In Myers & Briggs' personality typing, the Sensing/Intuition dichotomy describes how a person takes in information, whether through sensory-based experiences or by intuitively recognizing factual patterns and connections. Find your type Core Theory Mind: Intuitive (N) vs. Observant (S) Thought at Every Scale Our second personality scale includes the Intuitive (N) and Observant (S) styles. These traits describe what people are more likely to do with the information gathered from the world around them.
MBTI Understanding Personality Types
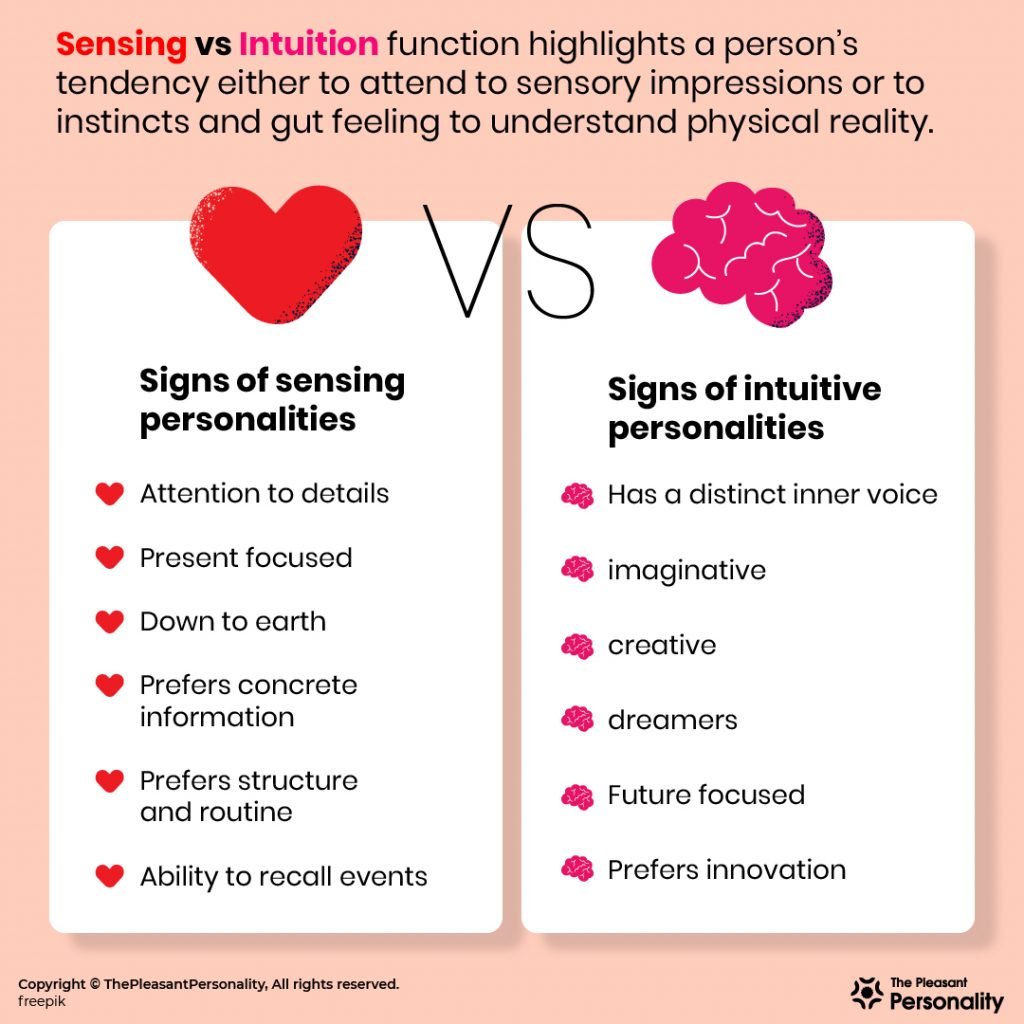
Created by renowned psychiatrist Carl Jung and popularized since the 1940s, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) uses tailored questions to find your combination of four sets of opposing traits: introverted versus extroverted; sensing versus intuitive; thinking versus feeling; and perceiving versus judging. Sensing types tend to pay attention to their immediate impressions, while Intuitive types are more inclined to believe in patterns, impressions, ideas, and future possibilities. Sensing types are present-focused and pay attention to details. They are practical and go by their senses when receiving outside information. Your highest percentages from the MBTI test are indicative of your dominant function. Every person has four functions based on the final score they receive from taking the test. People are either dominated by their sensing-to-intuition spectrum or their feeling-to-thinking spectrum. By Dr. A.J. Drenth. One of the primary dichotomies in the Jungian personality taxonomy is intuition (N) vs. sensing (S). It is sometimes cast as a preference for the "big picture" (N) vs. details (S), theory (N) vs. practice (S), or abstract (N) vs. concrete (S) matters. While each of these is relevant and appropriate in its own way, in.
Sensing vs Intuition Intuitive Personality Sensing Personality
Do you prefer to focus on facts and details or patterns and possibilities? This is the question that the Sensing or Intuition preference pair of the MBTI personality type helps you answer. Learn more about how these two ways of perceiving the world affect your behavior and communication. Advice for Intuitives | Expert Interview When talking to your friends, colleagues, or classmates in school, you might've heard them mention that they have a sensing or intuitive personality according to the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). Engage your senses. Appeal to your senses to make the learning experience more interactive. For example, turn memorization into songs or mnemonic devices, use different colored pens for notes, or wear a specific fragrance only when you study. Know when long-term goals are necessary. Short-term, practical goals are your bread and butter. In a nutshell, the difference between Sensors and Intuitives is this: Sensors prefer tangible information, whereas Intuitives prefer speculation and depth of insight.
