An axial flux motor (also known as an axial gap motor, or pancake motor) is a geometry of electric motor construction where the gap between the rotor and stator, and therefore the direction of magnetic flux between the two, is aligned parallel with the axis of rotation, rather than radially as with the concentric cylindrical geometry of the more. The axial flux motor, sometimes referred to as a 'pancake motor', is a type of electric motor where the magnetic field is aligned along the axis of rotation, hence its name. This structure is in contrast to the traditional radial flux motors, where the magnetic field follows a path along the radius of the motor. Components and Working Principle
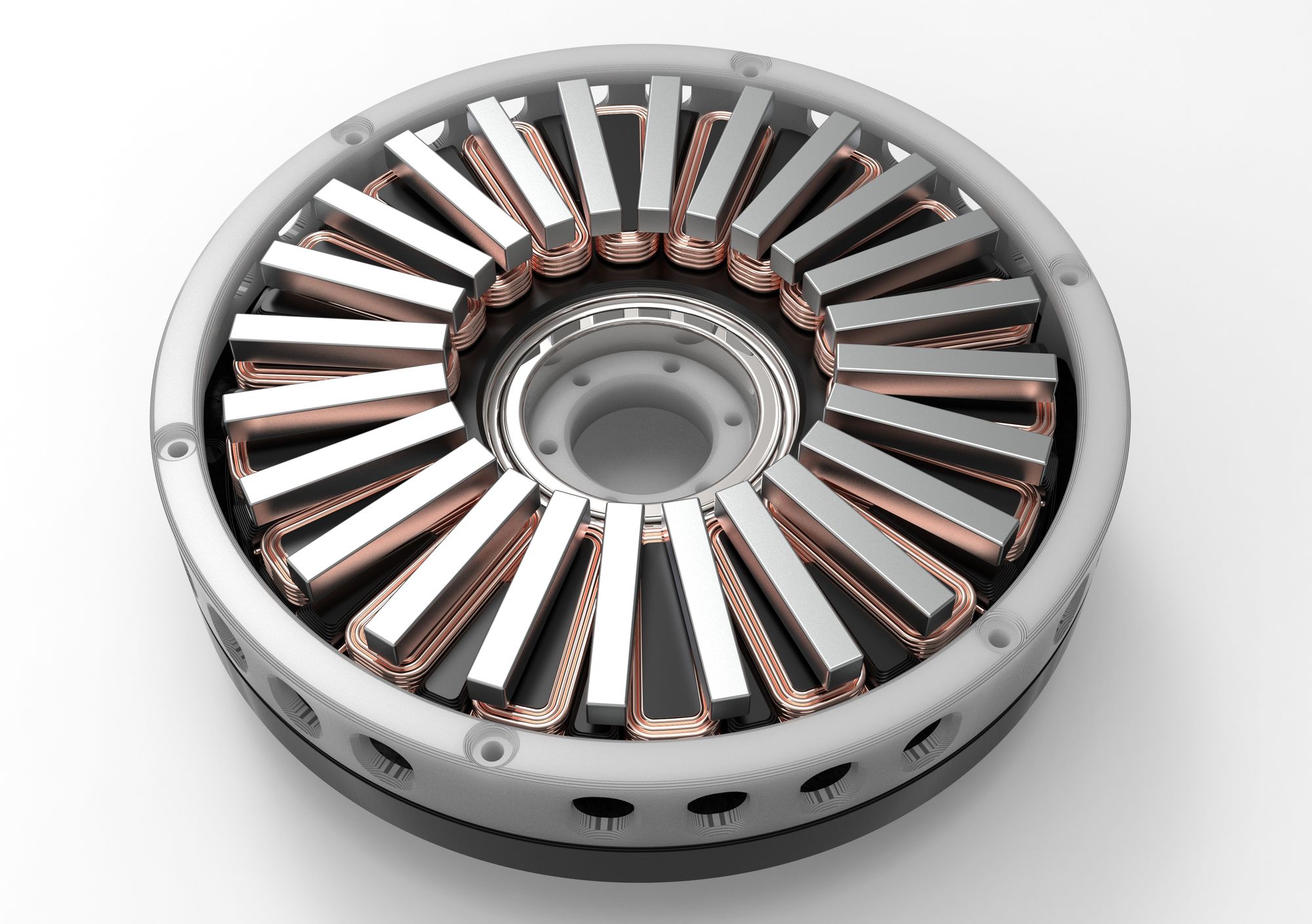

Designing an Ironless Axial Flux Motor
The axial flux design is actually one of the oldest ways of constructing a motor—it's just that, up until relatively recently, it was relegated to niche applications in which the primary requirement was maintaining a low profile. There's a bewildering number of ways to construct a motor, so a brief review of the nomenclature might be helpful. Axial-flux Design, Exploded: This view shows the guts of the Magnax motor, which differs from the traditional layout by putting the one moving part—the rotor—inside the stator. Refinements of this design make it particularly powerful, efficient, and easy to make. Image: Magnax The Infinitum Electric motor is what's known as an axial-flux motor, a design in which the stator's electromagnetic wiring stands parallel to a disk-shaped rotor containing permanent magnets. Axial-flux permanent-magnet (AFPM) motors are a kind of important motor with compact structure, high power density and high torque density. In this review, the progress of AFPM motors and their key technologies are analyzed and described, with emphasis on the topological structures, design and optimization methods and control techniques.
