Secretome, also known as conditioned medium, is a secreted molecule from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that has a variety of biological activities that can be used in various therapies, especially on the skin applications. A lack of conventional therapies makes secretome as a promising alternative t. Peptides conjugated with hydrophobic moieties are typical examples of supramolecular gelators (low molecular weight gelators, LMWGs), which can be designed or programmed to self-assemble to form.

ArtStation Cell, Arif Restu Concept art, Book art, Zelda characters
REST Is a Transcriptional Repressor of Neuronal Genes. Although Notch signaling and Hes activity have been shown to be fundamental in repressing neuronal differentiation during early embryogenesis, it remained at first unclear how repression of neuronal gene expression was maintained in non-neural cells—permanently throughout the life of a differentiated non-neural cell. Author Summary The RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) binds to DNA and has been shown to repress neuronal genes in non-neuronal systems, but more recent studies have expanded its functions much beyond this. At the molecular level, REST acts cooperatively with other proteins to execute its transcriptional regulatory roles. The dynamics of REST binding and cofactor recruitment and its. We show that REST binds and represses the cell cycle inhibitor gene p21, which is required for mouse cardiac development and regeneration. Rest deletion de-represses p21 and inhibits the. Beta cells are defined by the genes they express, many of which are specific to this cell type, and ensure a specific set of functions. Beta cells are also defined by a set of genes they should not express (in order to function properly), and these genes have been called forbidden genes. Among these, the transcriptional repressor RE-1 Silencing Transcription factor (REST) is expressed in most.

