The Hazen-Williams equation is not the only Manning's formula is commonly used to calculate gravity driven flows in open channels. The flow velocity can be calculated as v = 0.408709 q / d v = flow velocity (ft/s) The Hazen-Williams equation is assumed to be relatively accurate for water flow in piping systems when The Hazen-Williams equation is an empirically derived formula that describes the velocity of water in a gravity flow. Remember that the Hazen-Williams equation is valid only for water - applying it for any other fluid will give you inaccurate results.

HazenWilliams equation used by different authors Download Table
This friction loss calculator uses the Hazen-Williams equation to estimate the pressure or friction loss in pipes. The losses are calculated based on flow rates in circular pipes, the internal diameter of the pipe, the pipe length, and the type of pipe. You can calculate friction loss in five easy steps: Free Online Hazen-Williams Pipe Head Loss Calculator >> Drop your fears at the door; love is spoken here. Enjoy the free libre HawsEDC AutoCAD tools too. << Hazen-Williams Pipe Head Loss at Given Diameter, Roughness, and Flow Can you help me improve translations, program, or host these calculators? [Hide this line] The Hazen-Williams equation or pipe velocity equation is given by: \footnotesize v = k \cdot C \cdot R^ {0.63}\cdot S^ {0.54} v = k ⋅ C ⋅ R0.63 ⋅ S 0.54 where: v v - Velocity of water in m/s or ft/s; k k - Conversion factor dependent on the unit system ( k = 0.849 for the metric system and k = 1.318 for the imperial system); The Hazen-Williams equation can be used to calculate the pressure drop (psi) or friction loss in pipes or tubes. Hazen-Williams Formula in Imperial Units Hazen-Williams equation for calculating head loss in pipes and tubes due to friction can be expressed as: P = 4.52 q 1.85 / (c 4.8655 ) (1)
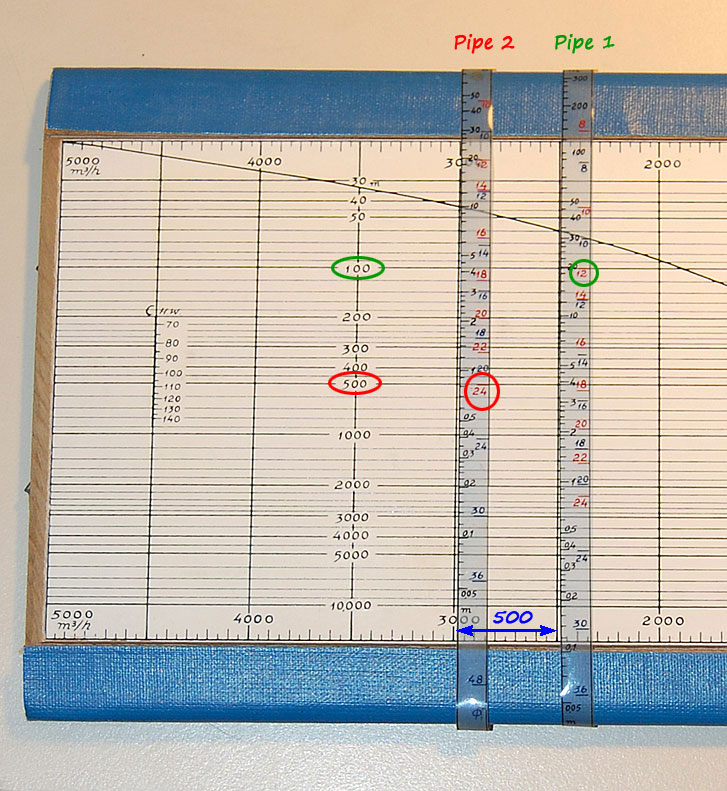
Elisha Kally’s water networks calculator, based on the HazenWilliams
The pipe friction calculator utilizes the Hazen-Williams formula to calculate friction loss. Furthermore, you can estimate the loss in pressure due to friction using the specific weight of water in the advanced mode of our tool, meaning this pipe friction calculator can find the pressure drop in a water pipe system. The Hazen Williams equation is used to calculate the head loss due to friction in a pipe. The formula is as follows: HL = (10.67 * Q^ {1.852} * L) / (C^ {1.852} * D^ {4.8655}) H L = (10.67 ∗ Q1.852 ∗ L)/(C 1.852 ∗ D4.8655) Variables: HL is the head loss due to friction (feet) Q is the flow rate (gallons per minute) The Hazen-Williams equation is typically used to analyze city water supply systems. For other liquids or gases, the Darcy-Weisbach method should be used. Major loss (h f) is the energy (or head) loss (expressed in length units - think of it as energy per unit weight of fluid) due to friction between the moving fluid and the pipe wall. The Hazen Williams formula is an empirical equation that can be used to calculate the pressure loss per one foot of pipe of a known diameter due to friction dependent on the flow. Here we can calculate for Discharge or Fluid Flow Rate, Friction Coefficient, Pipe Diameter, Hydraulic Grade Line Slope.
