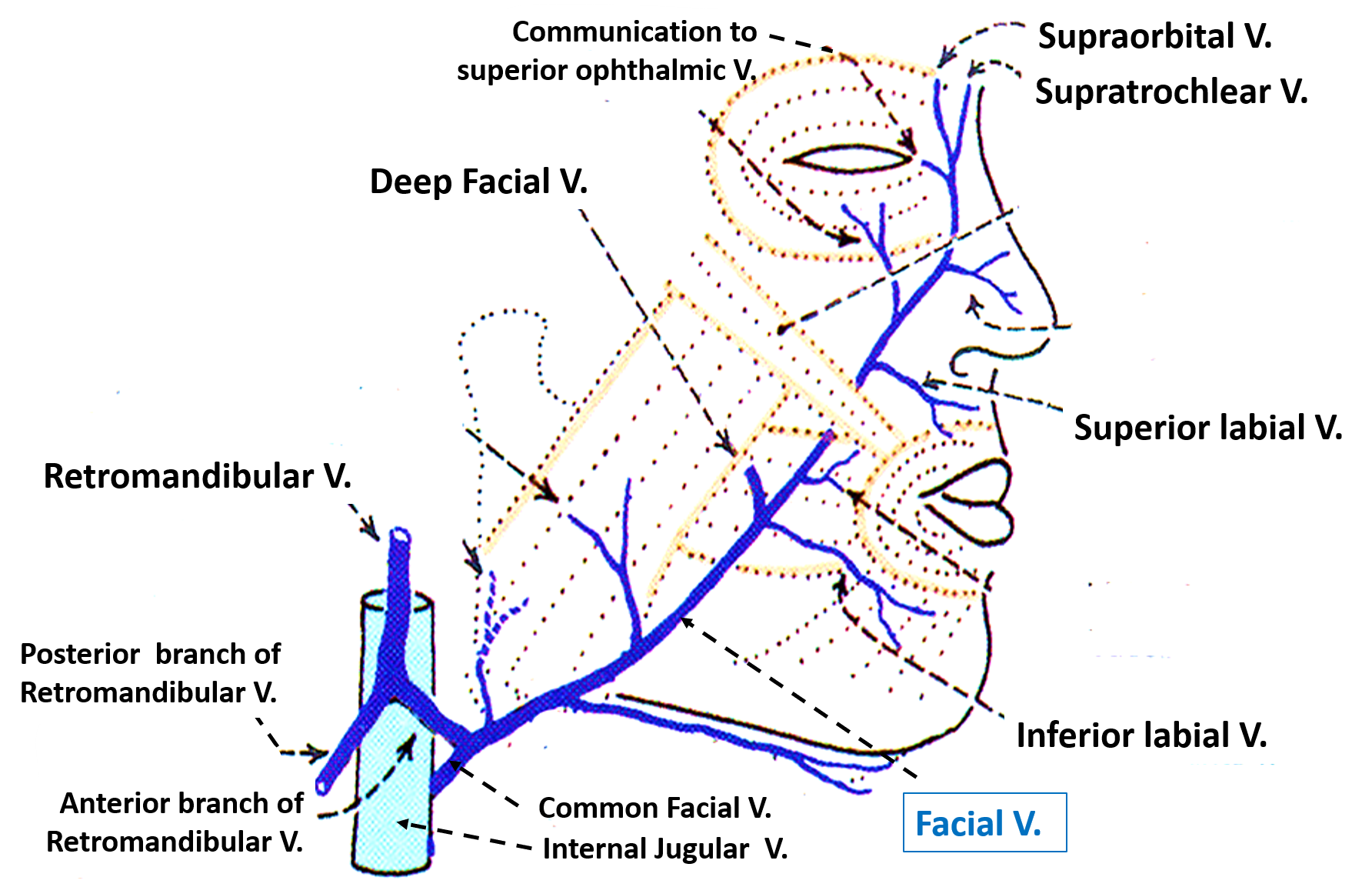
Anatomically, the venous drainage can be divided into three parts: Venous drainage of the brain and meninges: Supplied by the dural venous sinuses. Venous drainage of the scalp and face: Drained by veins synonymous with the arteries of the face and scalp. These empty into the internal and external jugular veins. The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. The facial veins stem from the angular veins on each side of the root of the nose.