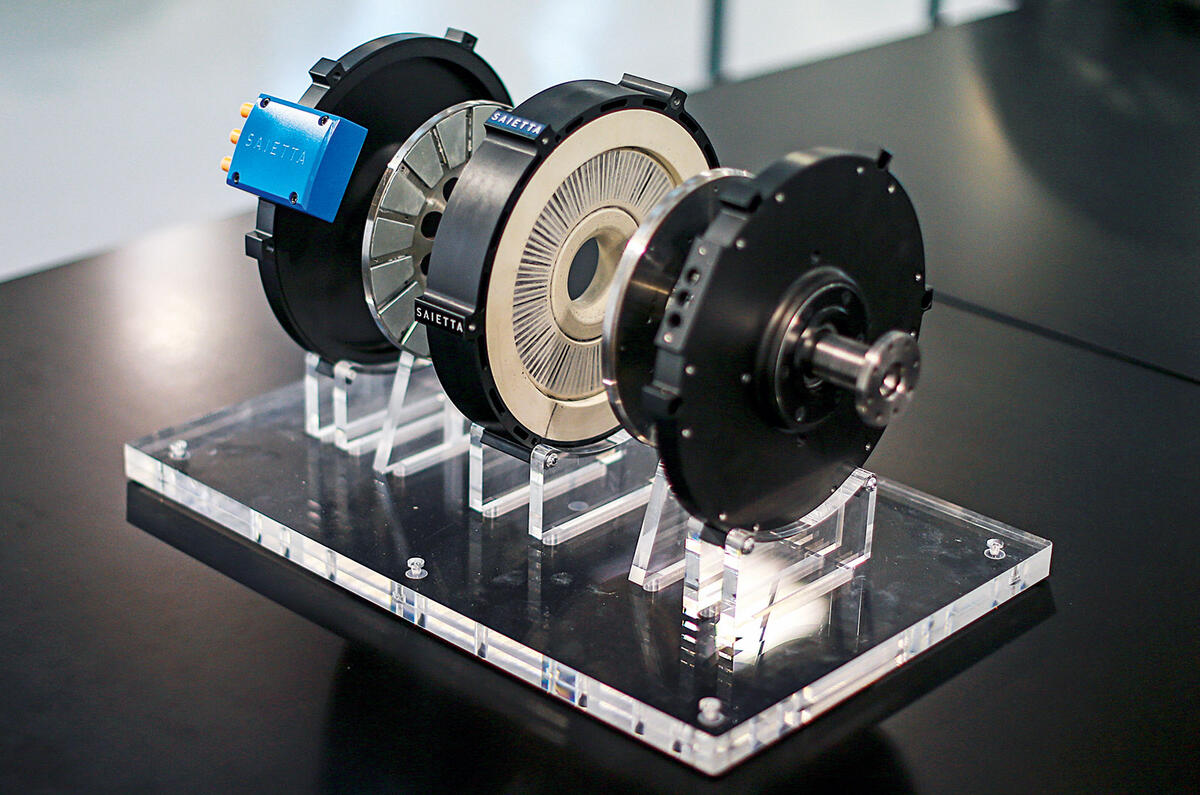
Under the skin is one UK firm's axial flux motor poised for mass
Axial flux permanent magnet (AFPM) motors offer superior power, efficiency, and torque density with their unique flat rotor and stator arrangement. Originally developed for vehicle applications, these motors have seen significant advancements in materials, making them even more powerful and compact. Ongoing research is focused on improving. This paper presents an axial-flux induction motor which has a single stator and two squirrel-cage rotors mounted on individual, independents shafts driving two wheels of an electric vehicle. This novel induction machine inherently behaves as an electromagnetic differential motor and thereby performs the function of both the engine and the differential of a conventional vehicle. Features of the. Axial flux motors, characterized by a unique pancake-like design, have a magnetic flux path parallel to the motor shaft. This configuration results in a compact, lightweight motor with high power density and efficiency. Axial flux motors find significant applications in electric vehicles (EVs) due to their space-efficient design, weight. This paper proposed a new external-rotor yokeless and segmented armature axial flux machine applied in-wheel traction. The loss analysis for the motor cooling casing is performed based on finite-element method, and the height of the cooling fins is optimized to decrease the eddy current loss and increase the efficiency of the motor. Subsequently, epoxy potting is developed to increase the heat.
