INTRODUCTION • GLYCOLYSIS is the sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions that converts glucose into pyruvate with simultaneous production on of ATP. • In this oxidative process, 1mol of glucose is partially oxidised to 2 moles of pyruvate. • This major pathway of glucose metabolism occurs in the cytosol of all cell. Microsoft PowerPoint - Glycolysis.ppt Glycolysis The Glycolytic pathway describes the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate with the generation of ATP and NADH It is also called as the Embden-Meyerhof Pathway Glycolysis is a universal pathway; present in all organisms: from yeast to mammals. In eukaryotes, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol

PPT Intro to Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis & Krebs Cycle
GLYCOLYSIS (Embden - Meyerhof Pathway) Glycolysis Glykys = Sweet, Lysis = splitting During this process one molecule of glucose (6 carbon molecule) is degraded into two molecules of pyruvate (three carbon molecule). Free energy released in this process is stored as 2 molecules of ATP, and 2 molecules of NADH. Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three-carbon molecules called pyruvates. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today 2, 3 . Glycolysis (10 Steps) By: Asar Khan Asar Khan (Zoologist) • 51.6K views Glycolysis- An over view Namrata Chhabra • 60K views Glycolysis heliomancer712 • 11.2K views 13 Biochemistry _ Glycolysis Prabesh Raj Jamkatel • 45.3K Glycolysis Maria • views Pawan Kumar • 7.2K Glycolysis (with animated pathway) Ashok Katta • PowerPoint Presentation. Glucose Metabolism (Glycolysis) " " " " * * Objectives By the end of this lecture, students are expected to: Recognize glycolysis as the major oxidative pathway of glucose List the main reactions of glycolytic pathway Discuss the rate-limiting enzymes/Regulation Assess the ATP production (aerobic/anaerobic.

What is Glycolysis? Process, Definition, and Equations
Glycolysis converts glucose (C 6H 12O 6) molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C 3H 4O 3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. glycolysis and respiration. Complete aerobic metabolism of glucose produces water and carbon dioxide as products. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O Energy is released in this process. The overall ΔG of glucose breakdown in cells is -720 kcal/mole. Normally about 32% of the energy released is captured through the formation of ATP. Colby College Biochemistry 3070 Glycolysis * * Glycolysis Other chemicals can enter the glycolysis pathway by converting them into glycolytic intermediates. For example, glycerin can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DAP): * Gluconeogenesis When levels of pyruvate are high and energy demands are low, pyruvate can be converted back into glucose by a series of reactions called "gluconeogenesis."
PPT GLYCOLYSIS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID456542
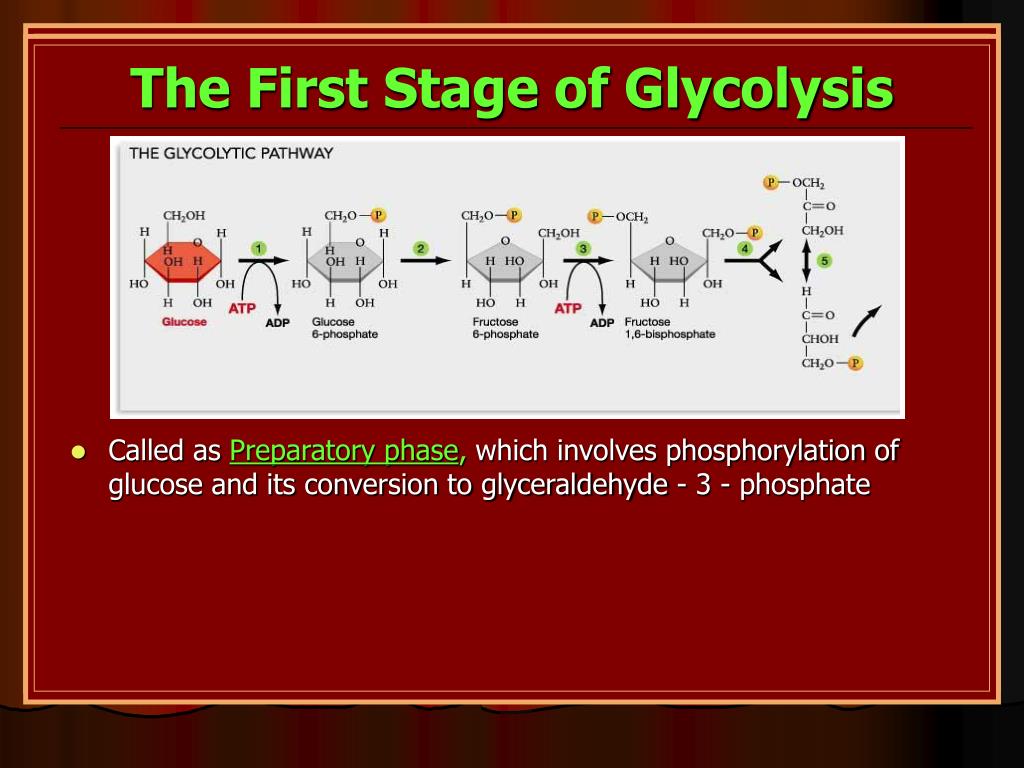
glycolysis VBCOPS Recommended GLYCOLYSIS & ITS REGULATION by GLYCOLYSIS & ITS REGULATION YESANNA 135.9K views • 53 slides Glycolysis by Glycolysis nj1992 143.6K views • 35 slides Krebs cycle by Krebs cycle Sathish Rajamani 117.5K views • 23 slides Hexose Monophosphate Shunt by Hexose Monophosphate Shunt Ashok Katta 37.3K views • 23 slides Step 1. The first step in glycolysis (Figure 9.1.1) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad specificity that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of glucose.
ÐÏ à¡± á> þÿ ` b þÿÿÿ[ \ a. Glycolysis Breaking down glucose "glyco - lysis" (splitting sugar) ancient pathway which harvests energy where energy transfer first evolved transfer energy from organic molecules to ATP still is.
PPT Glycolysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID585727
Glycolysis is a set of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Glycolysis PPT: Definition, Stages, Importance and Key-Point. Glycolysis is one metabolic pathway that doesn't require oxygen (In anaerobic conditions pyruvate is converted to lactic acid). Numerous species frequently undergo glycolysis, indicating that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Presentation 1 / 48 Download Presentation >> Glycolysis Sep 12, 2014 980 likes | 2.14k Views Biochemistry of Metabolism. Glycolysis. Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of cells. Glucose enters the Glycolysis pathway by conversion to glucose-6-phosphate . Initially there is energy input corresponding to cleavage of two ~P bonds of ATP. 1.




