The Bragard's sign (also: Braggard's test) is used to evaluate whether lumbar and/or ischiadic pain originates from lumbosacral radiculopathy (e.g. disc herniation causing nerve root compression). Technique The patient is in supine position. The purpose is to describe active and passive physical maneuvers that provoke or alleviate lumbosacral radiculopathy and/or sciatica to demonstrate how these maneuvers function in common orthopedic and neurological tests/signs. Methods
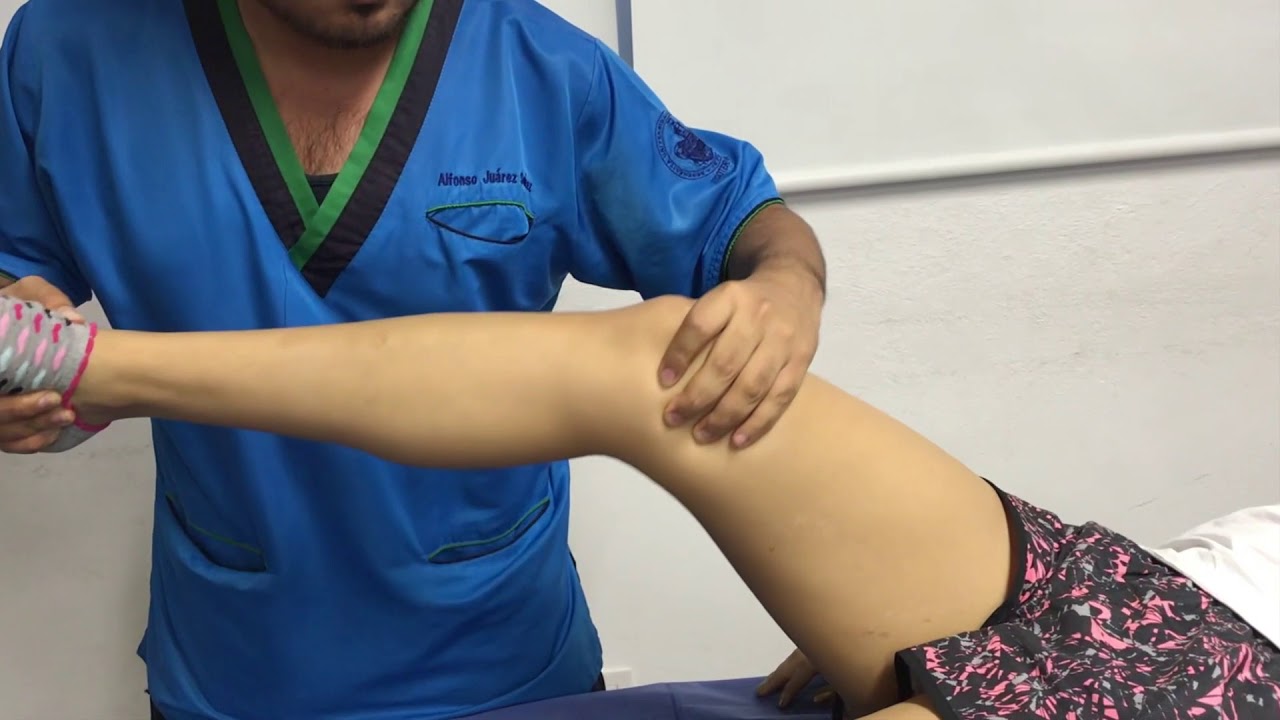
Prueba de Bragard Prueba de Bragard rodilla YouTube
Introduction Sciatica refers to radiating pain along the course of the sciatic nerve from the lower back or buttock to one or both legs or an associated lumbosacral nerve root. A common mistake is referring to any low back pain or radicular leg pain as sciatica [1]. In Bragard's test, external tibial rotation and knee extension bring the meniscus more anterior: if tenderness is felt along the joint line palpation, an articular surface irregularity (i.e. chondral lesion) or a meniscal tear is suspected. Bragard's sign is a physical examination technique used to assess for nerve irritation or compression in the lower back and legs, specifically the sciatic nerve. Here's how you can perform it: Position the patient in a supine position on an examination table. The Modified Bragard test is easy to perform and has an acceptable test performance, which can help to increase the discriminative power of clinical examination in patients with L5 or S1 nerve root compression who exhibit a negative SLR test result, especially in the acute phase of disease.

Figure 66 from Low Back Pain. Semantic Scholar
Conclusions: The Straight Leg Raise test and the Bragard test performed in a multiple parallel way and the combined test of the Slump Test and the Dejerine's triad have clinical validity to discard lumbar or lumbar-sacral radiculopathy. Keywords: lumbar radiculopathy, neurodynamic tension tests, orthopedic tension tests, magnetic resonance Go to: The Straight Leg Raise test and the Bragard test performed in a multiple parallel way and the combined test of the Slump Test and the Dejerine's triad have clinical validity to discard lumbar or lumbar-sacral radiculopathy. lumbar radiculopathy; magnetic resonance; neurodynamic tension tests; orthopedic tension tests. Low Back Pain / diagnosis* Bragard test is a modification of the SLR, where ankle dorsiflexion is applied at the end of the SLR. Dorsiflexion reduces the SLR angle at which the test is positive and can be used to discern neural symptoms from musculoskeletal . However, problems with this exist: there is no clear procedural definition and it is unclear whether it applies. The Bragard's sign (also: Braggard's test) is a manual test to diagnose and used to evaluate whether lumbar and /or ischiatic pain originates from lumbosacral radiculopathy, disc herniation, sciatica, low back pain, cauda equina syndrome, slipped disc, etc. Meniscal injuries may be the most common knee injury. Meniscus tears are sometimes related to trauma, but significant trauma is not.

