Build an Supply Chain that Reacts using Real-time Visibility. Adapt Quickly and Operate Sustainably with a Predictive Supply Chain. Product, Design, and Data Platforms. Take 5 with Kearney. The Kearney FDI Confidence Index®. The Kearney advisory network. FFWD: Business model innovation. Sustainability and social impact at Kearney. Diversity, equity, and inclusion. Kearney in the media. Transforming the telecom value chain—a platform business model.
Basic Value Chain For Services Industry PowerPoint Slides
There has been new-entrant disruption, with increased competition among traditional players as well as nontraditional players, which have shifted value toward technology-focused parts of the value chain (for example, software-defined networking in a wide area network [SD-WAN], software as a service [SaaS], and over the top [OTT]). 1 Value Chain Design in a Fast-Clockspeed World: Study the Industry Fruitflies Evolution in the natural world: FRUITFLIES evolve faster than MAMMALS evolve faster than REPTILES THE KEY TOOL: Cross-SPECIES Benchmarking of Dynamic Forces Evolution in the industrial world: The industry value chain for telecom operations provides a comprehensive overview of services for the telecommunications industry focused on wireline, wireless, and cable and satellite segments. Therefore, industry-wide value chain analysis will explore the challenges related to the supply of information and communication raw materials, technology-based cooperation, and legal and regulatory issues. This research aims to assess the value chain of the telecommunication services and define the gaps, which are drawbacks of the development.
.png/55052679-3398-23d5-c486-e6b594015265?t=1642069139000)
Transforming the value chain—a platform business model Kearney
Therefore, industry-wide value chain analysis will explore the challenges related to the supply of information and communication raw materials, technology-based cooperation, and legal and regulatory issues. This research aims to assess the value chain of the telecommunication services and define the gaps, which are drawbacks of the development. Once those use cases are identified, four key steps can help telcos maximize value from advanced analytics to unlock the next level of productivity in service operations. (See Exhibit 2 for the four steps.) 1. Think beyond the usual data. Analytics models depend on large quantities of data from multiple sources. Deconstruction of the telecommunications industry—a transaction cost analysis. The paper has illustrated the transformation of the telecommunications value chain into value networks, examined the underlying reasons for the changes, identified the different types of players involved in the new telecommunications industry and. Creating value in telecom is essential because the industry enables and supports an ever-expanding range of economic activities. Our research with the World Economic Forum in Europe shows that investments in telecom infrastructure generally pay for themselves, as measured by GDP growth, in 7 to 18 months.

The new value chain Download Scientific Diagram
Under such background, this paper introduces a new value chain model of telecom value-added ser-vices in the new environment, providing theoretic support for transformation of telecom. Dedrick et al. , in an analysis of the distribution of value from innovation in the global supply chain of the Apple iPad and iPhone, studied the value dynamics of the undisputed leading mobile telecommunications company—Apple. Policies and economics of value systems implemented by the firm have allowed it to capture the largest share of value from product innovations, even though raw.
Context 1. more restrictive approach is to identify the customer contact points and create a Value Chain for the company's customer support functions. In general for a typical telecom. Therefore, industry-wide value chain analysis will explore the challenges related to the supply of information and communication raw materials, technology-based cooperation, and legal and.

Information and Communications Technology Value Chain Analysis 2019
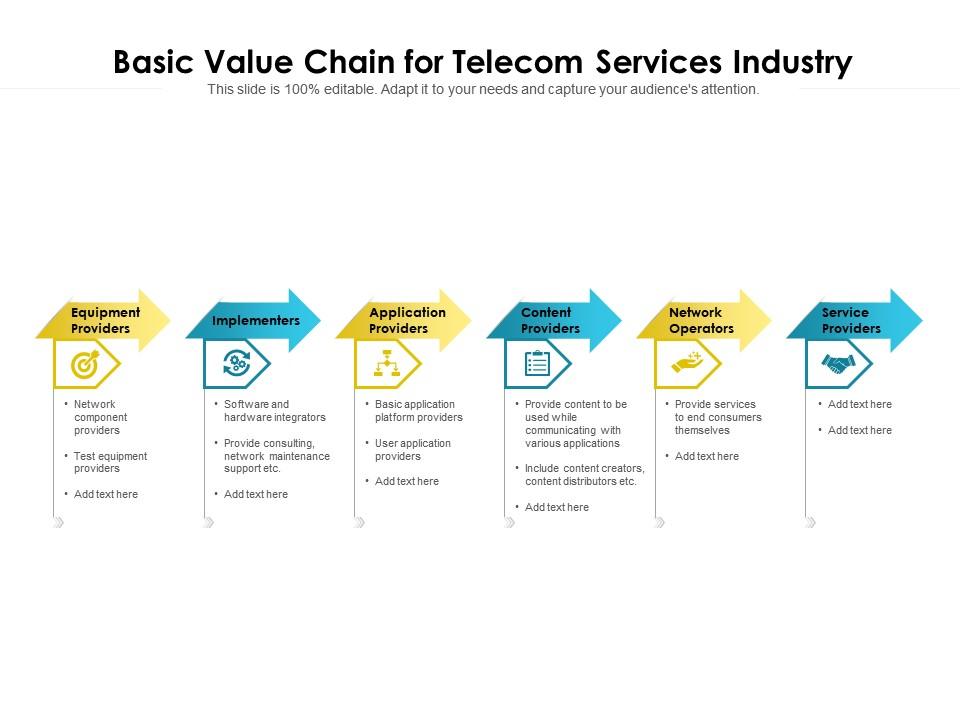
As a major telecommunications and technology company, we rely on a large and complex supply chain. In FY22 we engaged directly with more than 5,800 suppliers from 98 countries. Approximately 77 per cent of the total spend was with our top 100 suppliers. Additionally, these suppliers often have supply chains of their own, meaning our Value Chain in Telecommunications. The diagram above illustrates the basic value chain for residential broadband providers. In terms of the three broad areas of innovations described in the previous section, the most important players are equipment manufacturers and network operators. The figures below show the major actors in each category.

.png/55052679-3398-23d5-c486-e6b594015265?t=1642069139000)


