A virtual retinal display ( VRD ), also known as a retinal scan display ( RSD) or retinal projector ( RP ), is a display technology that draws a raster display (like a television) directly onto the retina of the eye. History Virtual Retinal Displays work more like the CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitors and TVs of days displayed, where an image raster is drawn on the back of a phosphorescent screen. Except, in this case, the image is drawn directly onto the retina of the eye.
Virtual Retinal Display Latest Seminar Topics Project Topics
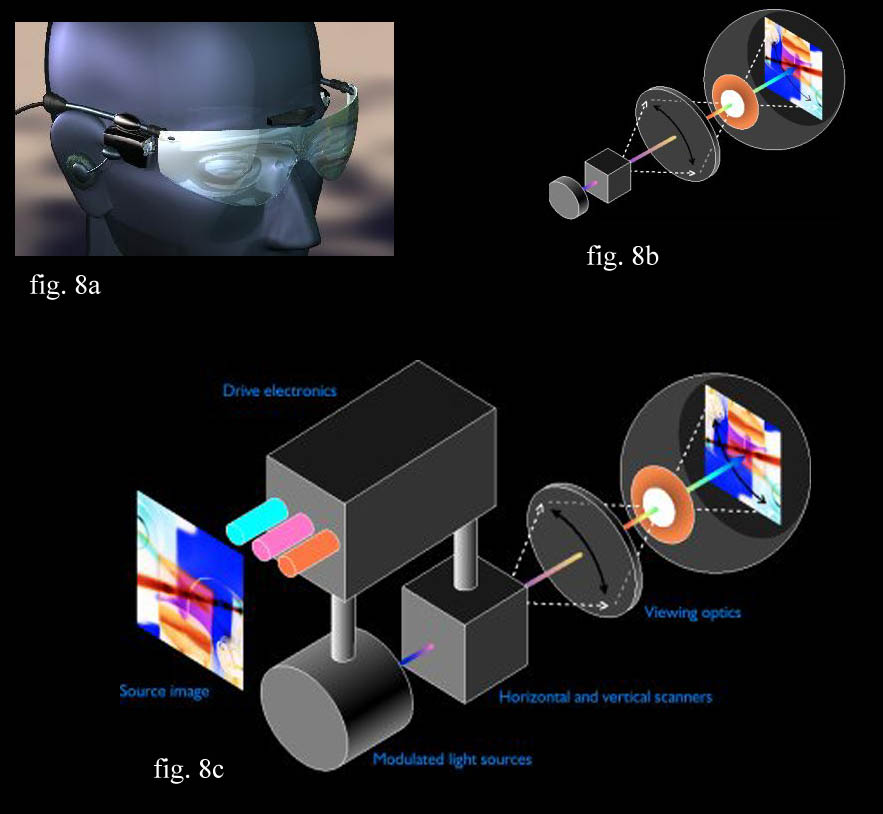
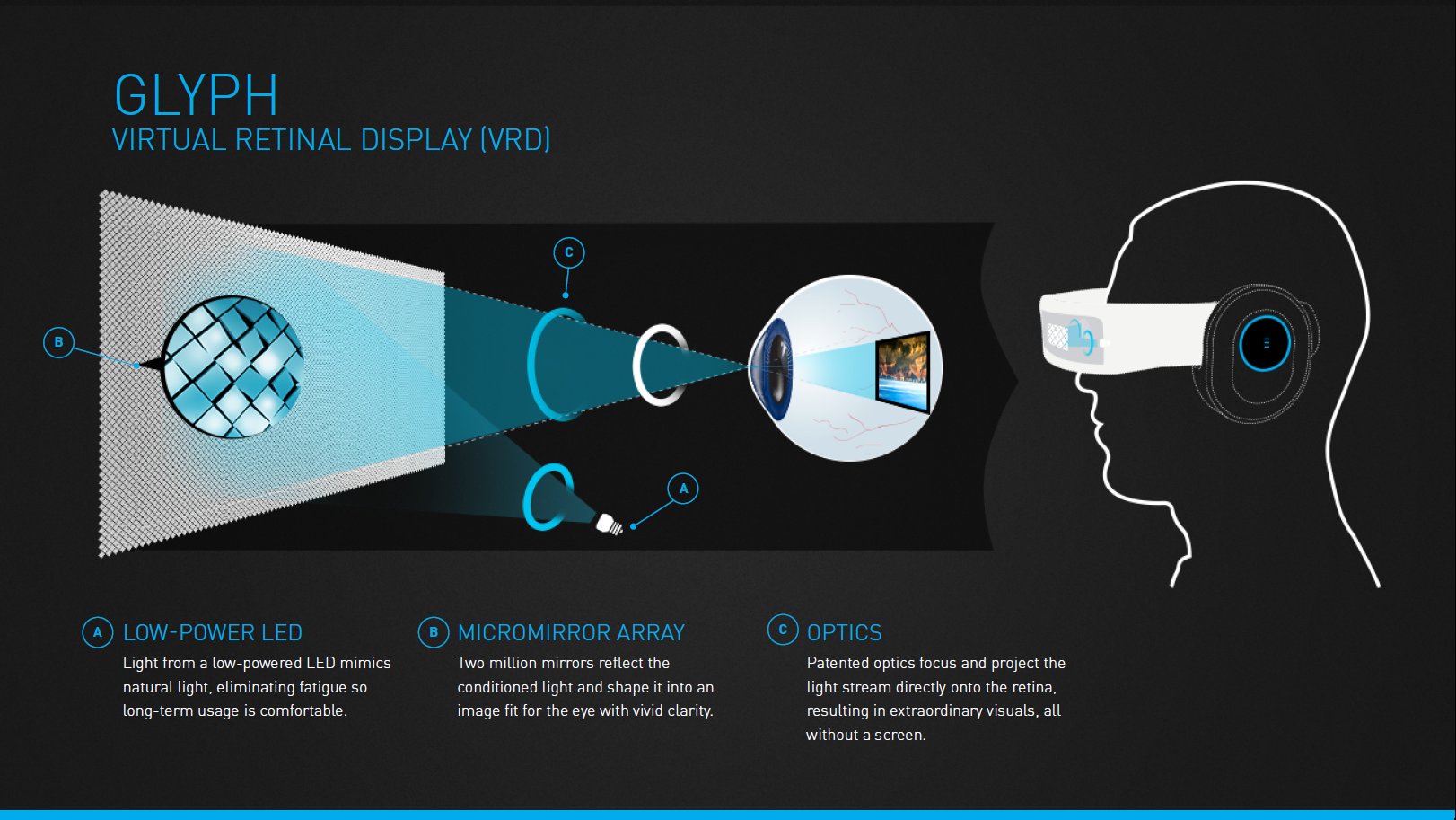
A Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is a type of display technology that projects images directly onto the retina of the eye. Unlike traditional display technologies like LCD and OLED screens, VRD technology eliminates the need for a physical screen, making it possible to display images directly in front of the user's eyes. The Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is a new display technology that scans modulated low energy laser light directly onto the viewer's retina to create a perception of a virtual image. The Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is a new technology for creating visual images. It was developed at the Human Interface Technology Laboratory (HIT Lab) by Dr. Thomas A. Furness III. The VRD creates images by scanning low power laser light directly onto the retina. INTRODUCTION: The Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is a new technology for creating visual images. It was developed at the Human Interface Technology Laboratory (HIT Lab) by Dr. Thomas A. Furness.
