The cadherin family is essential in maintaining cell-cell contact and regulating cytoskeletal complexes. The cadherin superfamily includes cadherins, protocadherins, desmogleins, desmocollins, and more. In structure, they share cadherin repeats, which are the extracellular Ca 2+-binding domains.There are multiple classes of cadherin molecules, each designated with a prefix for tissues with. 1. Introduction. Cadherins were originally identified by Takeichi as cell surface molecules involved in Ca 2+-dependent adhesion mechanism in Chinese hamster V79 cells [].Cadherins are highly sensitive to Ca 2+ and are readily degraded by proteolysis in the absence of Ca 2+ [].The cadherin superfamily consists of 114 calcium-dependent membrane proteins from three major cadherin families.

Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology
herin cell surface levels in a variety of mammalian tissues. Structural studies of the E-cadherin-p120 complex revealed that the cadherin JMD contains two types of p120-binding interfaces. The core p120-binding region is a highly conserved series of residues N-cad + cells were functional bone and marrow stromal progenitor cells (BMSPCs), giving rise to osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes in vitro and in vivo. Finally, ablation of N-cad + niche cells or deletion of SCF from N-cad + niche cells impaired rHSC maintenance during homeostasis and regeneration. herin in noninvasive, E-cadherin-positive cells produces an invasive cell, even though these cells continue to express high levels of E-cadherin; the data suggest that N-cadherin-mediated cell motility may be stimulated by FGF receptor signaling; and other cadherins, such as cadherin-11, may promote motility in epithelial cells in a manner. herin; also known as cadherin 1), antibodies that block the adhesive function of VE-cadherin dissociate endothelial cell layers in vitro [24] and enhance neutrophil extravasa-tion [25] and vascular permeability [26] in vivo. Despite there being several other adhesion molecules located at endothelial cell contacts, the antibodies directed against
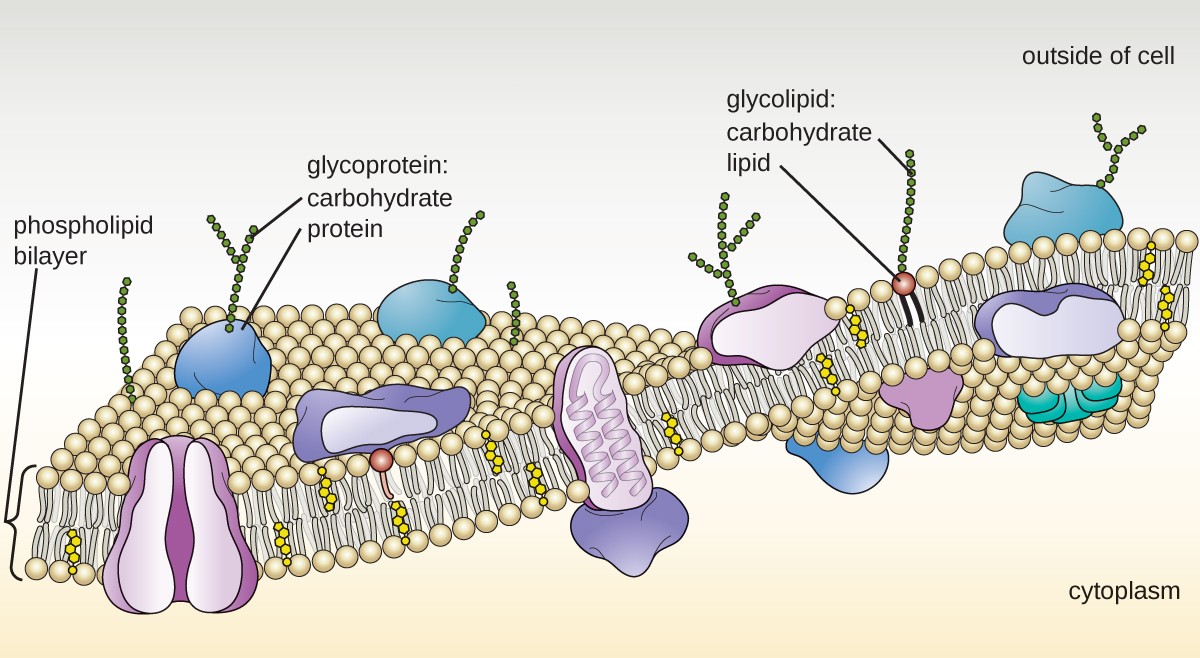
Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology
Cadherins may also contribute to cell segregation by dif-ferential levels of expression of a single cadherin type (Stein-berg, 1970). Indeed, cells expressing high levels of cadherin will sort out from cells expressing low levels of the same cad-herin (Friedlander et al., 1989; Steinberg and Takeichi, 1994). herin cell adhesion system by various mechanisms during mul-tistage human carcinogenesis. The structure of β-catenin is remarkably similar to that of the Armadillo protein, an important element in the Wingless/Wnt signaling pathway of the fruit fly Drosophila.6, 7) Wingless is a cell-cell signal in