Windows's default allocation unit size is 4096 bytes (4 kilobytes), which is pretty small, and on most computers, it's unlikely this will lead to a lot of wasted space. If you make your allocation unit size too small, it can lead to a slower system - allocation will take longer, as there will be more allocation units assigned to each file. Each allocation unit winds up holding only a fraction of the total file. For example, if you have a 4096-byte allocation unit size and you have a 12 KB file, you'd need to use three allocation units (or blocks) to store the complete file. The more blocks you use to store a file, the greater the possibility for fragmentation, and the more blocks.

Which Allocation Unit Size Is Best for Your Drive? Make Tech Easier
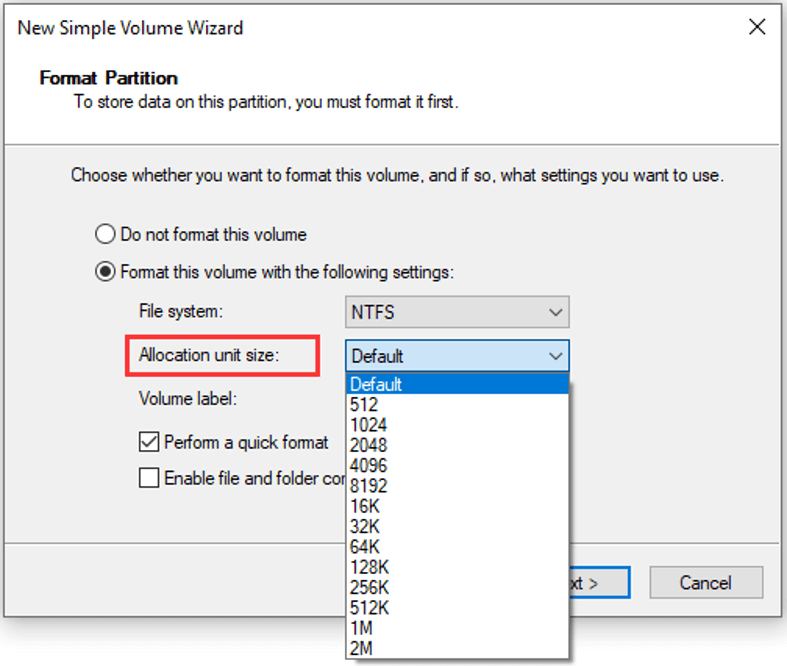
Formatting a volume from Windows Explorer when the Allocation Unit box in the Format dialog box lists Default Allocation Size. By default, the maximum cluster size for NTFS under Windows NT 4.0 and later versions of Windows is 4 kilobytes (KB). This is because NTFS file compression is not possible on drives that have a larger cluster size. You can change allocation unit size for a certain partition in File Explorer, which is also a common way to check the cluster size. Here's the steps: Step 1: Double-click This PC to open File Explorer. Step 2: Right-click the partition for which you want to change cluster size, and then choose Format. Step 3: In the pop-up window, you can see. The allocation unit size directly affects how efficiently your hard drive or SSD can read and write data. Here's why it has such a big impact: Smaller units - Your drive has to scan through more units to find all the blocks for a file. This causes more latency when accessing data. Larger units - Fewer units means faster lookups and less. An allocation unit is a part of the file format system in which a storage drive is formatted. In Windows's default file format system, all drives below 16TB have a default allocation unit size of 4KB. The allocation unit is the unit of storage a file can take up on the drive. This means that if you end up with a file one byte short of 4KB, it.
