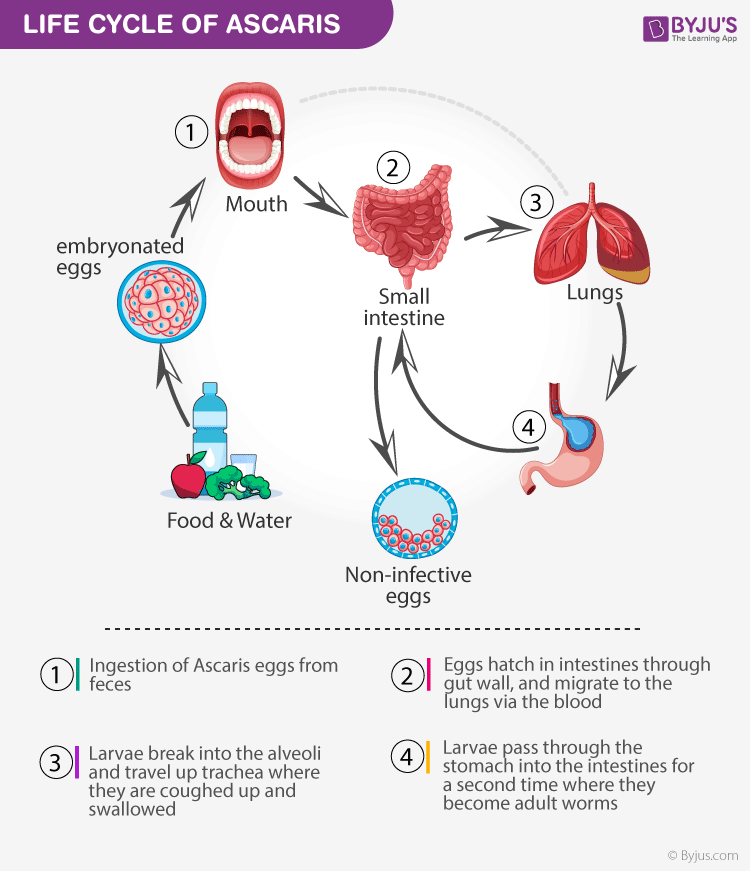
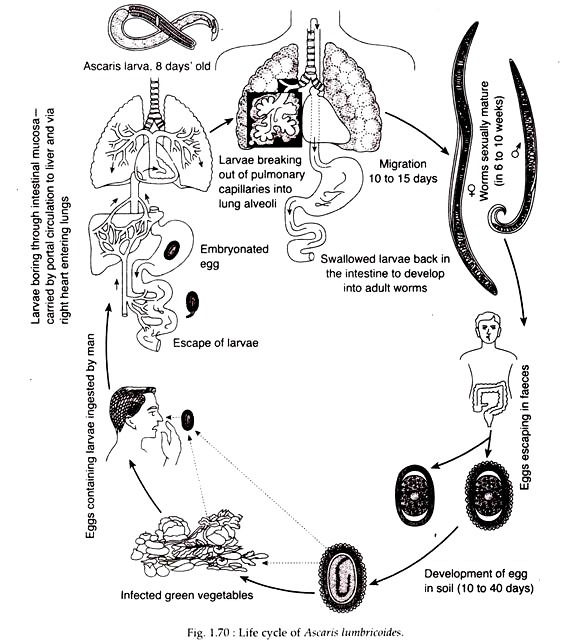
Life Cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides 1. Adult worms live in the small intestine of people. There, females may produce about 200,000 eggs per day. The eggs are excreted with stool. 2. Only fertilized eggs cause infection. 3. The fertilized eggs develop in the soil. The eggs develop best in moist, warm, shaded soil. 4. Life Cycle: View Larger Adult worms live in the lumen of the small intestine. A female may produce approximately 200,000 eggs per day, which are passed with the feces . Unfertilized eggs may be ingested but are not infective.

life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides inside and outside of the human body. Download Scientific
Ascaris lumbricoides Structure and Life Cycle: Introduction, Diagram and Life Cycle, FAQs Ascaris lumbricoides is a nematode roundworm. They are parasitic worms falling under the family Ascarididae, the class Secernentea and the order Oxyurida. Ascaris causes the disease called Ascariasis. Login Study Materials NCERT Solutions Ascaris lumbricoides life cycle Adult worms (females 20 to 35 cm; males 15 to 30 cm) (1) live in the lumen of the small intestine. A female may produce approximately 200,000 eggs per day, which are passed with the feces (2). Unfertilized eggs may be ingested but are not infective. Life cycle Image showing life cycle inside and outside of the human body of one fairly well described helminth: A. lumbricoides Ascaris lumbricoides, a roundworm, infects humans via the fecal-oral route. Eggs released by adult females are shed in feces. Unfertilized eggs are often observed in fecal samples but never become infective. Ascaris lumbricoides Life Cycle 1. Adult Ascaris worms live in the lumen of the small bowel. 2. A female may produce about 200,000 eggs/day; the eggs are excreted with feces. Unfertilized eggs may be ingested but are not infective. 3.
Ascariasis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis,Treatment and Prevention
Life Cycle Infection in humans is acquired through ingestion of the embryonated eggs from contaminated soil. Ascaris lumbricoides is one of the soil-transmitted helminths, other most commons soil-transmitted helminths are whipworm ( Trichuris trichiura ), and hookworm ( Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus. Download scientific diagram | Diagrammatic representation of the life cycles of Ascaris, Trichuris and hookworm. From CDC, Creative Commons (Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2015. The Ascaris Life Cycle. Adults reside in the small intestines of humans and are either male or female. When a female releases fertilized eggs, they exit the human body through feces. Only. Ascaris lumbricoides is one of the most common parasitic infestations of the gastrointestinal tract worldwide. During the intestinal phase of the disease, the adult worms usually remain.
Study Notes on Ascaris Aschelminthes
Download scientific diagram | Diagram of the life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides , the most common human nematode infection worldwide ( Adapted from C.E. Archer & C.C. Appleton, Unpublished ©). Life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides 1. Egg in feces 2. Development in soil 3. Infection to host Pathogenicity of Ascaris lumbricoides 1. By Migrating Larvae 2. By adults Clinical manifestation of Ascaris lumbricoides 1. Intestinal ascariasis 2. Pulmonary ascariasis References and Sources Life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides
Life Cycle, Pathogenicity and Prophylaxis of Ascaris lumbricoides.pdf - Google Drive. Species: lumbricoides Ascaris lumbricoides is elongated, cylindrical, and tapering at both ends. It is a large sized nematode showing sexual dimorphism, i.e., sexes are separate. They can be easily distinguished externally, i. e the male is smaller in size than the female, in male tail is curved.

Ascaris Lumbricoides Life Cycle Life cycle Ascaris Lumbricoides part 2, by Dr. Farheen
The Ascaris life cycle consists of four stages. These are ingestion, migration, maturation, reproduction. Moreover, this entire process takes 2-3 months to complete successfully. However, it can survive in the human body for almost two years. 8. 1. Cuticle 2. Epidermis 3. Muscle Layer Body Cavity or Pseudocoel of Ascaris Lumbricoides Digestive System of Ascaris Lumbricoides 1. Alimentary Canal 2. Mouth 3. Pharynx 4. Intestine 5. Rectum 6. Food, Feeding and Digestion Excretory System of Ascaris Excretory Organs Physiology Nervous System of Ascaris Lumbricoides




