Whether you are an experienced power supply designer, designing your first switching power supply or responsible for a make or buy decision for power supplies, the variety of information in the Switch−Mode Power Supply Reference Manual should prove useful. Introduction to Switched Mode Power Supplies. SMPS circuits are considerably more complex than the linear stabilised power supplies described in Power Supplies Module 2. The main advantage of this added complexity is that switched mode operation gives stabilised designs that can deliver more power for a given size, cost and weight of power unit.

Switching power supply
DC power is usually available to a system in the form of a system power supply or battery. This power may be in the form of 5V, 28V, 48V or other DC voltages. All of the following circuits are applicable to this type of duty. Since voltages are low, isolation is not usually required. Table 1. This manual includes basic information for switching power supply, general specifications, safety regulations, EMC standards, CE, reliability, operation notes, technical Q&A, and notes on failure correction. Figure 1: The step down "Buck" regulator The power device is switched at a frequency f = 1/T with a conduction duty cycle, δ = t on /T. The output voltage can also be expressed as: V out = V in . δ Device selection: * Power switch: V cev or V DSS > V in max * Rectifier: V RRM ≥V in max I F(AV) ≥ I out (1-δ) ∆I I cmax or I D max > I out + 2 ∆ Switch-mode power supplies (SMPSs) are frequently used to provide the various levels of DC output power needed for modern applications, and are indispensable in achieving highly efficient, reliable DC-DC power-conversion systems. Why SMPS? The majority of electronic DC loads are supplied from standard power sources.
Ac Dc Switching Power Supply Schematic
The semiconductor switches used to implement switch mode power supplies are cont inuously switched on and off at high frequencies (50 kHz to several MHz), to transfer electrical energy from the input to the output through the passive components. An switching model is like breadboarding on the PC The switching component is back in place, leading to: the analysis of current and voltage stresses the study of leakage and stray elements impacts the analysis of the input current signature - EMI a longer simulation time… Why Switching Simulations? Switching approach 1 vout 2 il 3.50 4.50 5.50 AC/DC Switch Mode Power Supply Design Guide Fairchild Power Switch (FPS) Green FPS Part Application PO(max) (W) PO(max) (W) Peak Current HV-FET Rating R DS(ON) max (Ω) Switching Frequency Package Number 85-265VAC 230VAC ±15% Limit (A) (V) Frequency (V) Mod. (kHz) FSCM0565RC STB, LCD Monitor 70 85 2.5 650 2.2 66 Yes TO220-5L Power supply unit (PSU) usually works to convert utility AC voltage into regulated DC voltages to be used by the equipment. In most PSU, the energy flow is controlled with semiconductors which are continuously switching on and off with high frequency. Such kind of PSU are referred to as switch mode power supplies or SMPS .

Build a Switching Power Supply Circuit Diagram Electronic Circuit
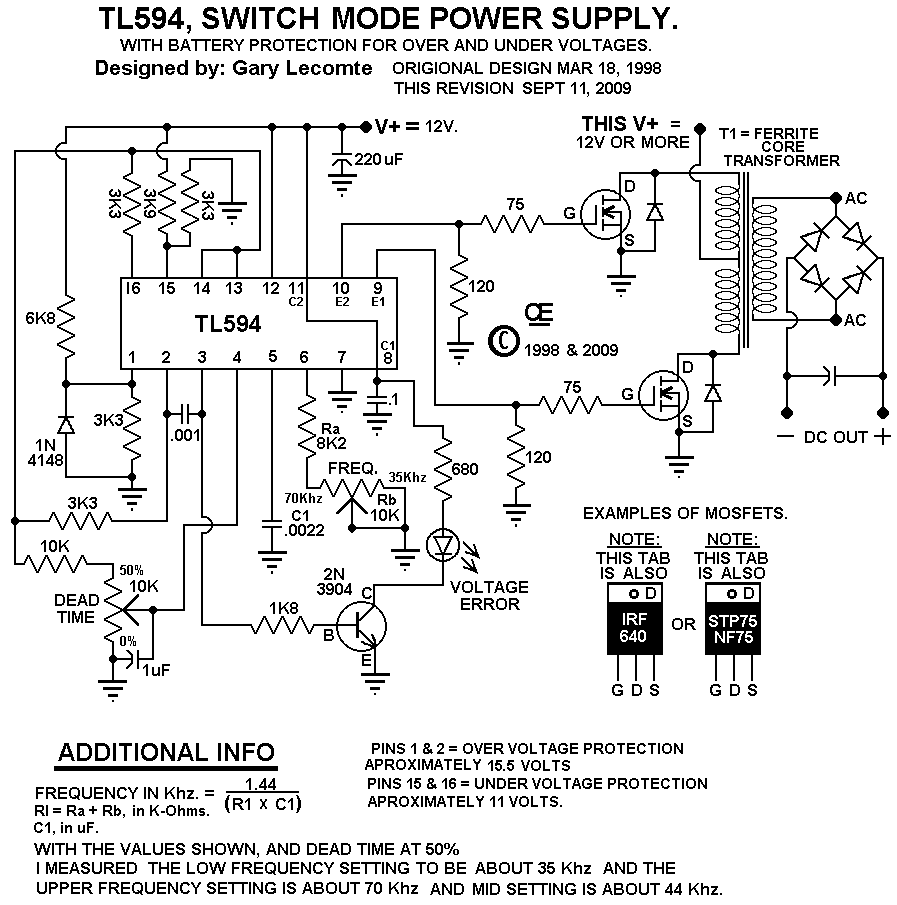
There are three types of switching power supplies: Step down regulator - sometimes called a "buck" regulator. Step up regulator - sometimes called a "boost" regulator. Inverting regulator - sometimes called a "flyback" regulator. In Project #2 we will focus on buck and boost regulator design. The Basic Device. The design of the TL494 not only incorporates the primary building blocks required to control a switching power supply, but also addresses many basic problems and reduces the amount of additional circuitry required in the total design. Figure 1 is a block diagram of the TL494.
