It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Chemistry in its element: germanium For a good fifty years, germanium was little more than a box on the periodic table. It really wasn't good for anything. It was only with the development of electronics that germanium's value as a very effective semiconductor came to light.

Chemist Atom of Germanium Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of
germanium (Ge), a chemical element between silicon and tin in Group 14 (IVa) of the periodic table, a silvery-gray metalloid, intermediate in properties between the metals and the nonmetals. Germanium Ion From: Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2022 Process Simulation: Kinetic Monte Carlo I. Martin-Bragado, M. Jaraiz, in Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering, 2016 2.1 Si: Amorphization and Recrystallization Ionic radius (1+ ion) - Ionic radius (2+ ion) 87 pm : Ionic radius (3+ ion) - Ionic radius (1- ion) - Ionic radius (2- ion) -. Electrical conductivity : 3 S m-1: Freezing/Melting point: 938 o C, 1210.6 K : Discovery of Germanium. Dr. Doug Stewart. Germanium was one of the elements whose existence was predicted in 1869 by Russian. Germanium is the 32nd element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'Ge'. In this article, I have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of germanium. What is the electron configuration of germanium? The total number of electrons in germanium is thirty-two.
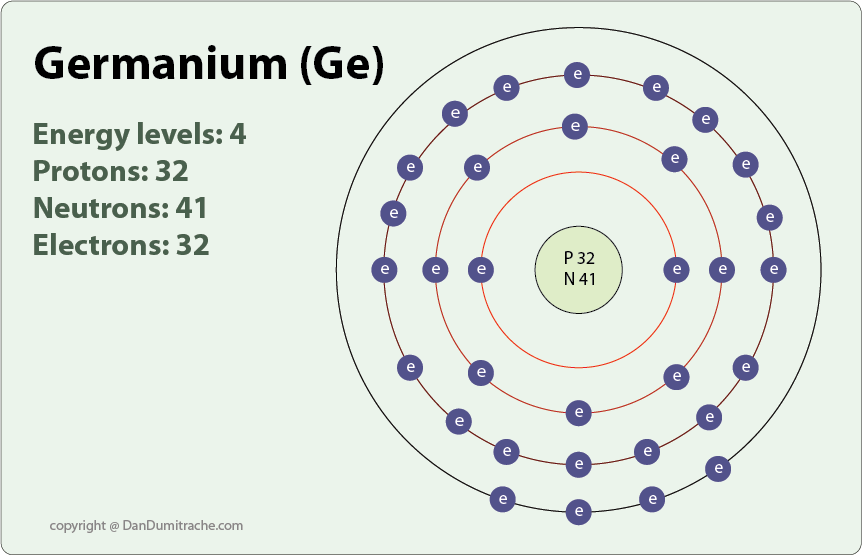
What is the atomic structure of germanium? Socratic
MELTING POINT: 937.4°C. BOILING POINT: 2,830°C. DENSITY: 5.323 g/cm 3. MOST COMMON ION: Ge 4+ Ge 2+. Germanium has chemical and physical properties similar to those of silicon. It was predicted as an element ("eka-silicon") by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1871 from calculations made during the construction of his periodic table, and it was discovered. This great but unpredictable progress was fertilized by three basic parameters: the continuous development of new and efficient laser sources and processing methods, the deeper understanding of the underlying laser-matter interactions, and the evolution of the optical fiber from a simple optical cable to a versatile and efficient photonic device. In chemistry, germanate is a compound containing an oxyanion of germanium. In the naming of inorganic compounds it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central germanium atom, [1] for example potassium hexafluorogermanate, K 2 GeF 6. [2] Germanium is similar to silicon forming many compounds with tetrahedral {GeO 4 } [2] units. Germanium does not appear in commercial quantities as a native ore but is produced principally as a by-product of zinc processing, with a smaller amount from the processing of copper. The germanium-containing metallic zinc is first distilled under nonoxidizing conditions.. 22.1.2 Ion exchange. Precipitation. Dowex-50 cation-exchanger retains.
