The gametocytes, male (microgametocytes) and female (macrogametocytes), are ingested by an Anopheles mosquito during a blood meal . The parasites' multiplication in the mosquito is known as the sporogonic cycle . While in the mosquito's stomach, the microgametes penetrate the macrogametes generating zygotes . Anopheles, the mosquitoes that spread malaria, like to lay their eggs in marshy areas or near the banks of shallow creeks and streams. Adult, female mosquitoes lay eggs one at a time directly on water. The eggs float on the surface of the water. Adult, female mosquitoes lay 50-200 eggs at a time. Eggs do not tolerate drying out. Larvae
Anopheles Mosquito Public Health
Anopheles ( / əˈnɒfɪliːz /) is a genus of mosquito first described by J. W. Meigen in 1818. Its members are sometimes called nail mosquitoes or marsh mosquitoes. [1] Many are vectors of the Plasmodium parasite of malaria in birds, reptiles, and mammals including humans. The gametocytes, male (microgametocytes) and female (macrogametocytes), are ingested by an Anopheles mosquito during a blood meal . The parasites' multiplication in the mosquito is known as the sporogonic cycle C. While in the mosquito's stomach, the microgametes penetrate the macrogametes generating zygotes . The malaria parasite develops both in humans and in the female Anopheles mosquitoes. The size and genetic complexity of the parasite mean that each infection presents thousands of antigens (proteins) to the human immune system.The parasite also changes through several life stages even while in the human host, presenting different antigens at different stages of its life