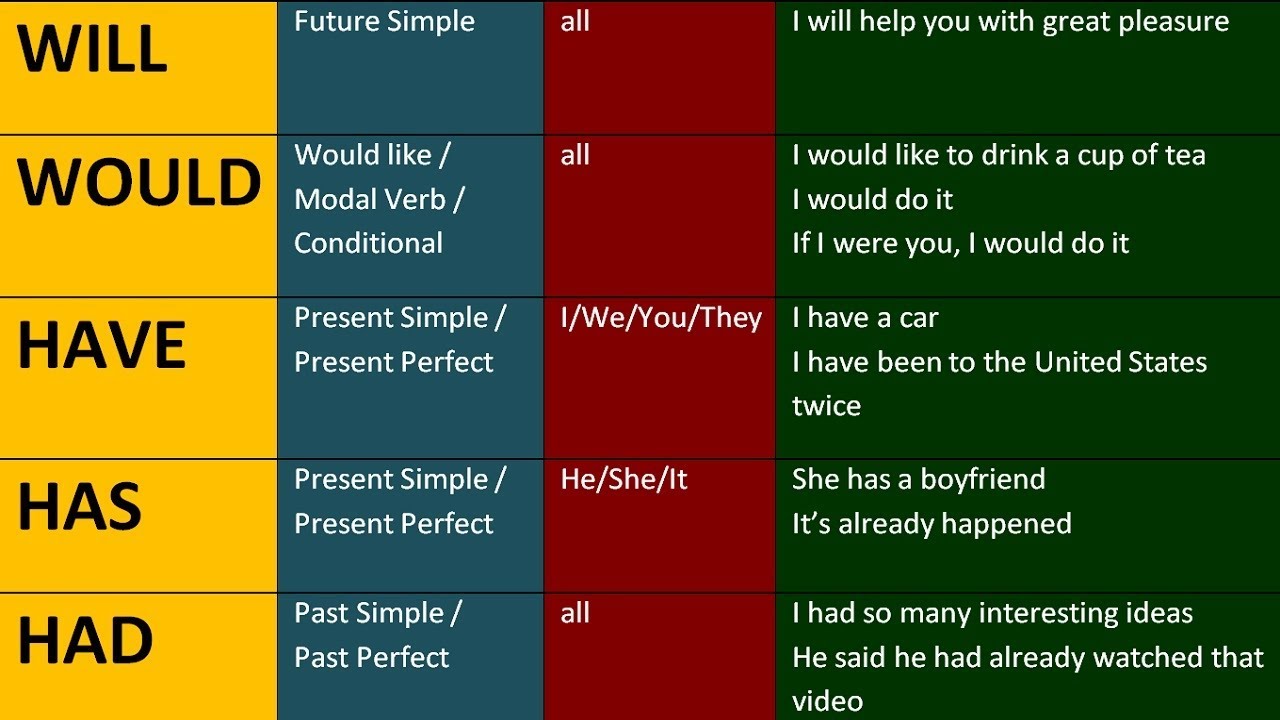
2. Use of "has / have / had " To possess or hold something, like: I have (got) some old coins He has (got) two kids They have not (got) much money. (or, they don't have much..) She hasn't got a job in an MNC. (or, she doesn't have a job….) They had a posh house in the colony. Note: "got" is optional and used mostly in spoken English This question already has answers here : "There Is"/"There are" depends on plurality of the first list element or not? (5 answers) Closed 3 years ago. 1) There has been a funeral, two weddings and three thefts since you left. OR 1) There have been a funeral, two weddings and three thefts since you left.
DO, DOES, AM, IS, ARE, WAS, WERE, WILL, WOULD, HAVE, HAS, HAD. ENGLISH
Confused about Where To Use "Is / Are / Am / Was / Were" And "Has / Have / Had"? We Are Here To Help! admin 2022-12-15 3 min read The past tense in English is a common complaint from my students. The past tense is formed by simply adding the suffix "-ed" to the end of a verb. Simple! . Recommended . 2023-09-05 . null mins read Table of Contents Present and Past Tenses - "Is/Am/Are/Was/Were" Present Perfect Tense - "Has/Have/Had" Avoiding Common Mistakes Improving Communication Skills Conclusion Effective communication is rooted in proper grammar usage, and mastering verb tenses is a fundamental aspect of this skill. This animation teaches the learner to define and identify helping verbs, use 'am', 'is', 'are', 'was', and 'were' as helping verbs, also 'has' and 'had' as. Has and have are two of the English language's most popular words to describe possession. But just because these words are used in everyday conversation doesn't mean we're familiar with the grammar rules on how to use them correctly. Has and have are both forms of the verb to have, but they are used in different grammatical contexts.
