Lucidchart's Flow Diagram Software Is Quick & Easy To Use. Free 7-Day Trial. Our Diagram Creator Makes It Easy To Share and Edit Your Diagrams—With Anyone, Anytime. Behavioral (or Dynamic) view: emphasizes the dynamic behavior of the system by showing collaborations among objects and changes to the internal states of objects. This view includes sequence diagrams, activity diagrams, and state machine diagrams. In UML 2.2 there are 14 types of UML diagrams, which are divided into these two categories:

Theory of Planned Behavior Diagram
Behavioral UML diagrams Behavioral UML diagrams focus on illustrating the dynamic aspects of a software system, showcasing how it behaves, responds to stimuli, and undergoes state changes during runtime. Types of Behavioral UML diagrams 1. State Machine Diagrams The behavioral diagrams are categorized as follows: use case diagrams, interaction diagrams, state-chart diagrams, and activity diagrams. Use Case Model Use case A use case describes the sequence of actions a system performs yielding visible results. It shows the interaction of things outside the system with the system itself. Activity Diagrams This is the activity diagram and it is powerful. Activity diagrams are very easy for non-technical users to see and understand. When working with a non-technical executive, they may have no idea what UML is, what it stands for, or the components. Behavior Diagrams (Dynamic Modeling): Use Case Diagram (Behavior): Illustrates system functionality from the user's perspective, showing actors and use cases. Activity Diagram (Behavior): Models the flow of activities and actions within a system, including parallel and conditional behavior. State Machine Diagram (Behavior):
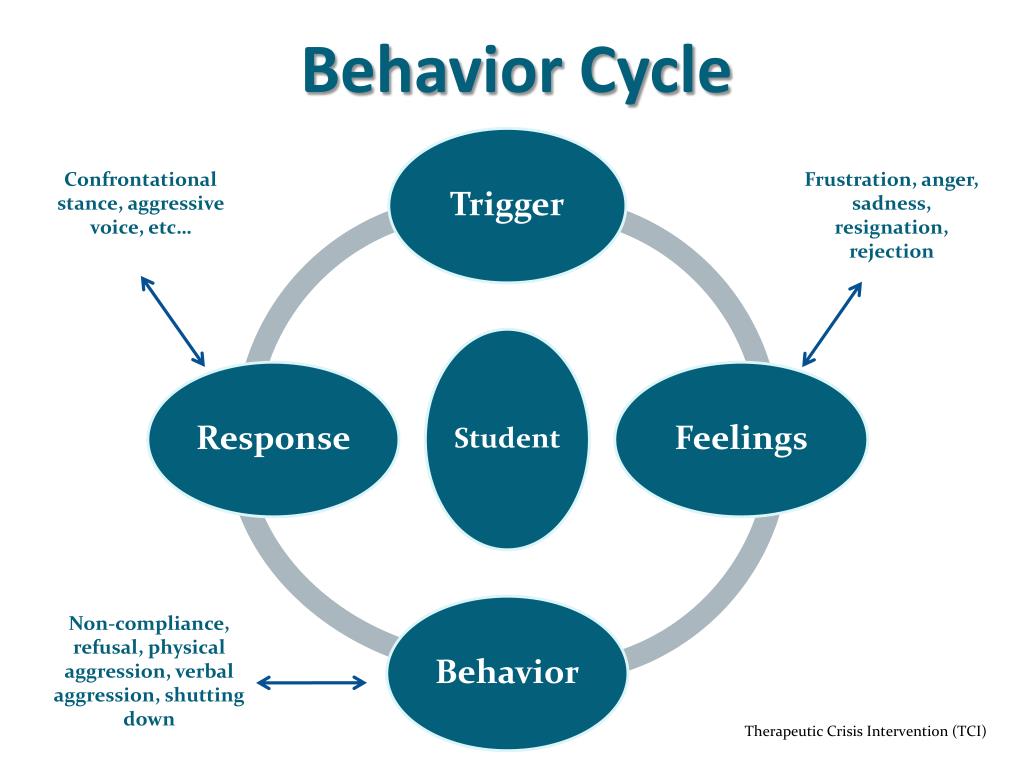
PPT Behavior Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2851146
Timing Diagrams; The UML's behavioural diagrams are used to visualise, specify, construct and document the dynamic aspects of a system. The dynamic aspects of a system represent its changing parts. The UML's behavioural diagrams are roughly organised around the major ways the dynamic aspects of a system are modelled: A behavior diagram is intended to provide clarity, for example, about internal processes, business processes or the interaction of different systems. Depending on the diagram used, a selected aspect is shown. In the Unified Modeling Language (UML), objects are modeled that can change their states through behavior. Behavioural diagrams . The focus here is on dynamic aspects of the software system or process. These diagrams show the functionality of a system and emphasise what must happen in the system being modelled. Let's take a closer look at the many different types of UML diagrams that fall under each category: 1. Structural UML diagrams . Class. In this video, we'll give you a summary and an example of each UML diagram type.00:00 Intro00:58 Class diagram01:19 Object diagram01:35 Component diagram01:5.
