PhET Global DEIB in STEM Ed Donate Build an atom out of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and see how the element, charge, and mass change. Then play a game to test your ideas! Build An Atom Player Information: In this game, use the basic building blocks of matter to build chemical elements. Find the answers you need using scientific tools like the Periodic Table. This game shows the most common form (isotope) of each element. There are others! You'll be asked general questions about elements.

3 Dimensional Atom Projects Atom project, Science project models, Atom model project
5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table. 5.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes. 5.1.1.4 Relative electrical charges of subatomic particles; 5.1.1.5 Size and mass of atoms; 5.1.1.6 Relative atomic mass; Edexcel Chemistry. Topic 1 - Key concepts in Chemistry. Atomic structure All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Approximately 50 million atoms of solid matter lined up in a row would measure 1 cm (0.4 inch). A convenient unit of length for measuring atomic sizes is the angstrom (Å), defined as 10 −10 metre. The radius of an atom measures 1-2 Å. Classroom Resources | Atomic Structure Unit Plan | AACT Atomic Structure Unit Plan (144 Favorites) LESSON PLAN in Atomic Spectra, Model of the Atom, Isotopes, Atomic Theory, Subatomic Particles, Emission Spectrum, Electrons, Orbitals , Ions, Unit Plans . Last updated September 18, 2023. Summary Atoms are composed of three main subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are grouped together in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons orbit about the nucleus. This page titled 2.2: Atomic Structure is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anonymous via source.
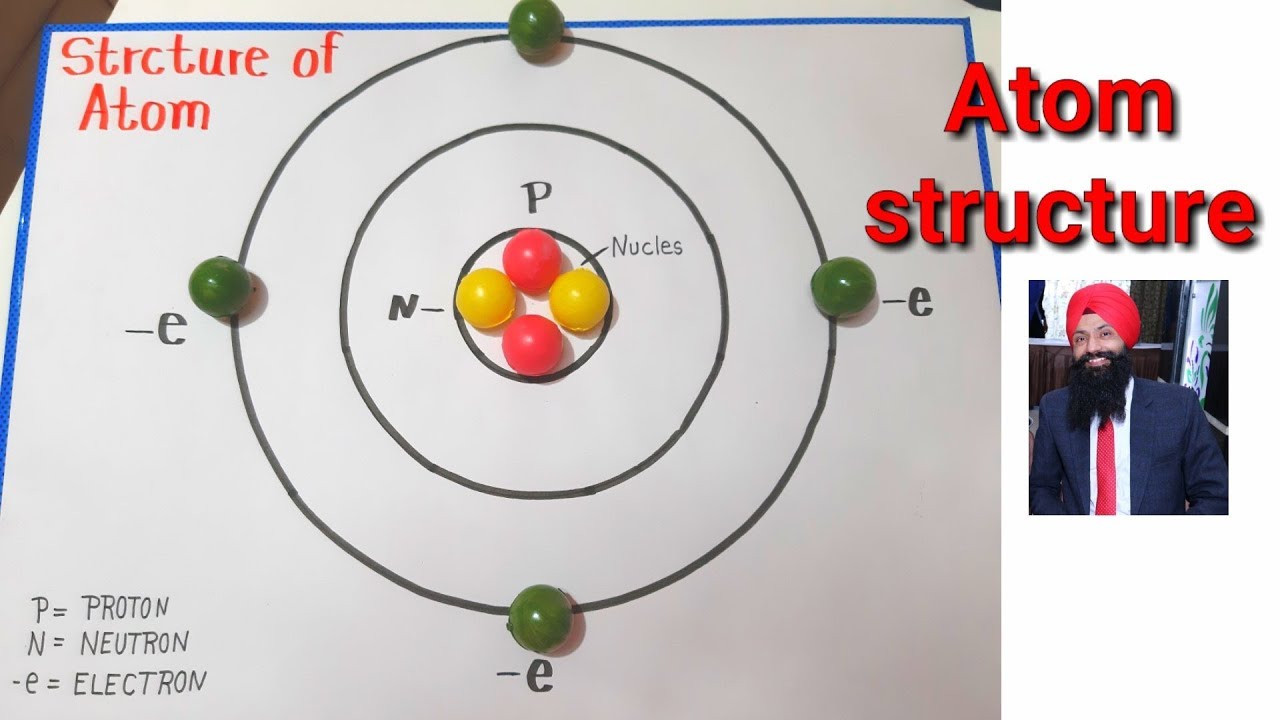
Atom structure model atom project for school Atom project making YouTube
Atomic Structure & Chemical Bonding Goal To understand why atoms form molecules. Objectives After this chapter, you should be able to interpret the properties of elements that are important for life from the periodic table. understand why and how atoms form bonds. draw Lewis dot and line structures to represent chemical bonds. What is life? 1.1 Atomic structure. 1.1.1 describe the structure of an atom as a central positively charged nucleus containing protons and neutrons (most of the mass) surrounded by orbiting electrons in shells; 1.1.3 define atomic number as the number of protons in an atom. 1.1.4 define mass number as the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom; Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms. representation of the state of electrons in an atom, such as 1s22s1 for lithium. detailed structure of atomic spectra produced by spin-orbit coupling. radiation produced by the excitation and subsequent, gradual de-excitation of an electron in an atom.

Chemistry Projects, Science Projects, School Projects, Projects For Kids, Craft Projects
8: Atomic Structure. In this chapter, we use quantum mechanics to study the structure and properties of atoms. This study introduces ideas and concepts that are necessary to understand more complex systems, such as molecules, crystals, and metals. As we deepen our understanding of atoms, we build on things we already know, such as Rutherford. Using the element you choose from part 1, create a model of an atom of that element. This project will help you to understand atomic structure. The following subatomic particles can be shown in the suggested colors and locations. You may pick other colors just make sure that the key reflects the colors: Electrons - orange - electron cloud
Three important kinds of radiation are α particles (helium nuclei), β particles (electrons traveling at high speed), and γ rays (similar to x-rays but higher in energy). 2.2: The Discovery of Atomic Structure is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Atoms, the smallest particles of an. Atomic structure is the structure of an atom that consists of a nucleus at the center containing neutrons and protons, while electrons are revolving around the nucleus. As atoms are made up of a very tiny, positively charged nucleus that is surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.

an art piece is hanging on the wall in front of a black with red, green and blue beads
The atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom comprising a nucleus (centre) in which the protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral) are present. The negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the centre of the nucleus. Download Complete Chapter Notes of Structure of Atom Download Now September 20, 2020 Are you looking for new ways to make learning about atoms fun? Check out my favorite activities for teaching atoms that your students are sure to love! 1. Use an Analogy I love to use analogies in class!




