Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by five protozoa: Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale, and most recently implicated P.knowlesi. Infection with P. falciparum is being accounted for more than 90% of the world's malaria mortality and therefore remains an important threat to public health on a global scale. Malaria is a life-threatening illness caused by infection of red blood cells by Plasmodium parasites. Transmission of malaria to humans occurs through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Several species of Plasmodium cause malaria in humans: Plasmodium falciparum — responsible for the majority of malaria related deaths worldwide.

Severe P.falciparum Malaria Case Study Immunopaedia
Malaria infection typically presents with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, chills, sweats, headache, and myalgia. In Western countries, almost all malaria occurs in travelers; therefore, the diagnosis may be missed if a history of travel is not elicited. Microscopic examination of a Giemsa-stained blood film remains the diagnostic test of. Malaria factsheet. Published 16 December 2013. 1. What malaria is. Malaria is a serious and potentially life threatening febrile illness caused by infection with the protozoan parasite, Plasmodium. Clinical features of malaria include: Fever (often 39°C or higher), sweats, and/or chills — absence of fever should not remove the suspicion of malaria. Headache. General malaise, lethargy, and fatigue — somnolence is more common in children than in adults. Anorexia, gastrointestinal disturbance (such as nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting. Malaria is a parasitic infection transmitted by the Anopheles mosquito that leads to acute life-threatening disease and poses a significant global health threat. Two billion people risk contracting malaria annually, including those in 90 endemic countries and 125 million travelers, and 1.5 to 2.7 million people die in a year.[1] The Plasmodium parasite has a multistage lifecycle, which leads.

Sahara Group How do You Solve a Problem like Malaria?
Objective Malaria infection could result in severe disease with high mortality. Prognostic models and scores predicting severity of infection, complications and mortality could help clinicians prioritise patients. We conducted a systematic review to assess the various models that have been produced to predict disease severity and mortality in patients infected with malaria. Design A systematic. P. vivax malaria will relieve some of the most vulnerable populations of a significant illness that causes disruption to schooling and work, and can be fatal. If P. vivax malaria is conquered, not only will international targets to eliminate malaria from 35 countries by 2030 be achieved, but a pathway will be The exact number of annual clinical attacks has not been reliably estimated, but it is thought to be more than 100 and less than 400 million.2 That number, whatever it really happens to be, is likely of the same order of magnitude (low hundred millions) as the estimated number of clinical attacks of falciparum malaria, i.e. 247 million according to the World Health Organization,3 or 451. Malaria is a treatable disease. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are the most effective antimalarial medicines available today and the mainstay of recommended treatment for Plasmodium falciparum malaria, the deadliest malaria parasite globally. ACTs combine 2 active pharmaceuticals with different mechanisms of action, including derivates of artemisinin extracted from the plant.