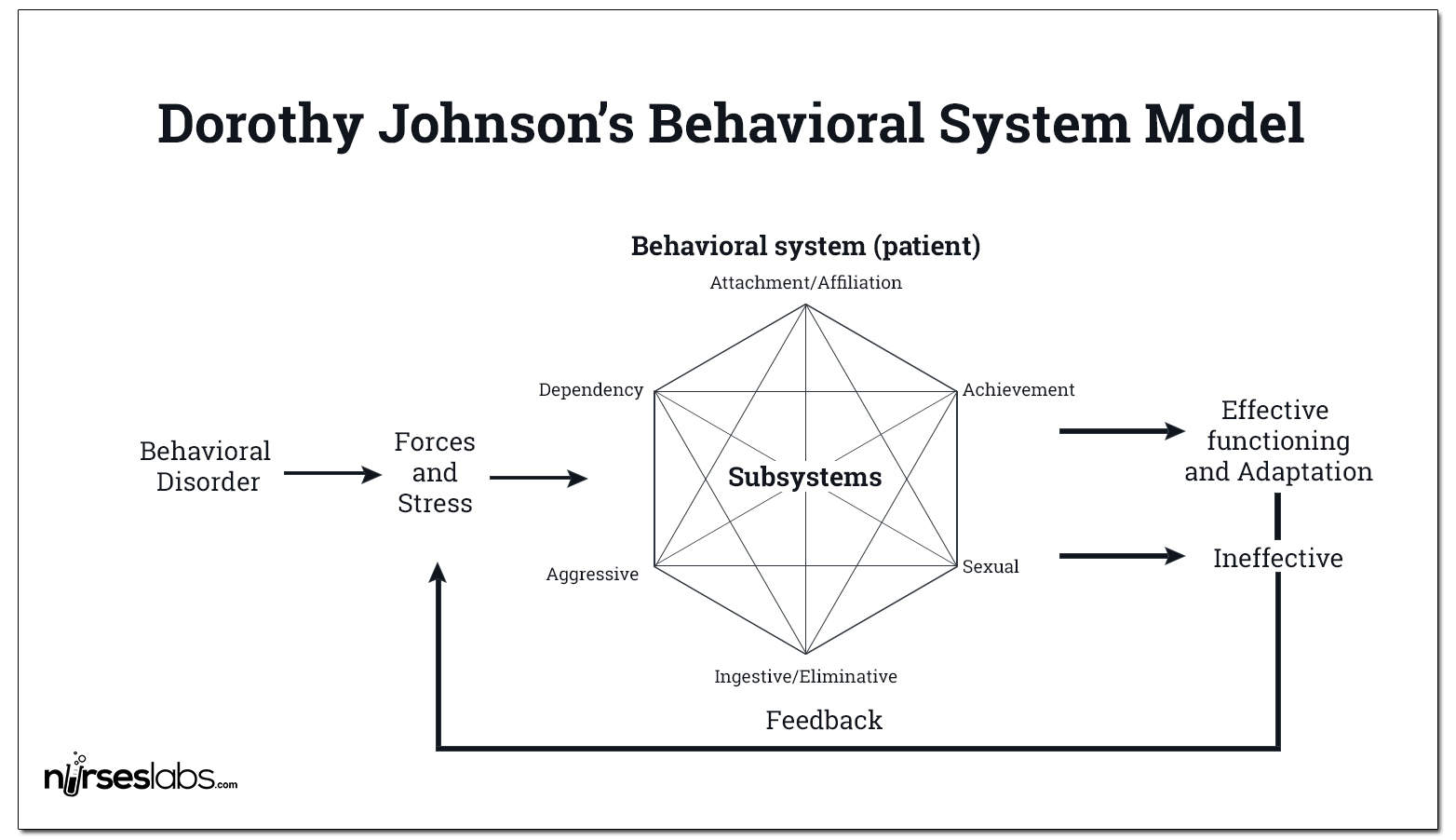
Dorothy Johnson Behavioral System Model Nurseslabs
UML 2.1 defines thirteen basic diagram types, divided into two general sets: structural modeling diagrams and behavioral modeling diagrams. Part two will deal with behavioral modeling diagrams. The Object Management Group (OMG) specification states: "The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a graphical language for UML Behavioral Diagrams depict the elements of a system that are dependent on time and that convey the dynamic concepts of the system and how they relate to each other. The elements in these diagrams resemble the verbs in a natural language and the relationships that connect them typically convey the passage of time.
