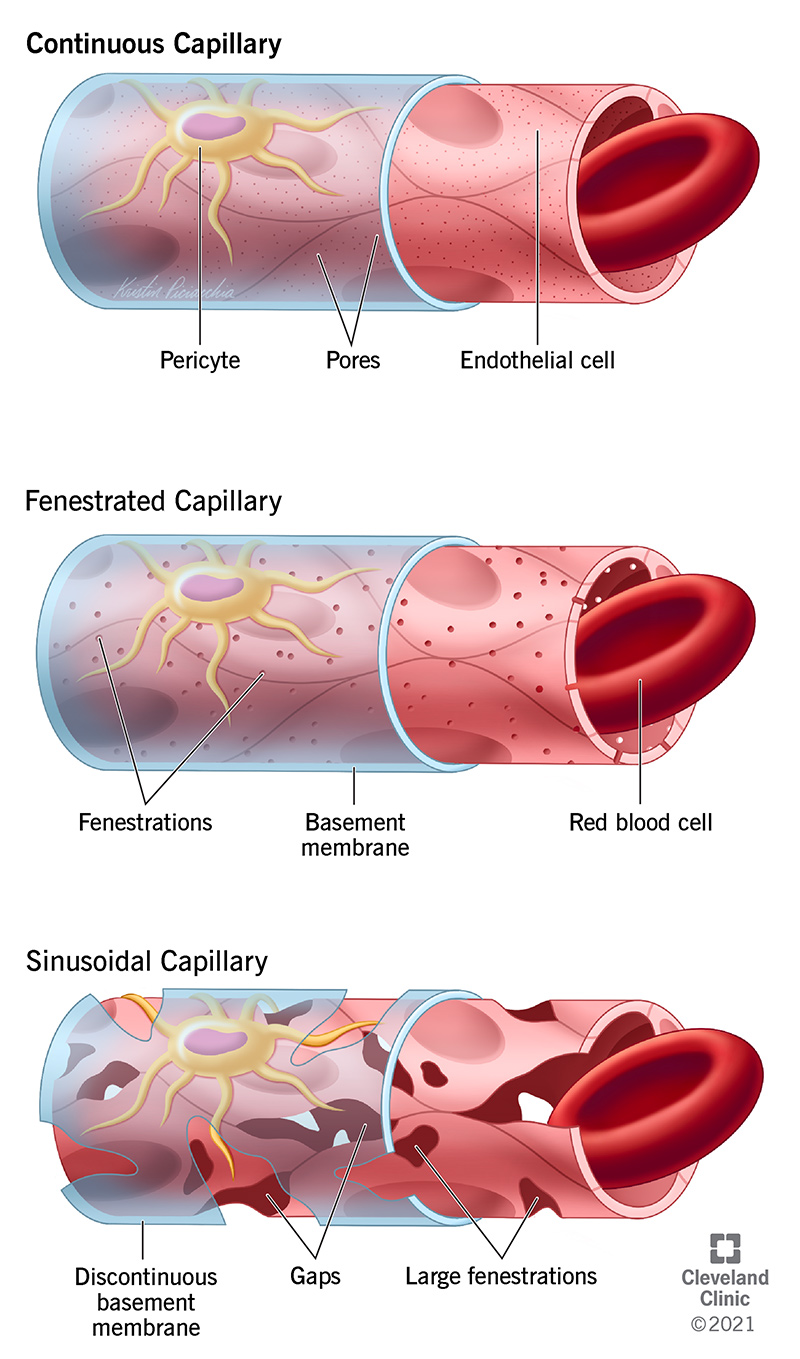
Types Blood capillaries are categorized into three types: continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoidal (also known as discontinuous). Types of capillaries: (left) continuous with no big gaps, (center) fenestrated with small pores, and (right) sinusoidal (or 'discontinuous') with intercellular gaps Continuous Diagram of a continuous capillary Contents Capillary structure Continuous Fenestrated Sinusoidal Highlights Sources + Show all Capillary structure Most capillaries are 3 to 4 µm (micrometers) in diameter, but some can be as large as 40 µm. They are composed of a thin layer of epithelial cells and a basal lamina, or basement membrane, known as the tunica intima.
