A snubber is a device used to suppress ("snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electrical systems,. In AC circuits a rectifier diode snubber cannot be used; if a simple RC snubber is not adequate a more complex bidirectional snubber design must be used. Mechanical and hydraulic systems Table 2 is an index to the snubber circuits de-scribed in this article and gives the page number that the description of that snubber begins on. Duality in Snubber Operation Snubbers have a duality which is a drawback in some applications. A snubber which controls the switch voltage at turn off will create a current pulse.
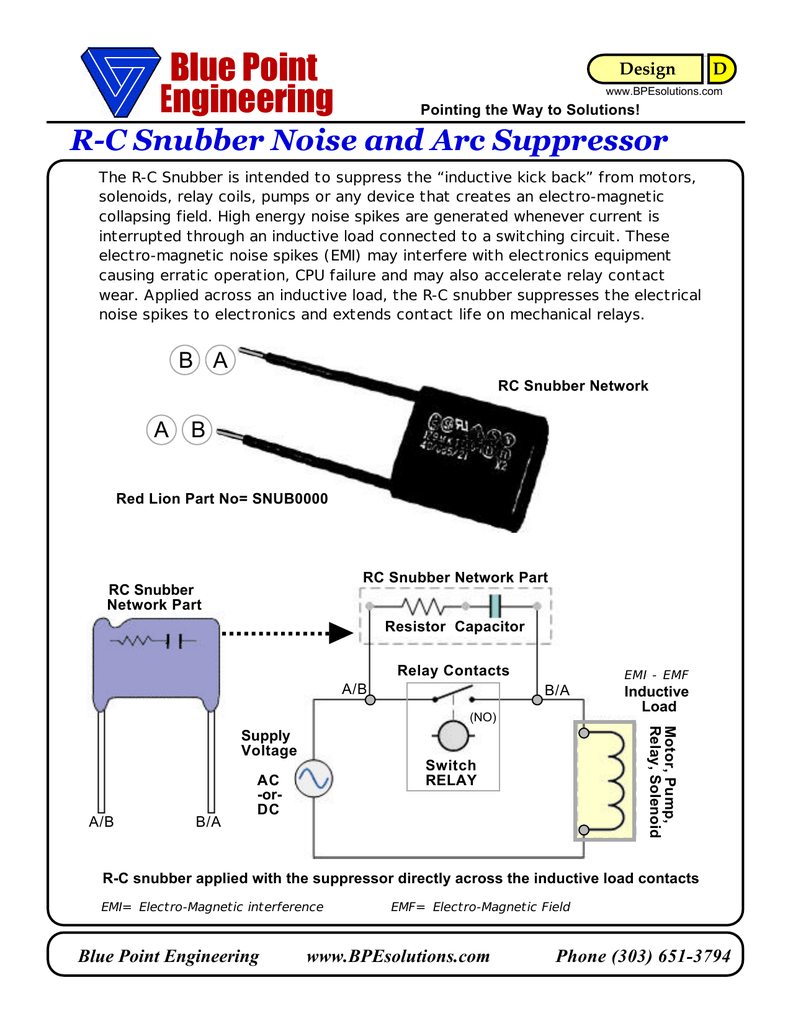
SNUBBER Circuit Blue Point Engineering
Purpose of Snubber Circuit. The main purpose of Snubber Circuit is to prevent the unwanted triggering of SCR or thyristor due to high rate of rise of voltage i.e. dv/dt. We already know that if the rate of rise of anode to cathode voltage of SCR is high then it may lead to false triggering. This is commonly known as dv/dt triggering. Snubber circuit design methods SiC MOSFET is getting more popular in applications where fast and efficient switching is required, such as power supply applications. On the other hand, the fast switching capability causes high dv/dt and di/dt, which couple with stray inductance of package and surrounding circuit, A snubber circuit absorbs excess energy by providing a path for the current to follow, either dispersing it as heat or storing it for later use. This operation limits the rate of voltage change (dV/dt) and current change (dI/dt) and clamps voltage spikes. Types of Snubber Circuits. Fig. 1: A snubber (RC) network is used for transient voltage protection. Every thyristor has maximum permissible value of di/dt. The thyristor can di be protected from excessive di/dt by using an inductor in series as shown in Fig. 2. The inductance opposes for rapid current variations di/dt.