Face Venous and Lymphatic Drainage , Anatomy QA
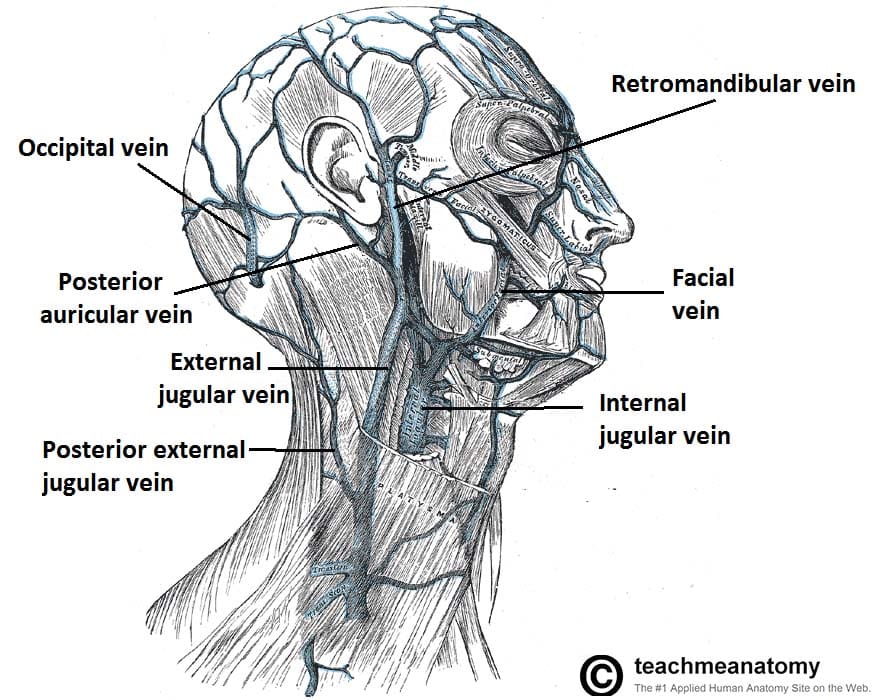
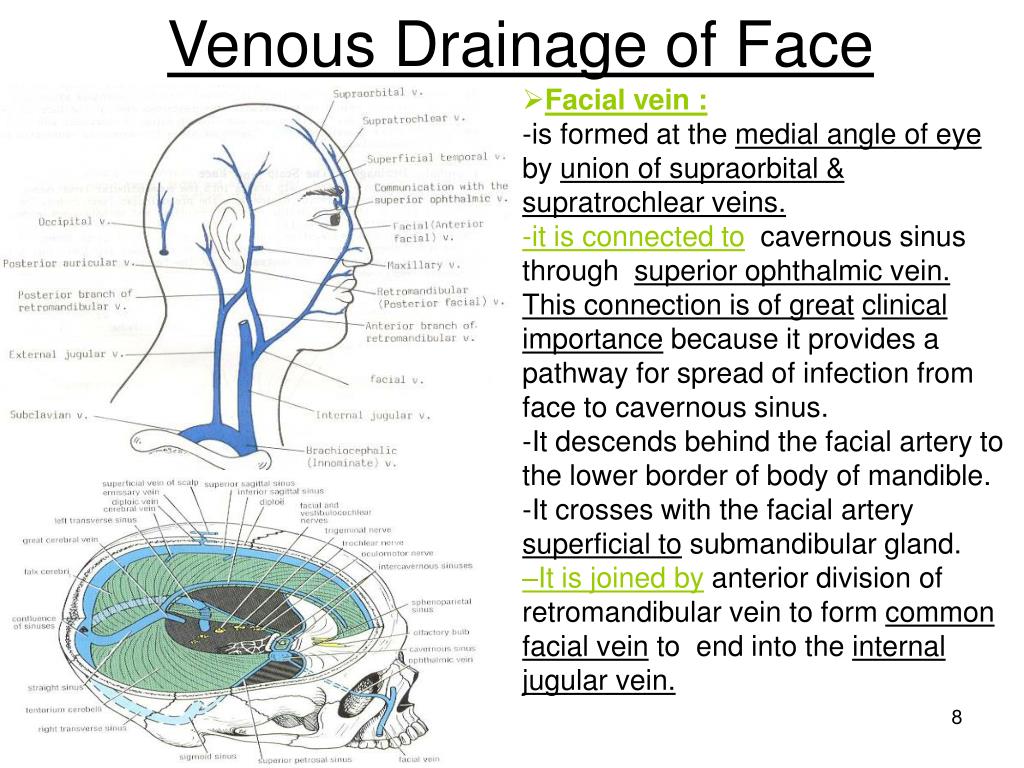
The venous drainage of the scalp divides into superficial and deep. The superficial veins of the scalp, starting anteriorly and moving posteriorly, are the supratrochlear and supraorbital veins, respectively, the superficial temporal veins and their branches, the posterior auricular vein, and the occipital vein and its branches. This article will discuss the arterial supply and venous drainage of the face and scalp. Contents Facial artery Angular artery Inferior labial artery Superior labial artery Maxillary artery branches Buccal artery Inferior alveolar artery Submental artery Other branches of the external carotid artery Posterior auricular artery Occipital artery Venous drainage of face Most of the venous blood from the tissues of the face is drained into the internal jugular vein ( Read more! ). Extracranial veins of the face form several important connections with the intracranial veins. These also include a clinically relevant pathway involving the cavernous sinus. Check it out Many variations in the anatomy of the common facial vein have been described, including the unusual drainage of the common facial veins into the subclavian and the external jugular veins bilaterally, along with an undivided retromandibular vein continuing as the external jugular vein and the anterior facial vein opening into the internal jugular.
Venous Drainage of the Head and Neck Dural Sinuses TeachMeAnatomy
The main venous drainage of the face is completed by the facial, buccal, mental, and infraorbital veins. They drain into the internal jugular or the pterygoid plexus. The venous drainage of the scalp is rich and is provided by the occipital, posterior auricular, and superficial temporal veins. The veins of the face and scalp are highly variable. The systemic venous channels are further classified as superficial veins, deep veins, or venous sinuses. The superficial, or cutaneous, veins reside just beneath the surface of the skin. They channel blood from cutaneous tissues to deep veins via perforations in the deep fascia. Most of the deep veins share routes with the arteries, and many. Venous Drainage. The venous drainage of the scalp can be divided into superficial and deep