Restucell
Hair follicles, which are connected to sebaceous glands in the skin, undergo cyclic periods of regeneration, degeneration, and rest throughout adult life in mammals. The crucial function of hair. Liquid biopsy startup Delfi Diagnostics has snagged Susan Tousi, Illumina's chief commercial officer, as its new chief executive. She's the fourth senior executive to leave Illumina since June. The resting membrane potential is the result of the movement of several different ion species through various ion channels and transporters (uniporters, cotransporters, and pumps) in the plasma membrane. These movements result in different electrostatic charges across the cell membrane. Neurons and muscle cells are excitable such that these cell types can transition from a resting state to an. Figure 2. The (a) resting membrane potential is a result of different concentrations of Na + and K + ions inside and outside the cell. A nerve impulse causes Na + to enter the cell, resulting in (b) depolarization. At the peak action potential, K + channels open and the cell becomes (c) hyperpolarized. When the membrane is at rest, K + ions.
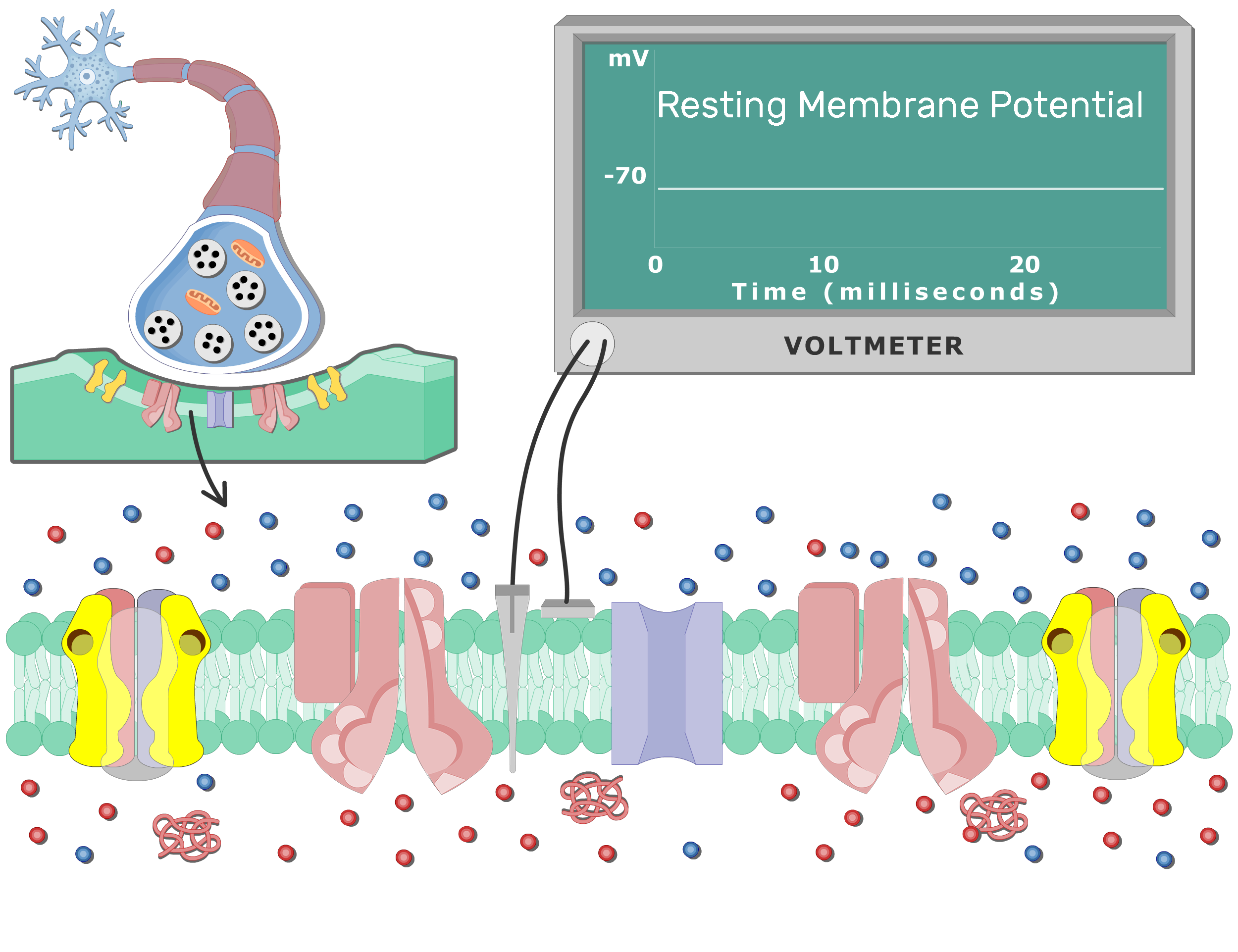
Postsynaptic Neuron Resting Membrane Potential GetBodySmart
In most resting neurons, the potential difference across the membrane is about 30 to 90 mV (a mV is 1 / 1000 of a volt), with the inside of the cell more negative than the outside. That is, neurons have a resting membrane potential (or simply, resting potential) of about − 30 mV to − 90 mV . Share your videos with friends, family, and the world
A resting membrane potential is the difference between the electric potential in the intracellular and extracellular matrices of the cell when it isn't excited. Every cell of the body has its own membrane potential, but only excitable cells - nerves and muscles - are capable to change it and generate an action potential . Explore the neuron resting membrane potential, a stable charge separation across the cell membrane. Discover the roles of anions and cations, and how their concentration differences create this potential. Uncover how neurons use these electrochemical driving forces to perform their functions.

YUDA ARMI(RESTU CELL)
FreeCell is a variation of Solitaire where the goal is to move all 52 face-up cards to the foundation. You do this by freeing up cards in the tableau by sequencing them and using four open cells where any playable card can be placed. Learn more with our instructional video. The present study reports that a short oligopeptide D-P1, consisting of only five D-amino acids, self-assembled into entangled nanofibers to form a hydrogel that functioned as a scaffold for cell cultures. D-P1 (Ac-D-Phe-D-Phe-D-Phe-Gly-D-Lys) gelated aqueous buffer solution and water at a minimum gelation concentration of 0.5 wt%.