Behavioral Diagrams - focus on dynamic aspects of the software system Use-case, Interaction, State Chart, Activity Behavioral Diagram Use Case Diagram - high-level behaviors of the system, user goals, external entities: actors Sequence Diagram - focus on time ordering of messages Unlike Structural Diagrams, Behavioural Diagrams can be subdivided into five types of diagrams. Use case Diagram: Use case diagrams consist of a set of use cases, actors and their respective relationships. These diagrams seek to represent the use case view of a system. A diagram of this type illustrates the functionality of a system.
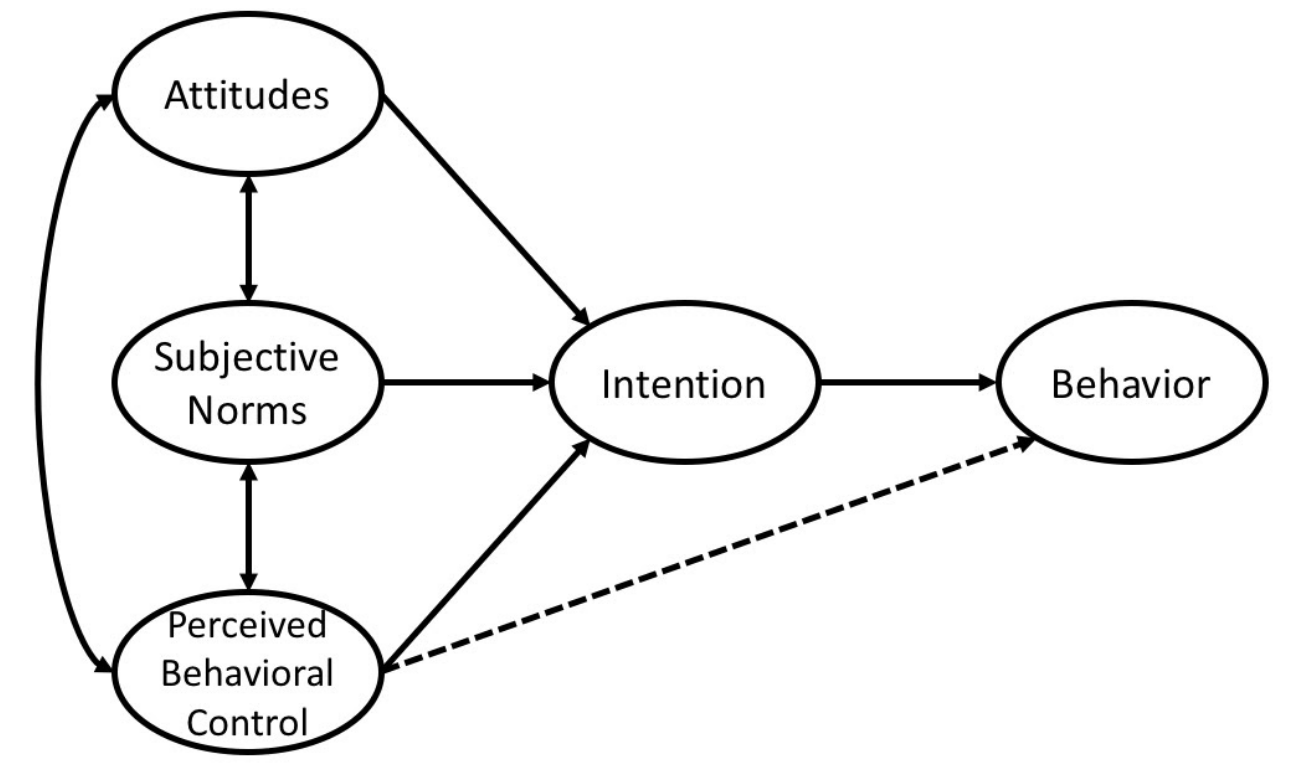
perceived behavioral control example Rebecca Poole
in this video we'll discuss behavioral diagrams of UML ( unified Modeling Language) it represent the dynamic view of the system. in pervious video we have di. Behavioural models may be realised using seven types of UML diagram, which are: use case diagrams, state machine diagrams, activity diagrams and interaction diagrams, of which there are four types communication, timing, interaction overview and sequence diagrams. Behavioural modelling is illustrated by looking at a single diagram the state machine diagram where a simple example was taken and.