components. The superficial drainage follows the arterial supply: superficial temporal, occipital, posterior auricular, supraorbital and supratrochlear veins.. The deep (temporal) region of the skull is drained by the pterygoid venous plexus.This is a large plexus of veins situated between the temporalis. The facial vein (or anterior facial vein) is a relatively large vein in the human face.It commences at the side of the root of the nose and is a direct continuation of the angular vein where it also receives a small nasal branch. It lies behind the facial artery and follows a less tortuous course. It receives blood from the external palatine vein before it either joins the anterior branch of.

Face Muscles, Facial artery and Vein, Nerve supply Anatomy QA
These findings suggest that blood from the dermis of the face is collected by the polygonal venous network and enters the loop vein through the cutaneous branches, after which blood flows away from the face through the superficial temporal vein, the facial vein, and the communicating branches and enters the deep veins. In this video we will study about the venous drainage of Face in brief. #eoms
The facial vein, also referred to as the anterior facial vein, is a paired vessel and the main vein of the face. The facial veins stem from the angular veins. The Venous Drainage of the Central Nervous System star star star star star_half based on 77 ratings Original Author (s): Sam Barnes Last updated: July 18, 2023 Revisions: 43 format_list_bulleted Contents add The central nervous system consists of the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem and spinal cord.
PPT Skin innervation of the face PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID966517
The common facial vein drains into the Internal jugular vein. Deep Connections of Facial Vein Facial communicates with the cavernous sinus through: the angular vein and superior ophthalmic vein -> Cavernous sinus. the deep facial vein and pterygoid plexusus-> emissary vein-> cavernous sinus. Background and Objectives: The facial vein is the main collector of venous blood from the face. It plays an important role in physiological as well as pathological context. However, to date, only limited data on the course and tributaries of the facial vein are present in contemporary literature.