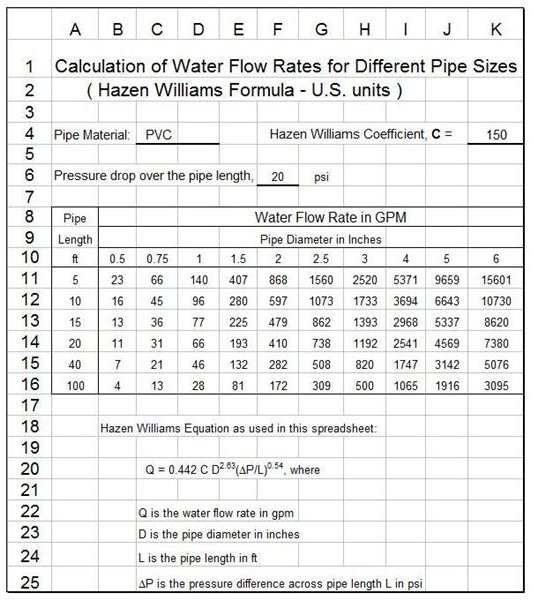
Water Flow Rates for Pipe Sizes with Excel Formulas, Using the Hazen
Utilize our user-friendly Hazen-Williams Equation Calculator to accurately determine water flow rates in pipes. Perfect for hydraulic engineers and water system designers, this tool provides precise calculations for pipe diameter, hydraulic gradient, and flow rate, considering various pipe materials. Simplify your water distribution system planning with our efficient calculator. This friction loss calculator employs the Hazen-Williams equation to calculate the pressure or friction loss in pipes. Losses are calculated on the basis of flow rates in circular pipes, the internal diameter of the pipe, the length of the pipe, and the type of pipe. Friction loss can be calculated following five easy stages:
The Hazen-Williams equation can be used to calculate the pressure drop (psi) or friction loss in pipes or tubes. Friction head loss (ft/100 ft) vs. water flow in plastic pipes like PVC, PP, PE or PEH. Gases and Compressed Air Sanitary Drainage Systems Hazen-Williams friction loss coefficients for commonly used piping materials. Hazen-Williams formula: V = k C R 0.63 S 0.54 Where: Full flow circular pipes Hazen-Williams R = D / 4 By Continuity Q = V A V = fluid velocity, m/s (ft/s), C = factor for relative roughness Hazen-Williams coefficient R = hydraulic pipe radius, m (ft), S = Slope of the energy linie (head loss divided by pipe length),
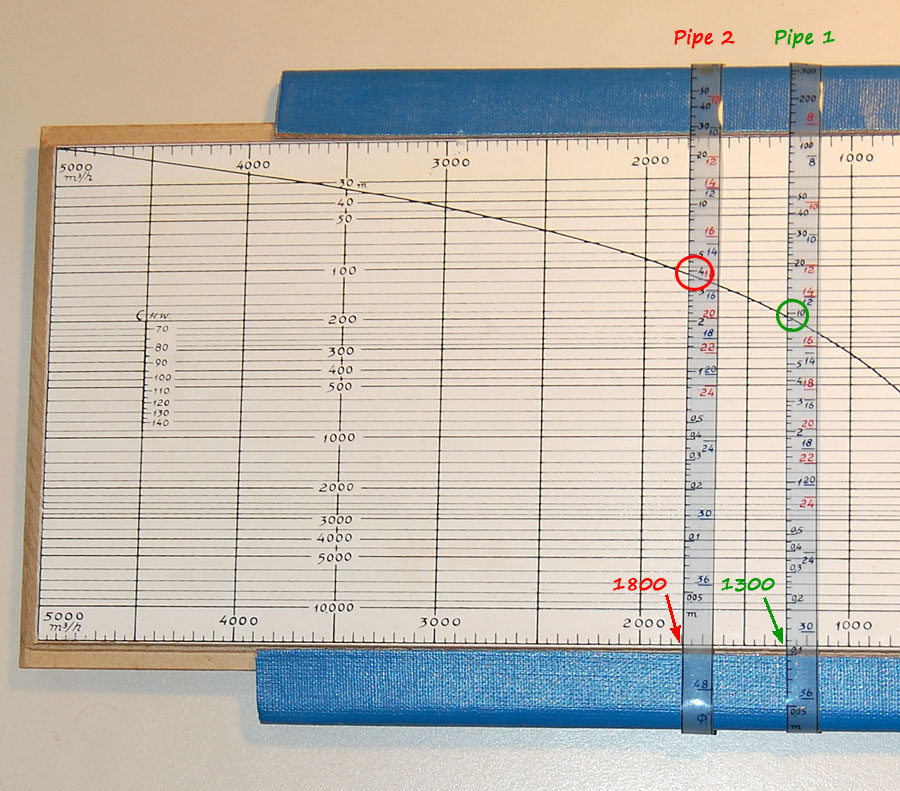
Elisha Kally’s water networks calculator, based on the HazenWilliams
The Hazen-Williams equation is an empirical relationship which relates the flow of water in a pipe with the physical properties of the pipe and the pressure drop caused by friction. It is used in the design of water pipe systems [1] such as fire sprinkler systems, [2] water supply networks, and irrigation systems. Hazen Williams, Darcy Weisbach and Fanning Churchhill are all commonly used methods to calculate friction loss. Hazen Williams in generally the most conservative method as well as the most common method, so Power Zone uses and recommends this method of calculating friction loss above the other two methods.