HAS HAD, HAVE HAD, and HAD HAD in English usages, examples and
Story of "Is, Am, Are, Was, Were, Has, Have, Had Been | Concept/Usage/Conditional Sentences/Practice Dear Sir 16.7M subscribers Join Subscribe Subscribed 341K Share 7.6M views 3 years ago. The main difference between "has" and "have" lies in which subjects they use. "Has" is used with the third-person singular subjects "he," "she," and "it," or a singular noun. "Have" is used with first-person ("I," "we"), second-person ("you"), and third-person plural ("they") subjects. Examples: Johnny has to leave soon. 1 Answer Sorted by: 5 You are quite right: these both require plural verbs. Any dictionary should give you the conjugations of have and be In this comprehensive English grammar tutorial, you will learn how to properly use "is, am, are, was, were, has, have, and had" in your writing and speaking..
Use of Has and Have Worksheets for Grade 1 Kidpid
Chances are, you're familiar with one difference between was and were: the fact that was is the first- and third-person singular past tense form of the verb to be, while were is the second-person singular past and the plural past form of to be. Understanding Has vs. Have (Definition and Examples) | GrammarBrain Home / English / October 3, 2022 Understanding Has vs. Have (Definition and Examples) In our minds, the difference between has and have are evident. As a native English speakers, we use these verb forms flawlessly.