How To Design A Snubber Circuit For Diode watcherlasopa
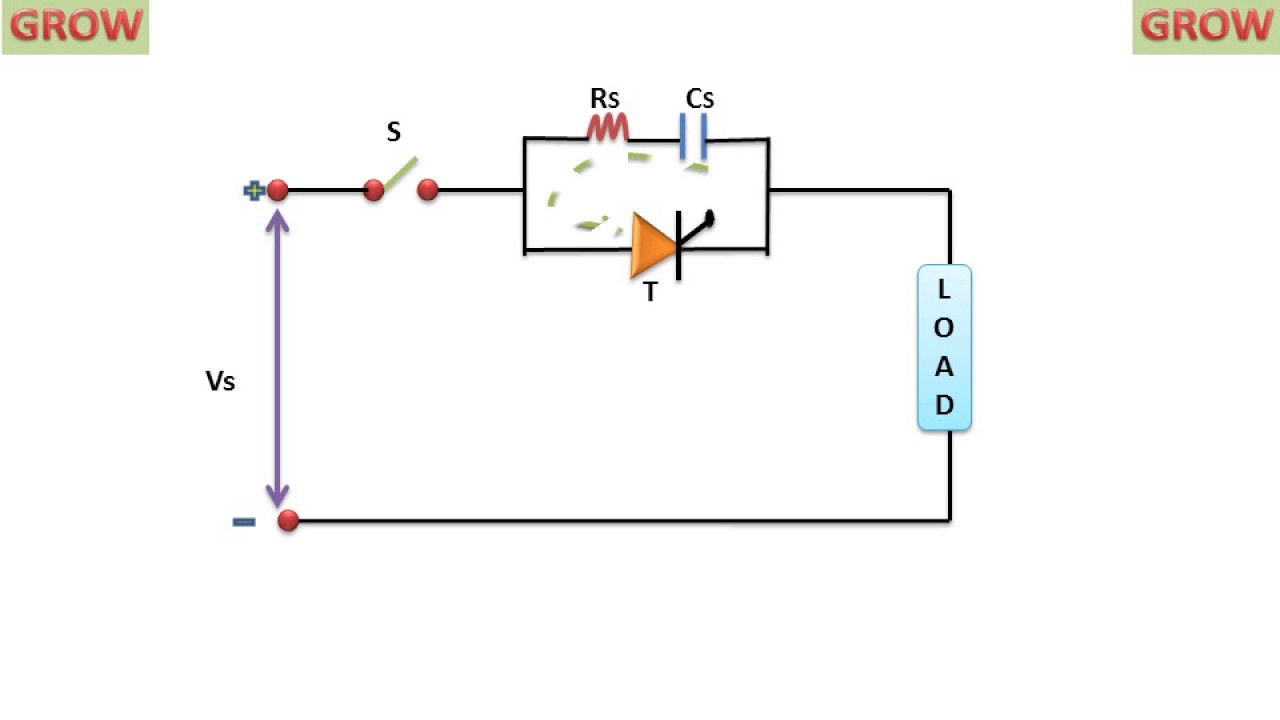
RC snubber design. An RC snubber, placed across the switch as shown in figure 4, can be used to reduce the peak voltage at turn-off and to damp the ringing. In most cases a very simple design technique can be used to determine suitable values for the snubber components (R and Cs). In those cases where a more opti-. s. Snubber circuits are essential for diodes used in switching circuits. It can save a diode from overvoltage spikes, which may arise during the reverse recovery process. A very common snubber circuit for a power diode consists of a capacitor and a resistor connected in parallel with the diode as shown in Fig. 2.7. A snubber circuit limits or stops (snubs) switching voltage amplitude and its rate of rise, therefore reducing power dissipation. In its simplest form, a snubber circuit basically consists of a resistor and capacitor connected across the thyristor. They are capable of doing many things, including: Reducing or eliminating voltage and/or current. An RC snubber circuit improves the TRIAC immunity against fast voltage transients. For example, regarding to the standard IEC 61000-4-4, a Z0109 standard TRIAC has a typical immunity level of about 0.7 kV, without any snubber circuit. With a snubber circuit (1 nF and. 47 Ω), the Z0109 immunity level can reach 4.0 kV.

Snubber Circuit A Safeguarding Circuit for Protecting Against Power Surges
Figure 5. Snubber Circuits. Figure 5 shows two different snubber circuits: a diode-Zener (DZ) snubber and a resistor-capacitor (RC) snubber. A snubber circuit works by absorbing excess energy due to the leakage inductance L l, thereby protecting the IC from potentially dangerous high voltages or excessive ringing.The DZ snubber ensures a well-defined and consistent clamping voltage and has. A flyback topology application circuit using the MAX1856 is shown in Figure 4. This is an example of using two snubber circuits for different objectives. D3, C11 and R11 form a clamp to limit the drain voltage and R5 with C10 forms a RC snubber to damp the ringing at the secondary rectifier (D2).
A selection of snubber circuits - simple RC (A), RCD (B), lossless passive (C), active clamp (D). Image used courtesy of Bodo's Power Systems . The RCD snubber network (Figure 3B), provides a more secure clamping action of drain voltage and is preferred when the peak voltage expected at high line is close to the maximum for the switch. RC Snubber Circuit for SCR dv/dt Protection: This type of snubber circuit consists of a series combination of resistance R and Capacitance C in parallel with a SCR. When a reverse voltage is applied, commutation process is initiated and the forward current flow through SCR approaches zero. Due to the inductance, current continuous to flow due.

Single phase of a three level converter snubber circuit
Snubber is a form of circuit protection against voltage spikes, ringing and oscillation effects. Snubber works by either clamping voltage spikes but not altering the ringing frequency or does the same function. Snubber circuit design is one of the complex tasks in circuit design. It needs a deep knowledge on circuit's foundations to design a good snubber circuit. However, after reading this. The Snubber circuit is one type of dv/dt protection circuit of the thyristor. With the help of snubber circuit, the false turn-on of a thyristor due to large dv/dt can be prevented. RC Snubber Circuit for SCR dv/dt Protection: This type of snubber circuit consists of a series combination of resistance R and Capacitance C in parallel with a SCR. When a reverse voltage is applied, commutation.