Drosophila that triggers many key develop- herin cell adhesion complexes which control the epithelial tissue architectural integrity, while the protein also play a key role in the WNT/β-catenin pathway 13. In addition, epithelial cell. cells (for review see Fagotto and Gumbiner, 1996). Although -catenin is a critical component of the cad-herin cell adhesion complex, it also has a well-established role as an essential mediator of the Wnt signal transduc-tion pathway. Wnt/-catenin signaling mediates many in-Address correspondence to Barry M. Gumbiner, 1275 York Ave., Box
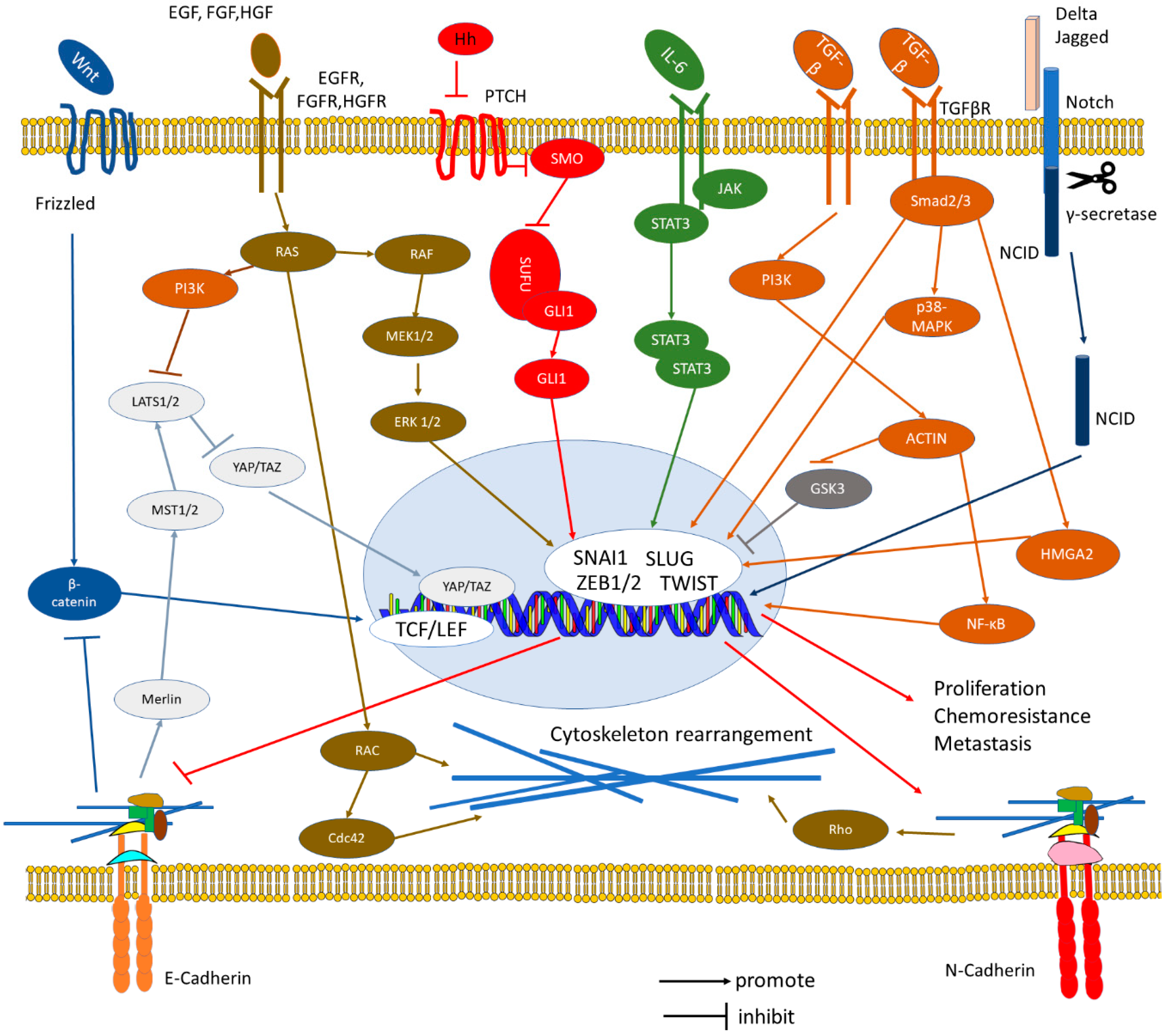
Cells Free FullText The ECadherin and NCadherin Switch in
Vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin is a strictly endothelial specific adhesion molecule located at junctions between endothelial cells. In analogy of the role of E-cadherin as major determinant for epithelial cell contact integrity, VE-cadherin is of vital importance for the maintenance and control of endothelial cell contacts. Pathophysiology. Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) is a transmembrane protein ( Histopathology 2016;68:57 ) Extracellular domain involved in intercellular adhesion and polarity maintenance. Cytoplasmic domain attached to actin units α / γ / β- and p120 catenins. Encoded by CDH1 (CaDHerin-1) gene located on chromosome 16 (16q22.1)
in cell culture, where it was demonstrated that disruption. If the interaction of catenins with the cad-herin cytoplasmic tail is disrupted in the intestinal cells of a mouse by tissue-specific transgenic overexpression of a competing cadherin cytoplasmic tail, critical cell-cell ad-hesion necessary both to form and to maintain the epi- Cadherins constitute a class of morphoregulatory proteins that bind to identical proteins on cell surfaces to mediate cell-cell adhesion in all soft tissue (1-3).They also facilitate cell sorting during tissue morphogenesis (1-4).These are single-pass transmembrane glycoproteins, and the homophilic association of identical opposed cadherin extracellular (EC) segments maintains the.

Physical Defenses of the Host Microbiology
herin homophilic cell-cell adhesion molecule are expressed differentially in developing and ma-ture brains, each being expressed in restricted neuronal groups. Cadherin-6 (cad6) is one of such cadherins. Recent studies of cad6 mRNA expres-sion in the postnatal mouse forebrain showed that it occurs in neurons constituting a specific Furthermore, an evolutionarily conserved cdc2 phosphorylation site (Thr-927) in HsEg5 is phosphorylated specifically during mitosis in HeLa cells and by p34cdc2/cyclin B in vitro. Mutation of Thr-927 to nonphosphorylatable residues prevents HsEg5 from binding to centrosomes, indicating that phosphorylation controls the association of this motor.