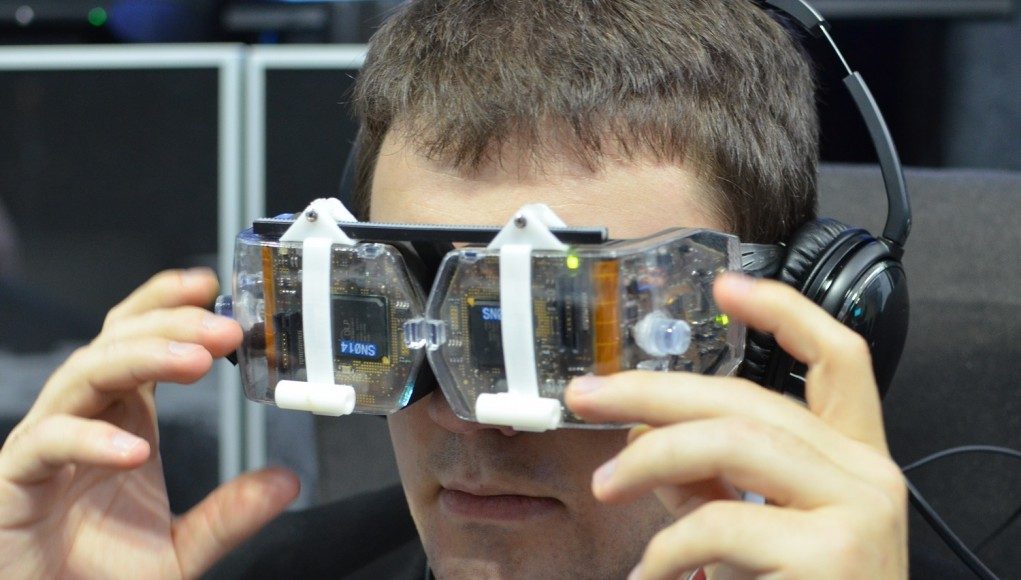

Avegant Virtual Retinal HMD Handson and CEO Interview Video
He also helped invent the virtual retinal display technology in the early 90s, which is being used as some of the basis of Magic Leap's lightfield display technologies. Tom has continued to be a virtual reality visionary, and has some pretty inspiring ideas the future of the metaverse and education through the Virtual World Society. Virtual retinal display technology Abstract: All the technological developments required to achieve useful operation of miniature, laser scanned, virtual retinal displays have been demonstrated. Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is an advanced technology for creating visual images. Dr. Thomas A. Furness III created it at the Human Interface Technology Laboratory (HIT Lab). Low power laser. The Virtual Retinal Display The VRD scans modulated, low-power laser light to form bright, high-contrast, and high-resolution images directly onto the retina. This technology is related to the technology underlying the scanning laser ophthalmo-scope (SLO) (4) but with the sole intent of image display, not acquisition. The VRD accepts the.

HandsOn with Avegant's Glyph Virtual Retinal Display Prototype (CES 2014) YouTube
In the naive and simplified model of virtual retinal display technology, three lasers (red, green and blue, for a full-color image) scan across the retina to allow the subject to perceive an. The Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is a unique approach to developing a high-resolution head- mounted display currently under development at the University of Washington's Human Interface Technology (HIT) Laboratory. Rather than looking at a screen though a magnifier or optical relay system, the viewer of the VRD has a scanned beam of light enter the pupil of the eye and focused to a spot on.
It is concluded that for a subset of low-vision users, the Virtual Retinal Display technology is very promising as a basis for future low- vision aids. This pilot study examined the performance of an alternative computer visual interface, the Virtual Retinal Display (VRD), for low-vision use. The VRD scans laser light directly onto the retina, creating a virtual image. Since visually impaired. At one end of the spectrum is virtual reality (VR) display, which effectively extends the field of view (FOV), blocks the entire ambient, and offers an immersive virtual environment independent of the user's real surroundings.
Brýle Avegant Glyph s virtuální realitou by mohly konkurovat Oculus Rift cdr.cz
INTRODUCTION The Virtual Retinal Display (VRD) is a new technology for creating visual images. It was developed at the Human Interface Technology Laboratory (HIT Lab) by Dr. Thomas A. Furness III. The VRD creates images by scanning low power laser light directly onto the retina. This special method results in images that are bright, high. Its most important underpinning technology is called Virtual Retinal Display, which offers Avegant a distinct advantage over competitors like Oculus and Google Glass. Those are fundamentally.