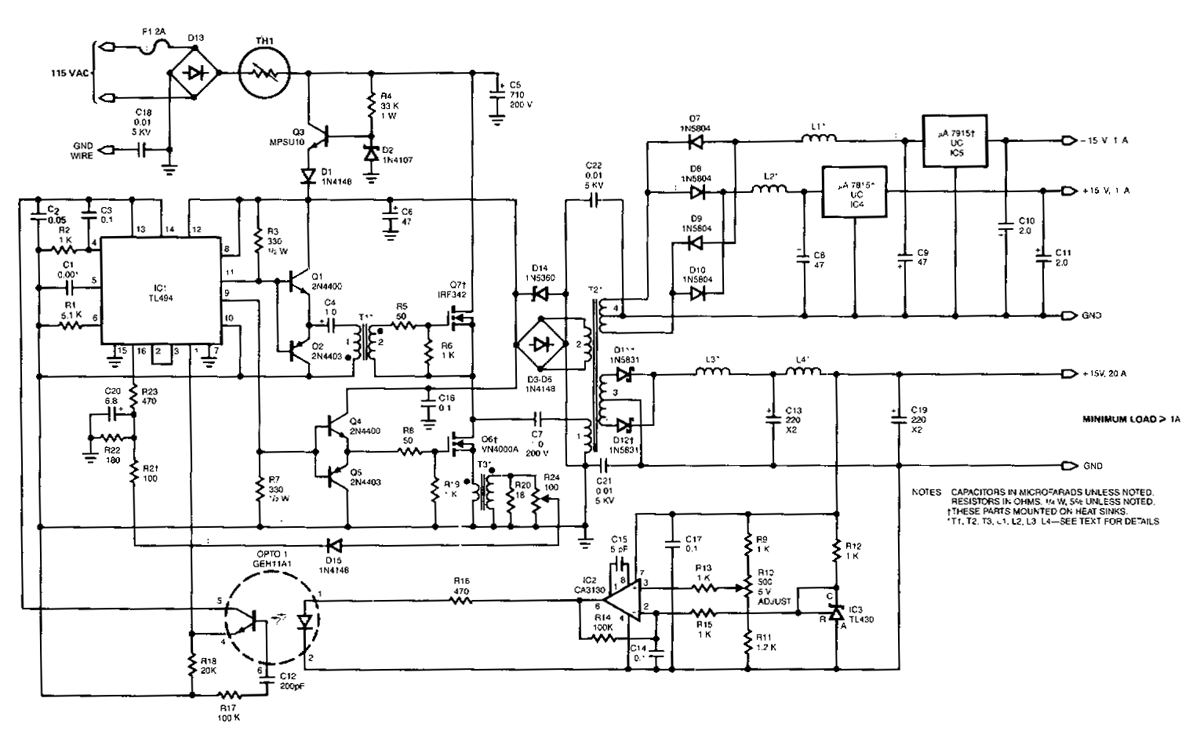
There are two main reasons, and both relate to cost. First, linear power supplies require large and expensive transformers. Second, the regulating transistor generates a lot of heat, which requires large and expensive heat sinks. For example, a 50V variable power supply set to output 5V at 2A might have (50V - 5V) * 2A = 90W of heat to dissipate. The switching power supply continues to increase in popularity and is one of the fastest growing markets in the world of power conversion. They offer the designer several. Motorola offers a wide range of power supervisory circuits that fulfill these needs in a cost effective and efficient manner. MOSFET drivers are also provided to enhance the
12 Volt Switching Power Supply Schematic
The most commonly used DC/DC converter circuits will now be presented along with the basic principles of operation. 2.1 Buck Regulator The most commonly used switching converter is the Buck, which is used to down-convert a DC voltage to a lower DC voltage of the same polarity. This is essential in systems that use distributed power rails (like TL494, NCV494. The TL494 is a fixed frequency, pulse width modulation control circuit designed primarily for switch mode power supply control. MAXIMUM RATINGS (Full operating ambient temperature range applies, unless otherwise noted.) Stresses exceeding those listed in the Maximum Ratings table may damage the device.