What Is Allocation Unit Size & How to Change It MiniTool Partition Wizard
Basically, the allocation unit size is the block size on your hard drive when it formats NTFS. If you have lots of small files, then it's a good idea to keep the allocation size small so your hard drive space won't be wasted. If you have lots of large files, keeping it higher will increase the system performance by having fewer blocks to seek. Allocation Unit Size, what is it and what to set it to? This video tutorial explains what Allocation Unit Size to use for what situation, to help you solve h. Allocation unit size does have an effect on drive performance. Especially mechanical hard drives. Basically, the bigger you make the allocation unit size, the fewer the total number of allocation units. This makes sense because your "plots" of drive real estate are larger. So when your computer has to look up the physical location of your. Using a larger size than the necessary allocation unit can cause unnecessary fragmentation on the drive. This is even more of an issue for hard drives, as solid-state drives ( SSD s) are less likely to cause performance issues due to fragmentation. In most cases, Microsoft recommends an allocation unit size of 4 KB.

Which Allocation Unit Size Is Best for Your Drive? Make Tech Easier
Format a Drive in File Explorer. To format a hard drive or SSD in Windows 11, open File Explorer, browse to "This PC," right-click the drive, and select "Format" to start the process. When formatting, consider the capacity, file system, allocation unit size, and volume label. Select NTFS if using the drive only with Windows and exFAT if also. Allocation Unit Size. When formatting a volume, most people never give the Allocation Unit Size option a second thought. Allocation Unit Size is set to default, and most users simply click Next to.
Open File Explorer. Click on This PC on the left side. Under the "Devices and drives" section, right-click the USB drive and select the Format option. (Image credit: Future) Use the "File system. Also known as the allocation unit size, cluster size represents the smallest amount of disk space that can be allocated to hold a file. Because ReFS and NTFS don't reference files at a byte granularity, the cluster size is the smallest unit of size that each file system can reference when accessing storage. Both ReFS and NTFS support multiple.
What Is Allocation Unit Size & How to Change It MiniTool Partition Wizard
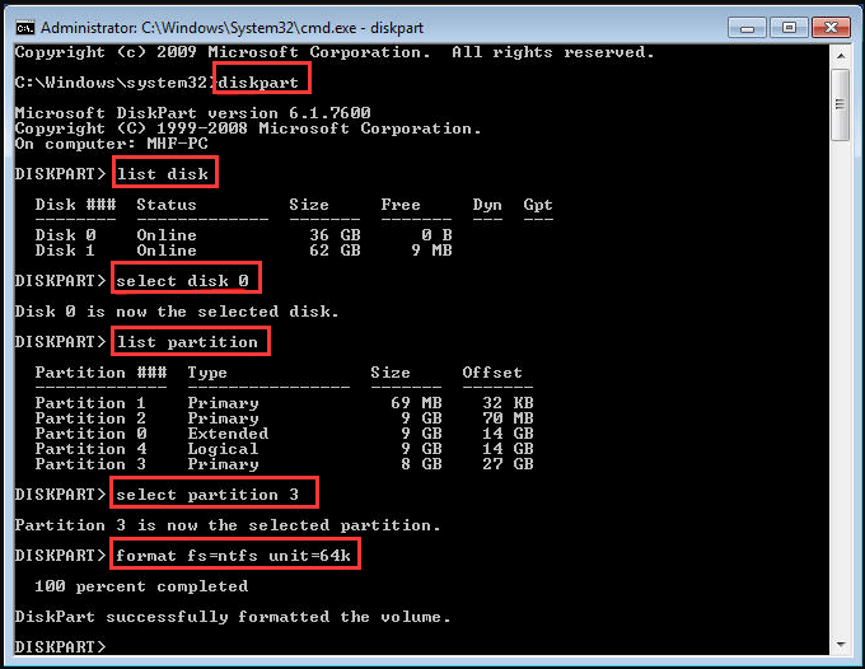
When formatting, you can frequently just select the default allocation unit size. Usually: For SD cards that are 32GB and smaller, select the file system FAT32 and allocation unit size 32 KB. For 64GB cards and larger, select the file system exFAT and allocation unit size 128KB. Employing various allocation unit sizes is not equivalent. Step 3: then type the following commands one by one and hit Enter after each: List disk. Select disk * (* refers to the number of the target disk or partition) List partition. Select partition *. Format fs=exFAT unit=32k (you can just change the 32k to other allocation unit sizes you want.) After the above commands are executed successfully.




