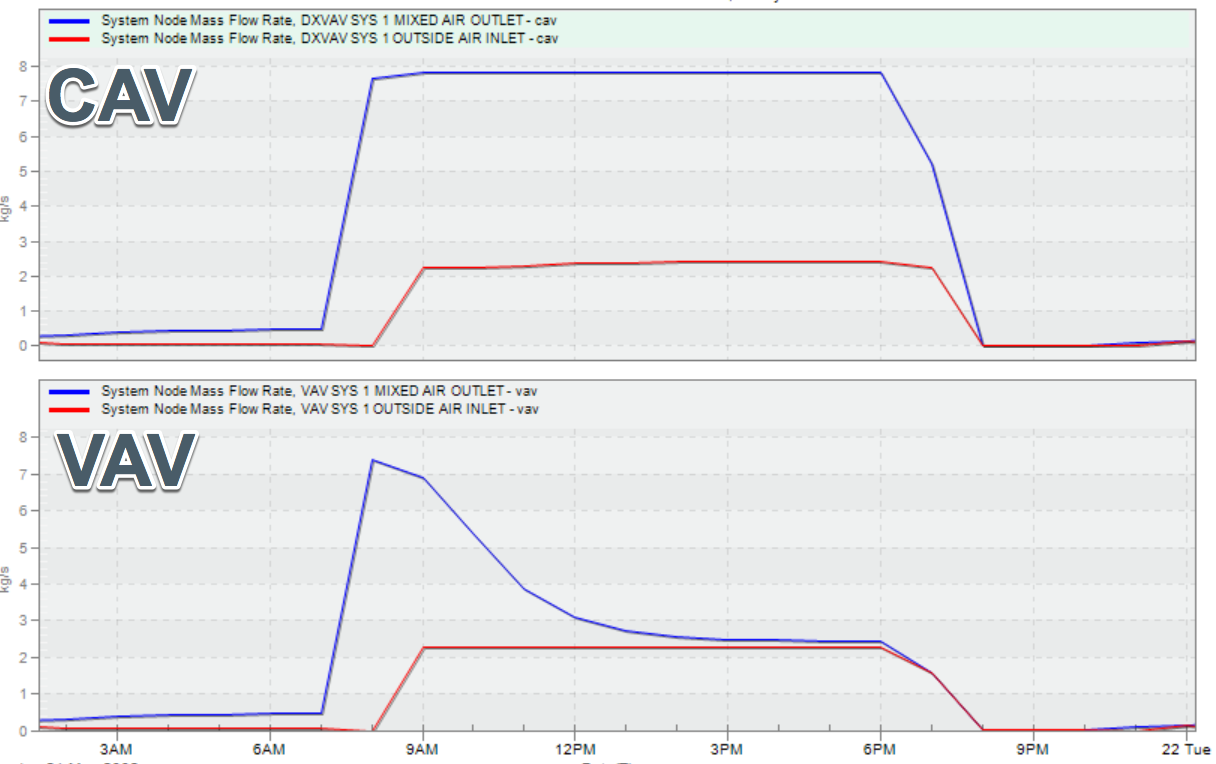
A key decision in HVAC design is selecting an adequate air-handling configuration: constant air volume (CAV) or variable air volume (VAV). Each option has advantages and disadvantages, and using the right configuration enhances comfort and efficiency. In this video, we discuss two common types of HVAC systems used in commercial buildings: Variable Air Volume (VAV) and Constant Air Volume (CAV). We cover th. The difference between a CAV and VAV box is that a VAV box can be programmed to modulate between different flowrate setpoints depending on the conditions of the space. In general, CAV systems are less expensive and simpler to design and install, while VAV systems offer superior performance and energy savings for a higher upfront cost. In most cases, VAV ventilation is the best option because long-term energy savings far outweigh the additional system cost.
Difference in AHU vs. Zone Heating in CAV and VAV Systems Sefaira Support
There are two main differences that define the systems. The first consideration is at the AHU. Specifically, should the AHU be fitted with a motor starter (MS) or a VFD? Figure 2 At the AHU, engineers have to allow for filter loading and future flexibility. Constant or Variable Air Volume? VAV systems are far better at servicing multi-zone buildings with variable HVAC requirements (a multi-story, multi-purpose commercial building for example). They also provide much finer climate control than CAV systems which generate a sawtooth-like temperature profile due to their on/off operation. Constant air volume (CAV) is a type of heating, ventilating,. Due to fan energy savings potential, variable air volume (VAV) systems are more common. However, in small buildings and residences, CAV systems are often the system of choice due to their simplicity, low cost, and reliability.. Definition & Meaning Variable Air Volume (VAV) System Basics, Meaning Let's understand the basics of variable air volume system. Some systems provide an immense advantage to humanity. It acts as shielding and offers maximum comfort. One of the efficient ones that help in practical ways is the VAV system.

VAV vs. CAV Right Answers to the Wrong Questions Engineered Systems Magazine
When desgning a ventilation system, we often come across the terms "VAV", "CAV" and "Constant Pressure Control". In this article I would like to explain what these terms mean exactly, when which option is used and what you need to pay attention to when designing and adjusting an automated ventilation system. March 10, 2022 0 5819 Variable Air Volume (VAV) is the most used HVAC system in commercial buildings. In this article we'll discuss the Variable Air Volume system and single duct VAV boxes with reheat coils.
A variable air volume (VAV) system is designed to meet the heating load of a building with the minimum supply airflow defined via the "Minimum Turndown Ration" value (typically 30% of the full airflow capacity). So the main difference in a VAV system, compared to a CAV system, is the VAV terminal. This is located just on the branch coming off of the main duct. Each VAV box serves a certain zone (room or group of rooms). The VAV box is connected via a cable to a thermostat which is located within the room, or the zone. The thermostat will indicate to.

VAV Systems in ApacheHVAC
The VAV damper modulates in response to variable static pressure to deliver a constant air volume Vconst. to the conditioned zone by the setpoint value within the limits of Vmin to Vmax. The main difference between a VAV and CAV is that: Variable air volume (VAV), the temperature of the air supplied remains constant, but the volume varies. Variable air volume (VAV) systems enable energy-efficient HVAC system distribution by optimizing the amount and temperature of distributed air. Appropriate operations and maintenance (O&M) of VAV systems is necessary to optimize system performance and achieve high efficiency.