Lumbar Spine Exam BragardSLR Test for Herniated Disc/Lumbar
The Bragard test is qualified as positive if the pain reappears when the foot is passively brought into dorsiflexion while the leg is lowered (compared to the appearance of characteristic pain during the Lasègue sign). This would indicate nerve involvement in the origin of the patient's pain. Bragard's Sign/Test: PURPOSE: To test for Meniscal Tearing, VIDEO DEMO, PROCEDURE 1 & 2, Positive Signs: Pain or tenderness along the medial aspect of the joint line indicates medial meniscus injury.
Here with @OrthoEvalPal I talk today about How to Perform the Braggard's Sign/Test for Lumbar Radiating Pain. I will discuss how it is different from the SLR. Lasegue sign or straight leg raising test (SLRT) is a neurodynamic exam to assess nerve root irritation in the lumbosacral area. [1] It is an integral element to the neurological exam for patients presenting with low back pain with or without radicular pain. The other less commonly used name is Lazarevic sign. Historical Evolution
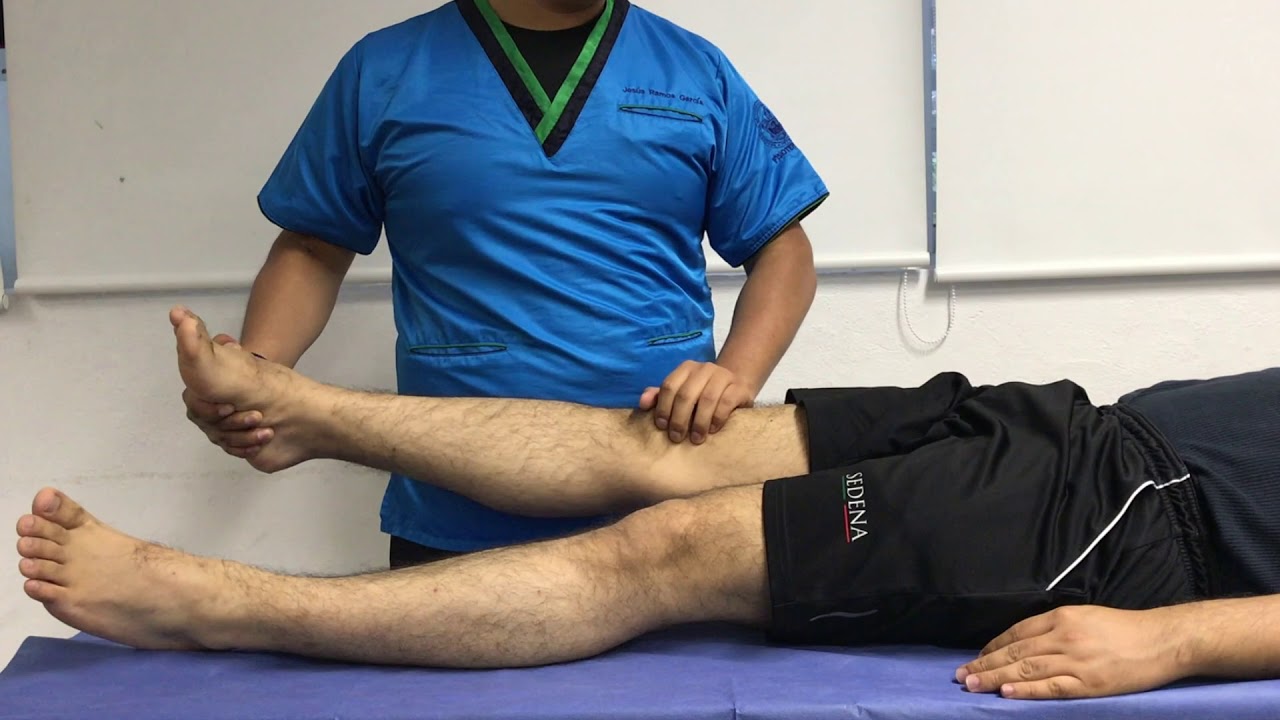
Prueba de Bragard YouTube
The straight leg raise test (SLR) and the crossed straight leg raising test (CSLR) are physical maneuvers that provoke the lumbosacral nerve roots. These tests are often used in making decisions about diagnostic imaging or hospital referral. 8 Another complementary physical maneuver is the Bragard test. It is used when the SLR test is positive. Bragard's Test. Demonstration. Explanation A confirmatory test following a positive Straight Leg Raise Test. Confirms suspicion of lower lumbar radiculopathy or sciatic nerve irritation. Also Known As. Bragard's Sign; Indication. Low back pain with unilateral radiation of symptoms to the posterior thigh, calf, or foot




