KS3 The pH scale Part of Chemistry Acids and alkalis Remove from My Bitesize Key points The pH scale shows how acidic a substance is. It can be measured using a pH meter which gives a. Eh-pH diagram, any of a class of diagrams that illustrate the fields of stability of mineral or chemical species in terms of the activity of hydrogen ions (pH) and the activity of electrons (Eh).
The pH Scale diagram on white background 1845080 Vector Art at Vecteezy
To give you the short answer: An acidic solution has a high concentration of hydrogen ions (H + ), greater than that of pure water. A basic solution has a low H + concentration, less than that of pure water. To see where this definition comes from, let's look at the acid-base properties of water itself. Autoionization of water pH + pOH = 14 (Eq. 3) This relationship can be used to convert between pH and pOH . In combination with Eq. 1a/b and Eq. 2a/b, we can always relate pOH and/or pH to [ OH −] and [ H +] . For a derivation of this equation, check out the article on the autoionization of water. pH (TITRATION) CURVES This page describes how pH changes during various acid-base titrations. The equivalence point of a titration Sorting out some confusing terms When you carry out a simple acid-base titration, you use an indicator to tell you when you have the acid and alkali mixed in exactly the right proportions to "neutralise" each other. The diagram below shows what happens to pH when a strong base is slowly added to a weak acid: Drawing pH Curves . 1. The starting pH is higher. As the acid is weak, it starts at a higher pH compared to a strong acid. 2. Initially the pH rises fast. At the start there is a rapid change in pH with a small amount of OH- ions added.

pH Of Acids And Bases Calculate pH Value Chemistry Byju's
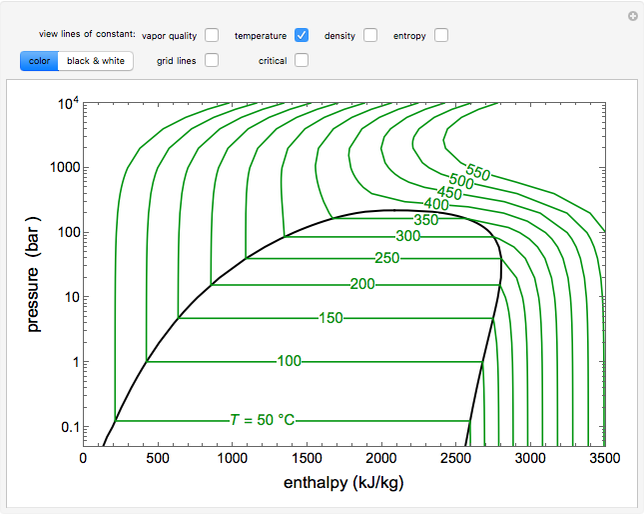
The log-C vs. pH diagram is constructed as s superposition of plots for each conjugate pair at its respective pKa. Note especially that the pH of a solution of glycine does lie exactly at the crossing point [Gly - ] = [H + ], but is slightly displaced from it according to the proton balance equation shown in the inset on the graph. As noted above, these diagrams are essentially phase diagrams that map the conditions of potential and pH (most typically in aqueous solutions) where different redox species are stable. We saw a simple example of such a diagram in section 4.2 for H 2 O. Typically, the water redox reactions are plotted as dotted lines on these more complicated diagrams for other elements. Figure 12. Example of a detailed conceptual model diagram for Low pH. Click on the diagram to view a larger version. pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration in an aqueous solution. pH decreases as hydrogen ion concentration increases, and these acidic conditions can adversely affect aquatic biota. In this video,I have explained Pressure Enthalpy ( P-H)Diagram.i explained basic line in PH diagram. how to draw all lines. why lines is drawn by this specif.

pH strip and pH scale. Download Scientific Diagram
In chemistry, pH (/ p iː ˈ eɪ tʃ / pee-AYCH), also referred to as acidity or basicity, historically denotes "potential of hydrogen" (or "power of hydrogen"). It is a scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution.Acidic solutions (solutions with higher concentrations of hydrogen (H +) ions) are measured to have lower pH values than basic or alkaline solutions. Online Interactive Pressure-Enthalpy (p-H) and Temperature-Entropy (T-s) Diagram for HVAC-R engineers.