Continuous Capillaries Anatomy and Function
Remote mount connections consist of a seal attached to a transmitter via capillary tube and are used in tuned or balanced systems, high temperature installations and remote transmitter mounting applications.. Use Rosemount™ 319 Flushing Rings for faster and easier removal of residue build-up from diaphragm seals that can create false. 1199 Diaphragm Seal Systems Applications Level, flow, pressure, interface, density Extreme hot and cold temperatures. (Capillary) connection on the low pressure connection. This improves overall performance and installation compared to a traditional Balanced Seal System. The capillary tubing or direct mount flange connects the diaphragm to the transmitter. When process pressure is applied, the diaphragm is displaced, transferring the measured pressure through the filled system, by way of the capillary tubing, to the transmitter. Diaphragm seals also enable remote mounting from the pressure port via a capillary that is custom suited for your unique application. And thanks to the wide range of available process connections (flanged, threaded, etc.), they can meet many industry standards. WIKA's Expertise and Excellence in Diaphragm Seals
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Discussion on how a capillary and diaphragm seal system solve the challenges that exist when using either wet legs or dry legs in DP Level Transmitters._____. Capillary inside diameter and length also impact system response time. A small inside diameter restricts the fill fluid flow causing slower response time. Capillary length relates to the time for a change in pressure to reach the transmitter-sensor. F L E X ©Endress+Hauser F L E X ©Endress+Hauser Specs at a glance Accuracy 0,075% + influence of diaphragm seal Process temperature -40°C.400°C (-40°F.752°F) Pressure measuring range 100mbar.40bar (1.5psi. 600 psi) Process pressure / max. overpressure limit 160bar (2400 psi) Main wetted parts Alloy C276 316L Monel Tantalum Definition Diaphragm seals are used for pressure measurements when the process medium should not come into contact with the pressurised parts of the measuring instrument. diaphragm seal has two primary tasks: Separation of the measuring instrument from the process medium Transfer of the pressure to the measuring instrument
PPT The Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels PowerPoint Presentation
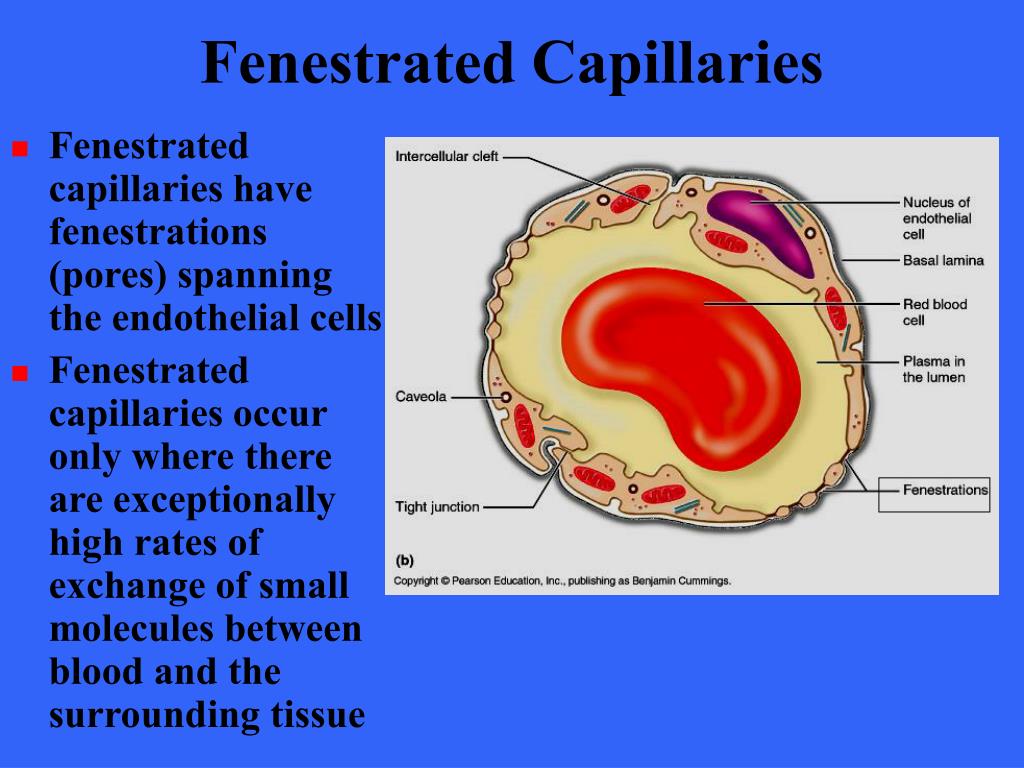
The diaphragm has a central thickening, the knob, with a diameter of about 100 Å. Epon has been used as the embedding medium, and lead hydroxide has been employed to increase the contrast of the structures. It is believed that, particularly, the use of Epon has facilitated the demonstration of the delicate diaphragm of the capillary fenestrations. Figure 2-56: Porous Diaphragm Capillary Pressure Device [1] Complete determination curve of capillary pressure with this method is time consuming owning to the vanishing pressure differentials causing flow as the core approaches equilibrium at each imposed pressure. Time to reach the equilibrium increases step by step because of the reduction.