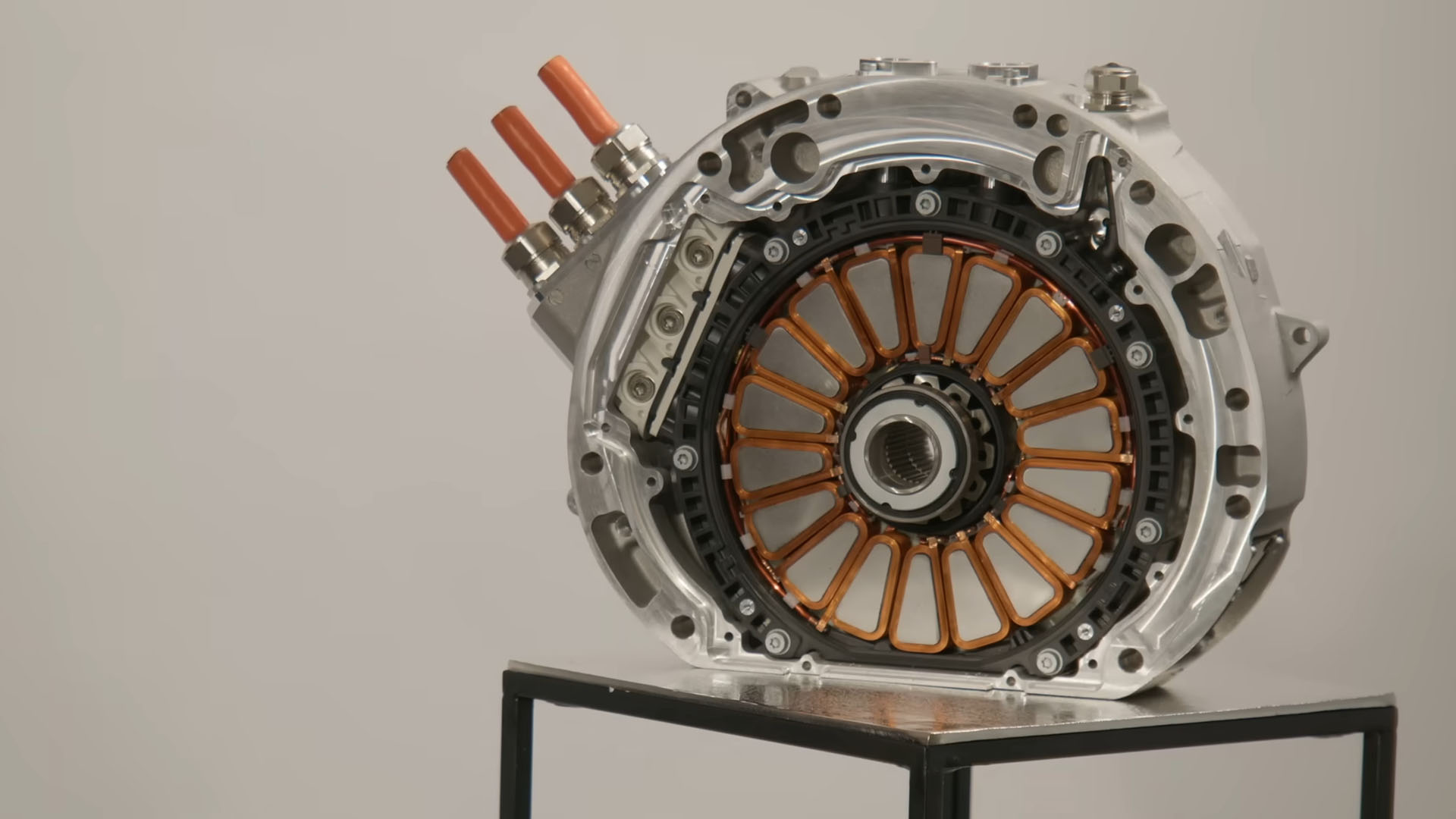
Why Axial Flux Motors Are a Big Deal For EVs The Drive
construction of axial flux machines is the axial attraction between stator and rotor, which is increased by shortening the air gap. This will be more critical in the case of motors, supply their magnetising current from the network, where the air-gap length is implemented as small as possible. The problem almost can be solved using thrust bearings. In terms of converting electricity into a spinning torque, axial flux motors are about as efficient as standard radial flux machines. The big difference is axial flux's smaller size and.
It is shown that an axial-flux permanent-magnet machine with one-rotor-two-stators configuration has generally a weaker efficiency than a radial-flux permanent-magnet machine if for all designs the same electric loading, air-gap flux density and current density have been applied. The Lynch motor, for example, is a type of axial flux motor that dates back to 1979. Usually, the impetus for using an axial flux motor is the ease of construction, but with the right design, they.

Axial Flux Induction Motor for Automotive Applications Electric
Axial flux motor is ideal for high torque density and space-constrained applications. Most people assume that high power density is only determined by fast speed, and they ignore the impact of torque density. The quest for high speed alone will result in limited-service duration and noise. Axial flux motors are considered the ultimate future of electric vehicles and most importantly of electric aviation because they have a high torque-to-weight.