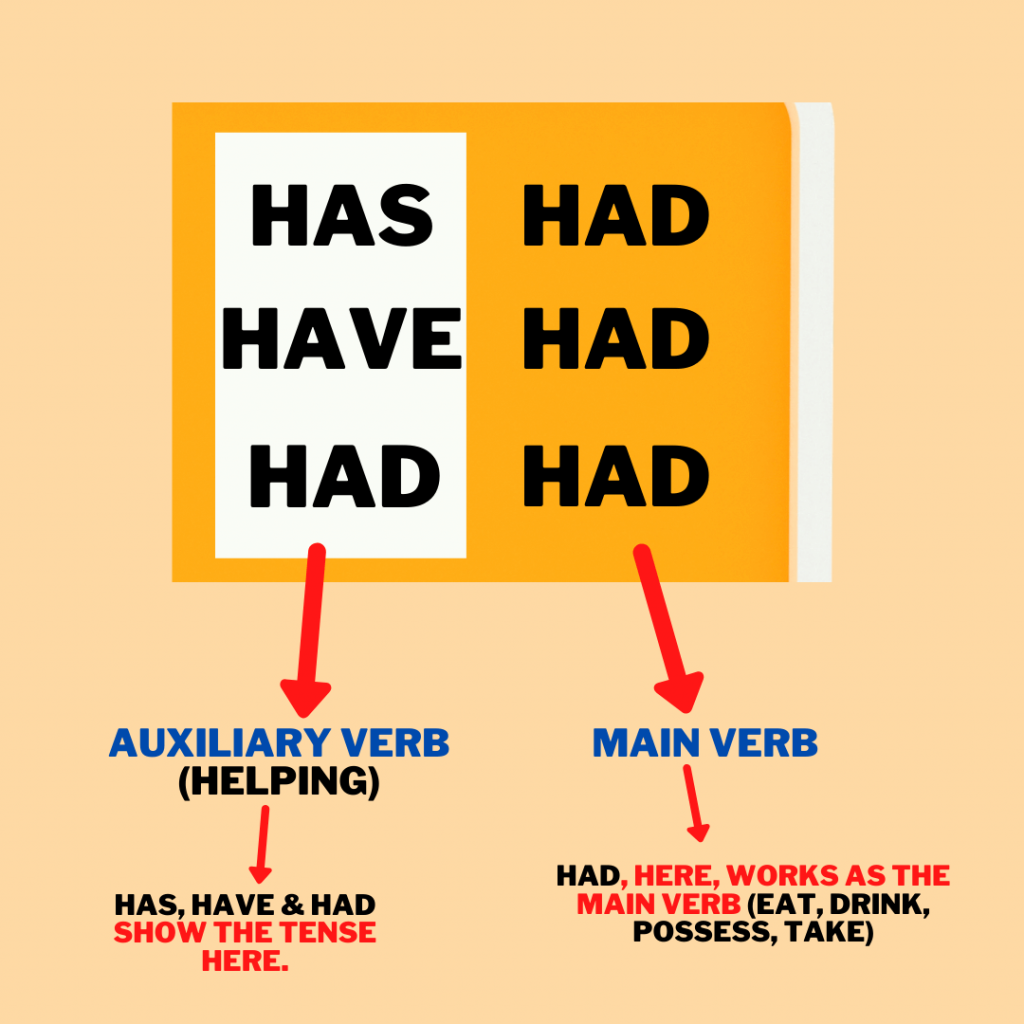
What Are Auxiliary Verbs? An auxiliary verb is used with a main verb to help express the main verb's tense, mood, or voice. For example (auxiliary verbs highlighted, main verbs in bold): Tense. The tense of a verb tells us when the action took place. Sally was eating the cake. Mood. To have means to possess or hold something. It also means to experience or undergo something. "Has" and "have" both mean the same thing as "to have." So why are there two different versions of the word? When Should I Use Have or Has? It's all to do with who we are talking about.

HAVE, HAS, HAD, HAVING and HAVING DONE. English grammar lessons for
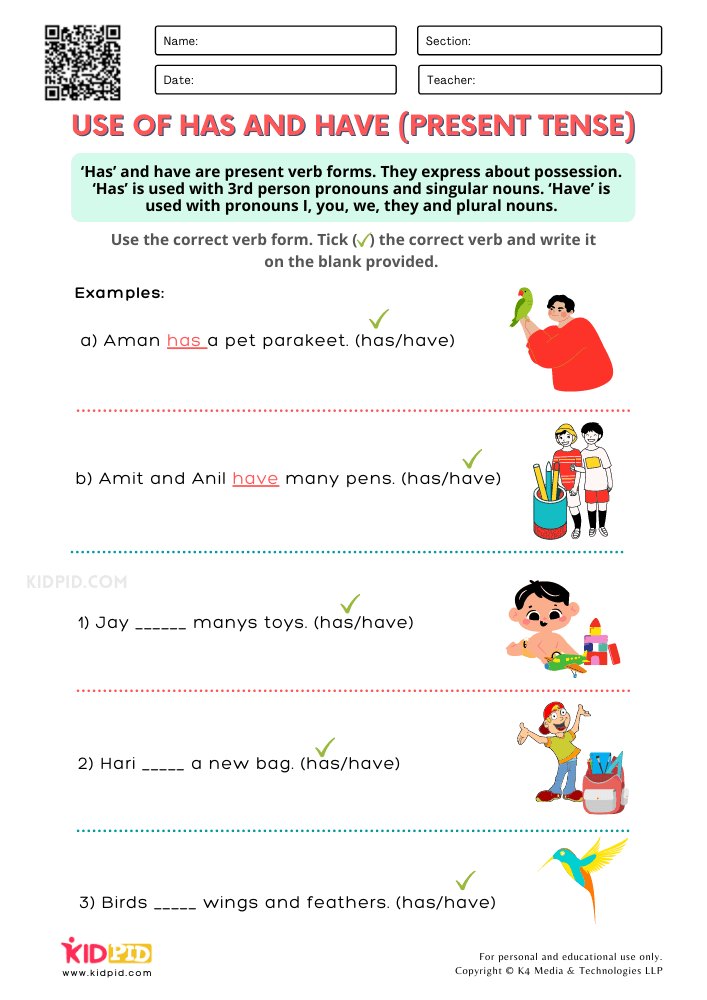
Even though "have" and "has" come from the same verb "to have," there are slight differences in the way they're used. Read about how to use them here. you (all) have. 3rd person: he, she, it, they. he/she/it has. they have. You'll notice that the only subject you should use "has" with is third person singular (he has, she has, it has). You should use "have" everywhere else. The subject "Al and Sue" is third person plural (the same as "they"), so use "have." Al and Sue have purchased a new home.