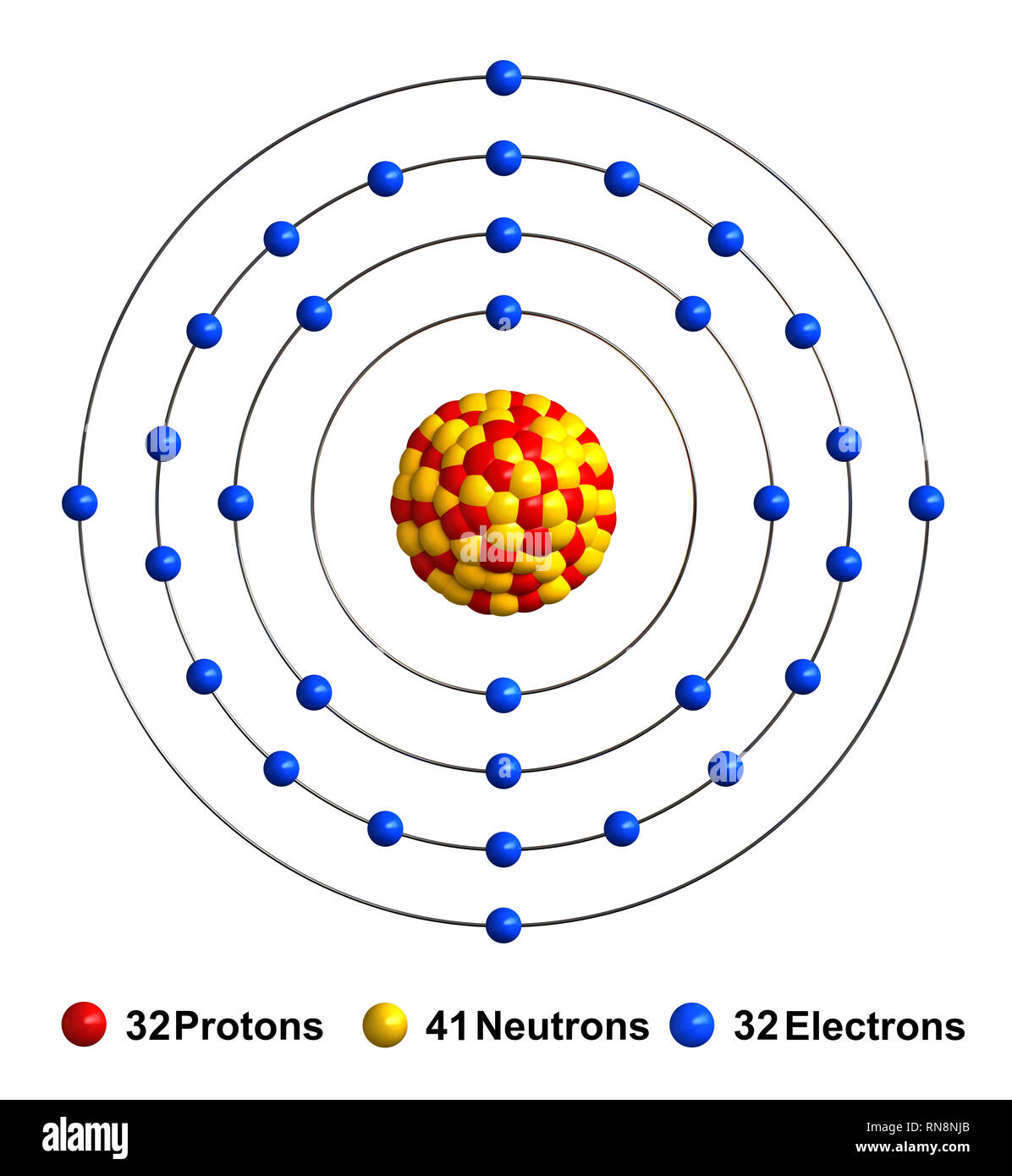
Germanium atom Cut Out Stock Images & Pictures Alamy
Germanium -. Ge: radii of atoms and ions. One measure of size is the element-element distance within the element. It is not always easy to make sensible comparisons between the elements however as some bonds are quite short because of multiple bonding (for instance the O=O distance in O 2 is short because of the the double bond connecting the. Germanium Ion After Ge ion irradiation, the XRD spectrum was typical of an amorphous phase and the electrical resistivity value was comparable to that measured in the as deposited amorphous film. From: Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2021 Related terms: Energy Engineering Nanoparticle Germanium Laser Excitation Aqueous Solution
Germanium - Ionization Energy. First Ionization Energy of Germanium is 7.9 eV. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom. Skip to content Menu Periodic Tables All Properties Atomic Numbers Atomic Masses Atomic Radii Densities Electron Configurations Electron Affinities Germanium (Ge) ion implantation into silicon waveguides will induce lattice defects in the silicon, which can eventually change the crystal silicon into amorphous silicon and increase the refractive index from 3.48 to 3.96.

Germanium Facts, Symbol, Discovery, Properties, Uses
Introduction Germanium (Ge) is a relatively rare metal, with a chemical symbol of Ge, that belongs to the carbon group of elements and is found in nature in minerals [ 1 ]. Germanium can also be extracted and refined from ores containing high levels of germanium, typically through methods such as smelting and extraction. The primary sources of worldwide germanium production are Zn-refinery residue and coal fly ash, with recycling of industrial scraps being the secondary source [12].Globally, the main producer of germanium is China, accounting for 80% of world production during 2012-2016 [7].Other producers are Russia, Finland, US, Japan, and Ukraine, with Finland accounting for 10%, Russia for 5% (primarily.