Capillary endothelial cells are morphologically and biochemically specialized to maintain the specific functions of individual organs, and a number of studies have investigated the relationship between their ultrastructural features and their permeability. 1, 2 In the capillary, where transendothelial exchange vigorously takes place, numerous transcellular pores or fenestrae exist to form. Capillary Connection (RF, RJ, HT & HV) Direct Mount (RF) Capillary Connection (RF, HT & HV) Connection to Transmitter Accessories Detailed Information Direct Mount Capillary Connection Name Flushing Connection Ring Name List of General Specifications (GS) Page Nos C80FW C81FD C82FD

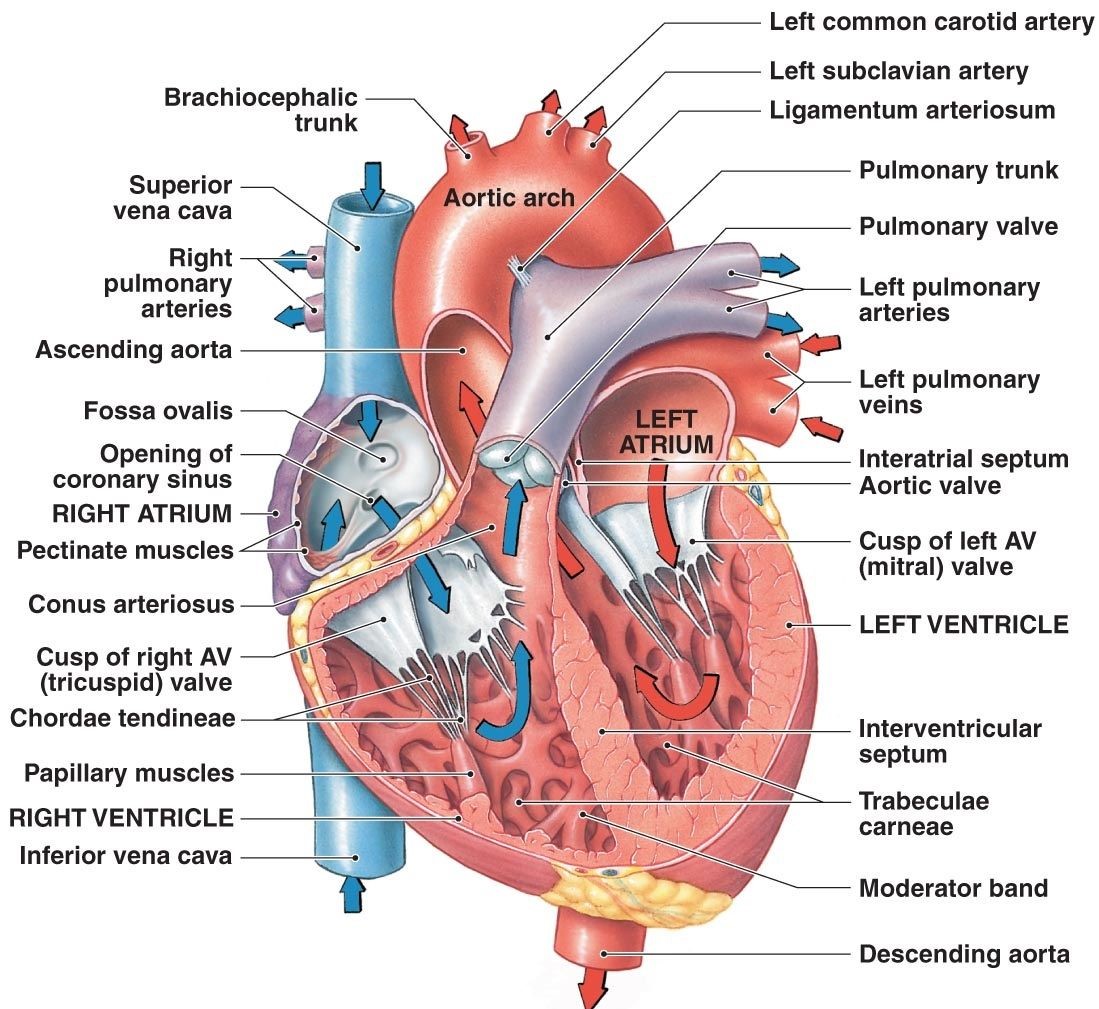
Attachments of the diaphragm to the body wall. IVC = inferior vena
A diaphragm seal is connected to the measuring instrument via a direct connection or capillary. The instrument side of the seal is separated from the process media by a flexible diaphragm. The chamber between the diaphragm and the instrument contains system fill fluid which transfers the pressure of the process media. DP Level Transmitter Calculation for Diaphragm seal type with capillary tube. For determining the DP level transmitter calibration range for this type, we need fill fluid density inside the capillary tube, Process fluid density, Distance between HP & LP tapping points, Maximum level to be measured. Sometimes the distance between HP & LP tapping.