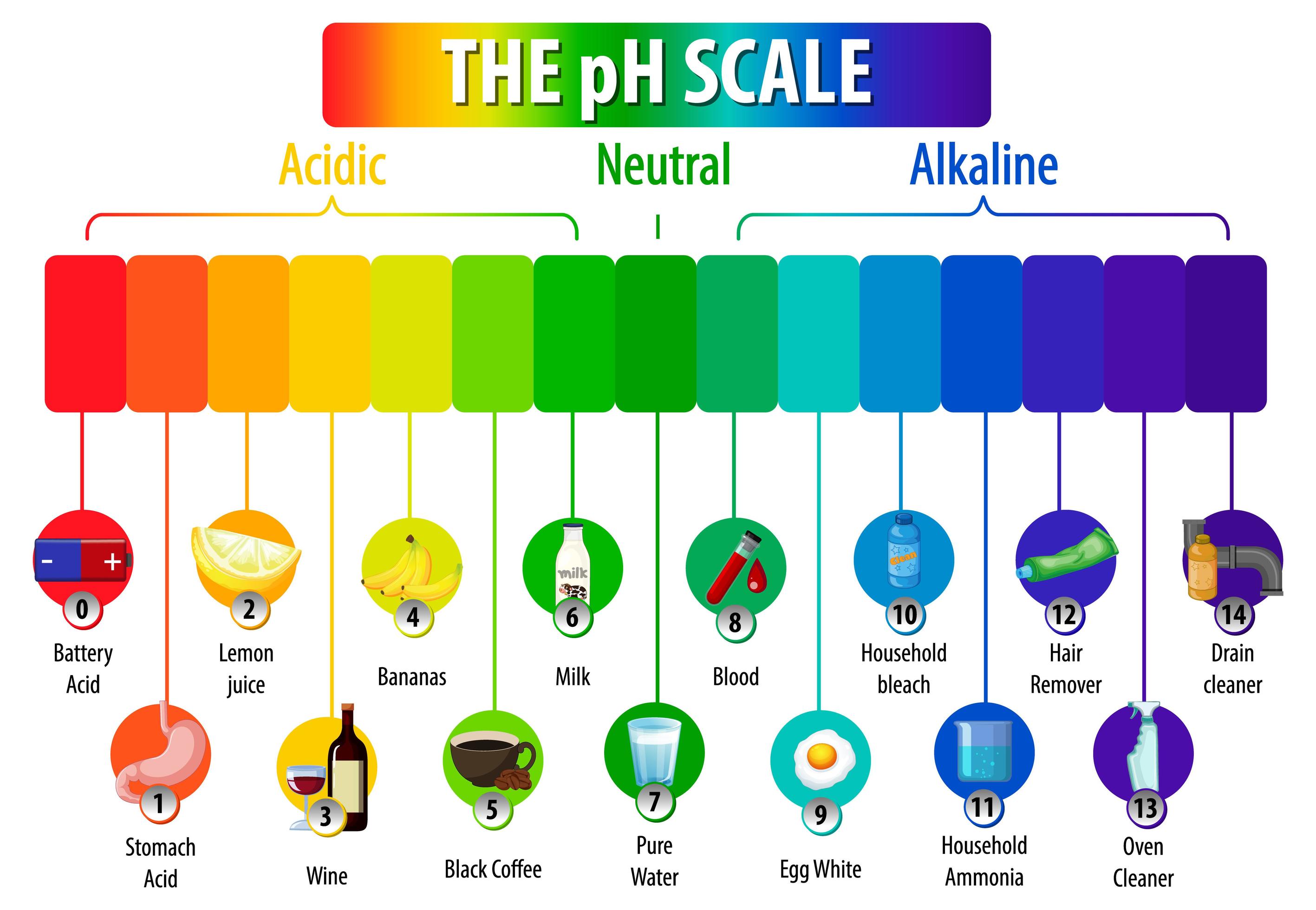
The pH scale. How acidic or alkaline a substance is (the pH of the substance) can be measured using the pH scale, a continuous range that stretches from below 0 to above 14. Most common pH values. This diagram describes the relationship of pressure and enthalpy of a select refrigerant. In order to properly understand this diagram, it is best to go through the vapor compression cycle on a P-H diagram. Understanding the P-H Diagram On the P-H diagram, pressure is indicated on the y-axis and enthalpy is indicated on the x-axis.
phdiagramforwater LearnChemE
The pH scale shows how acidic or basic a chemical is in aqueous solution (mixed with water). The scale runs from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most alkaline or basic), where 7 is neutral pH. Chemicals with pH values from 0 up to 7 are acids, those with a pH value of 7 are neutral, and those with pH values greater than 7 up to 14 are bases. pH is a representation of hydrogen ion activity in a liquid. It is the negative logarithm of the number of hydrogen ions (in moles) per liter of liquid. Thus: 10 -11 moles of hydrogen ions in 1 liter of liquid = 11 pH. 10 -5.3 moles of hydrogen ions in 1 liter of liquid = 5.3 pH. The basic pH scale extends from 0 (strong acid) to 7 (neutral.