cycle. Plasmodium. life cycle. The malaria parasite life cycle involves 2 hosts. During a blood meal, a malaria-infected female Anopheles mosquito inoculates sporozoites into the human host. Sporozoites infect liver cells. There, the sporozoites mature into schizonts. The schizonts rupture and release merozoites. This initial replication in the liver.
World Mosquito Day Tame the menace, control the spread of lifethreatening diseasesTech News
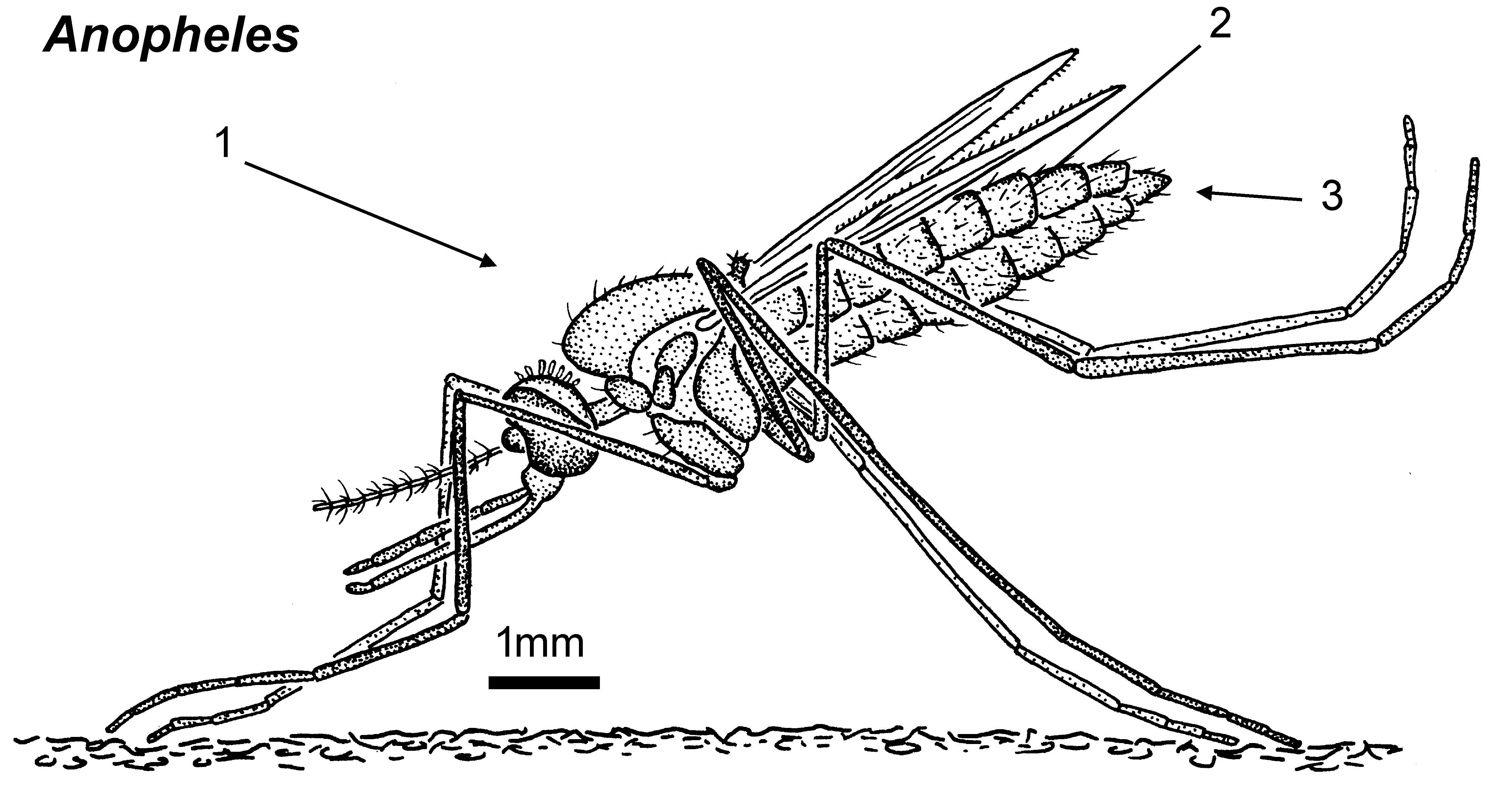
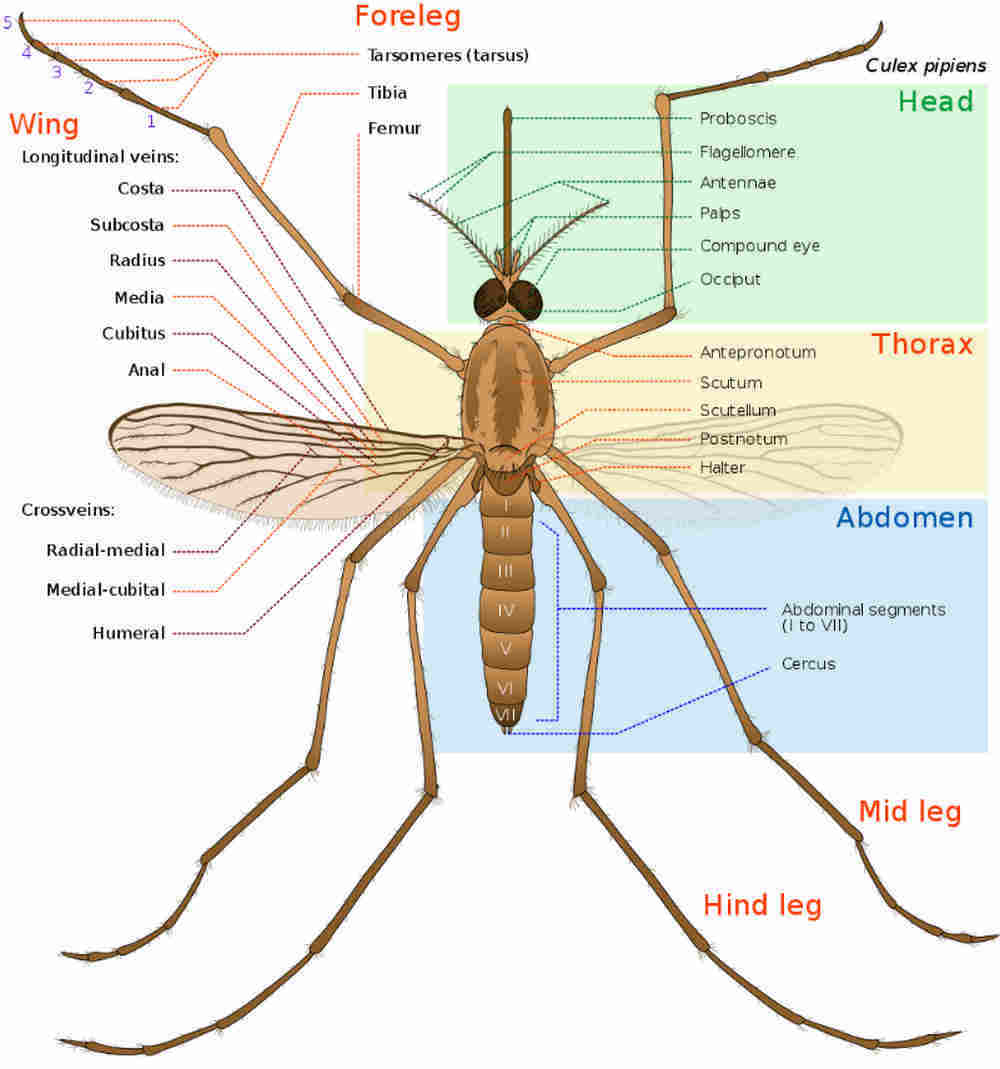
. are two main features that can be used to distinguish between adult anophelines and culicines: the maxillary palps ( Fig. 9) and the resting position (Fig. 10). Female species of the genus. The life cycles of Aedes, Culex, and Anopheles mosquitoes, from egg, to larvae, to pupae, to adult. 7 Citations 4 Altmetric Metrics Abstract Background The worldwide genus Anopheles Meigen, 1918 is the only genus containing species evolved as vectors of human and simian malaria. CDC Diagram of Female Adult Mosquito Page last reviewed: November 9, 2012 Global Health Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria Large diagram of an adult female mosquito.

a drawing of a mosquito on a white background
Anopheles gambiae Giles is the most efficient vector of human malaria in the Afrotropical Region (CDC 2010). Thus, it is commonly called the African malaria mosquito. The Anopheles gambiae complex of sibling species (White 1974; Fanello et al. 2002; Coetzee et al. 2013) comprises eight reproductively isolated species that are almost. reproduce. Only female mosquitoes bite and transmit malaria. Identification: Morphology: Worldwide, there are over 3,500 species of mosquitoes grouped into 41 genera. 