MALARIA PF/ PAN AG RAPID TEST KIT at Rs 25/piece Malaria Kit in
Malaria is a serious infection spread by mosquitoes. If it's not diagnosed and treated quickly, you can die from it. Check if you're at risk of malaria. Malaria is caused by being bitten by an infected mosquito. It can take just 1 bite to get it. The infection is very common in certain parts of the world. It's found in tropical regions, including: Treatment of Severe Malaria Evaluation and Diagnosis Malaria is a common cause of febrile illness in areas where it is transmitted; therefore, the diagnosis and management of malaria should routinely be considered for any febrile person who has traveled to an area with malaria in the weeks to months preceding symptom onset.
Prabin Dahal, Mayfong Mayxay, Elizabeth A. Ashley x Published: January 18, 2022 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003890 Article Authors Metrics Comments Media Coverage Reader Comments Abstract Background Plasmodium vivax infects an estimated 7 million people every year. Abdominal pain. Muscle or joint pain. Fatigue. Rapid breathing. Rapid heart rate. Cough. Some people who have malaria experience cycles of malaria "attacks." An attack usually starts with shivering and chills, followed by a high fever, followed by sweating and a return to normal temperature. Malaria signs and symptoms typically begin within a.
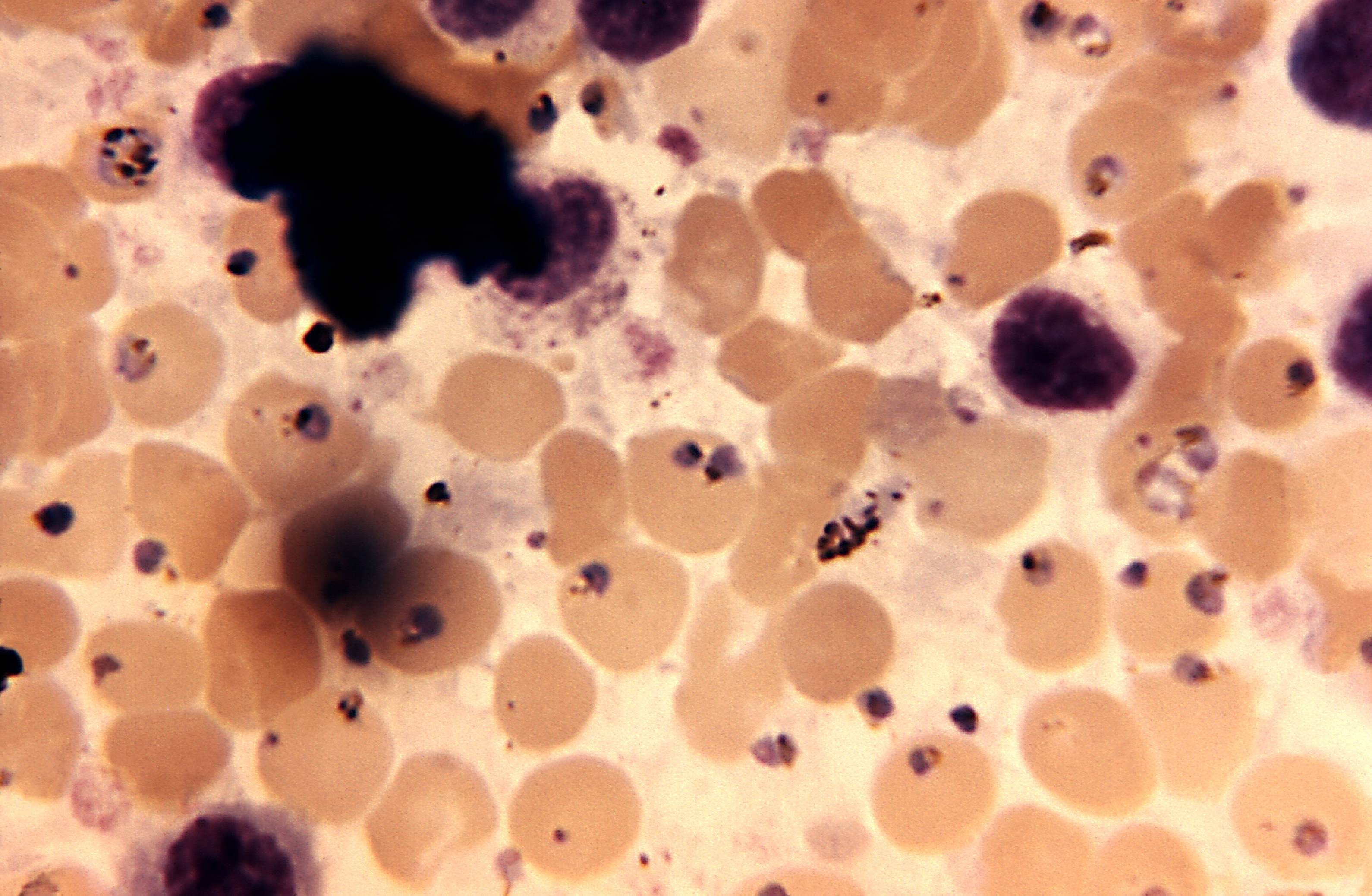
Kostenlose Bild Mikroskopaufnahme, Milz, Gewebe, Autopsie, malariae
Overview. Malaria is a life-threatening disease spread to humans by some types of mosquitoes. It is mostly found in tropical countries. It is preventable and curable. The infection is caused by a parasite and does not spread from person to person. Symptoms can be mild or life-threatening. Mild symptoms are fever, chills and headache. Malaria disease can be categorized as uncomplicated or severe (complicated). In general, malaria is a curable disease if diagnosed and treated promptly and correctly. All the clinical symptoms associated with malaria are caused by the asexual erythrocytic or blood stage parasites. When the parasite develops in the erythrocyte, numerous known.