NLP GLOSSARY MBTI Sensing and Intuition
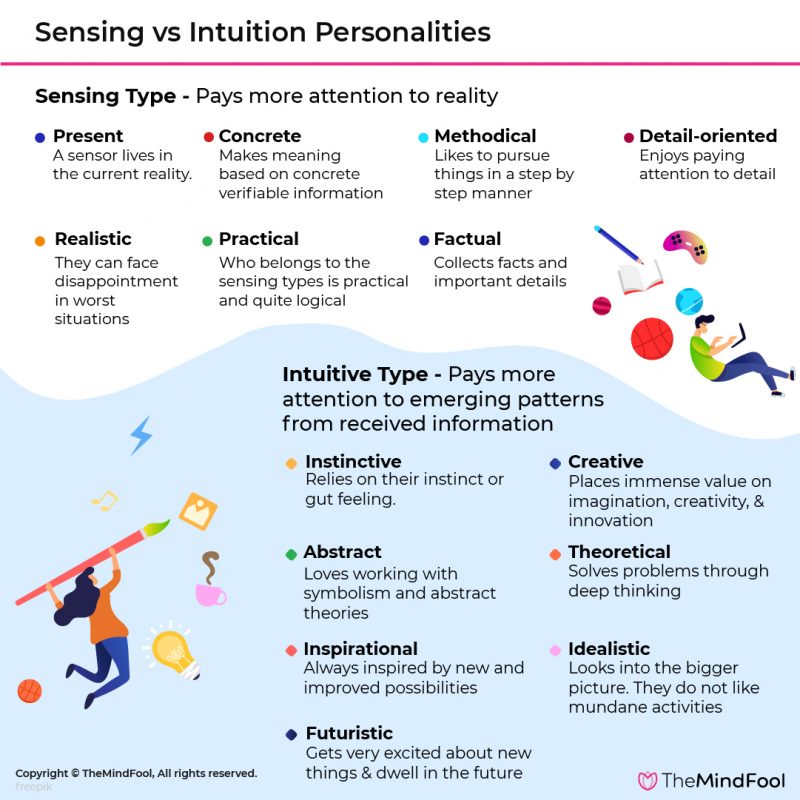
What makes you a sensor versus an intuitive? Let's explore, in detail, the ways in which each type interacts with the world around them. S Is For Sensing Those with personalities dominated by the sensing approach are known as sensors. An intuitive person thinks abstractly instead of on the details of a situation. Philosophers could be intuitive, thinking about implications and possibilities instead of details. What is the.
Personality Traits: Intuitive Vs. Sensing There are 8 Sensing Personality Types and 8 Intuitive Types. Sensing vs Intuition Examples Examples of Sensory Behavior Examples of Intuitive Behavior The sensing personality types include: The intuition personality types include: Why do you need to know if your personality is sensing vs intuitive? It means that you tend to: GRAY AREA. If you scored 0-83, you are closer to INTUITION, and if you scored 84 or more, you are closer to SENSING. However, your answers suggest that you use both preferences quite often. If you are trying to identify your four-letter type, consider both options.

Sensing (S) VS Intuition (N) S Vs N In MBTI By Asma YouTube
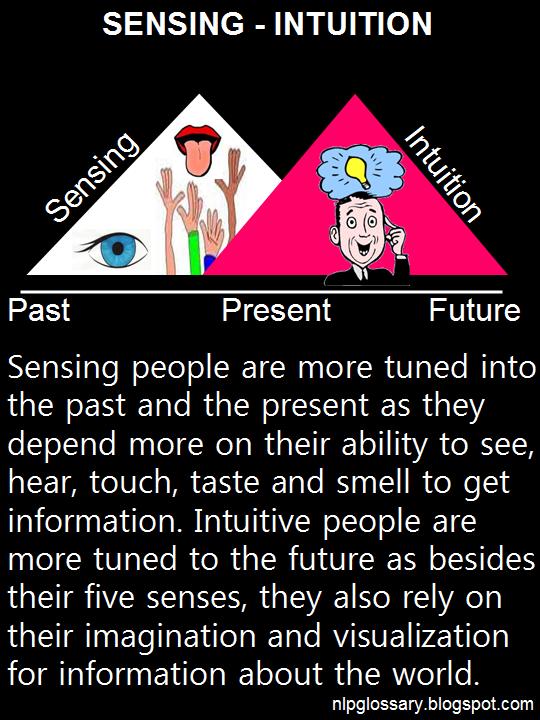
An S/N Example From My MBTI® Certification: Why Do Sensors and Intuitives Annoy Each Other? Sensors Focus On What Is Known While Intuitives Focus On What Is Unknown Why These Conversation Styles Can Cause Annoyance: The Sensing/Intuitive Difference in Relationships: So Can Intuitives and Sensors Have Happy Relationships? Intuition and sensing are two contrasting cognitive functions that form part of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality framework. These functions shape how individuals perceive and process information, make decisions, and interact with the world around them. While both intuition and sensing are essential for human cognition, they operate differently and can significantly impact how.