837 of those species are in Africa. Human malaria is transmitted only by females of the genus Anopheles. Of the approximately 430 Anopheles species, only 30-40 transmit malaria.
Like all mosquitoes, anophelines go through four stages in their life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The first three stages are aquatic and last 5-14 days, depending on the species and the ambient temperature. The adult stage is when the female Anopheles mosquito acts as malaria vector. The adult females can live up to a month (or more in. The classic formulae in malaria epidemiology are reviewed that relate entomological parameters to malaria transmission, including mosquito survivorship and age-at-infection, the stability index (S), the human blood index (HBI), proportion of infected mosquitoes, the sporozoite rate, the entomological inoculation rate (EIR), vectorial capacity (C) and the basic reproductive number (R0). The.

Anopheles mosquito lifecycle. Immature mosquitoes pass through aquatic... Download Scientific
Download scientific diagram | 3 External anatomy of mosquito larvae, dorsal view, with anal segment and siphon at posterior end rotated to provide better view. (A) Anopheline form (Anopheles. 114 Citations 19 Altmetric Metrics Abstract Background In 1987, Gillies and Coetzee published a pictorial key for the morphological identification of adult female mosquitoes. Since then, several new species of anopheline mosquitoes have been described. Methods The 1987 key to adult female mosquitoes was used as the template for the current key.




