Below you can see the block diagram of a basic PWM Class-D amplifier, just like the one that we are building. The input signal is converted into a pulse width modulated, rectangular signal using a comparator. This basically means that the input is encoded into the duty cycle of the rectangular pulses. A typical Class D power amplifier consists of a sawtooth waveform generator, comparator (based on an OPAMP), switching circuit, and a low pass filter. The block diagram of a Class D amplifier is shown in the figure below. Sawtooth waveform generator.
Diy Class D Amplifier Schematic
Class D Power Amplifiers - Circuit Diagram, Operation and Applications: Historically, audio amplifiers have been configured as class A, class B or class AB and the art of design is well known. Also well known is the poor efficiency of these amplifiers compared to that of class D amplifiers. A class-D amplifier or switching amplifier is an electronic amplifier in which the amplifying devices (transistors, usually MOSFETs) operate as electronic switches, and not as linear gain devices as in other amplifiers. Class AB vs. D Characteristic Comparison (2/2) Feature. Class D Advantage. Class AB. Linearity. Topology is inherently linear without feedback. Output device is non-linear; exponential in BJT, quadratic in MOSFET. Strong feedback is necessary to achieve good linearity. Linearity. This simplified functional block diagram illustrates a basic half-bridge Class D amplifier. Figure 2. The output-signal pulse widths vary proportionally with the input-signal magnitude. In order to extract the amplified audio signal from this PWM waveform, the output of the Class D amplifier is fed to a lowpass filter.
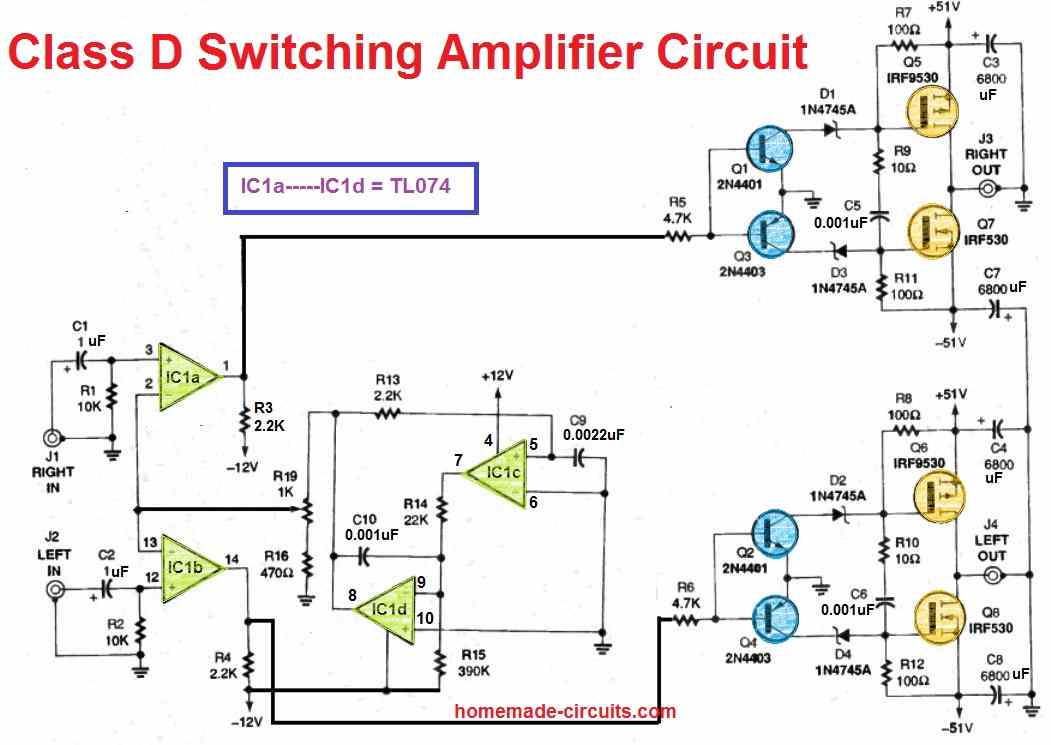
Make a Simple Class D Amplifier Circuit Homemade Circuit Projects
Bias Vcc Class AB amplifier uses linear regulating transistors to modulate output voltage. η = 30% at temp rise test condition. How a Class D Amplifier Works Feed back Triangle +VCC Nch Level Shift Error Amp COMP Dead Time Nch -VCC Class D amplifier uses MOSFETs that are either ON or OFF. A class D amplifier operates by deriving a two-state signal from a continuous control signal and amplifying it using power switches. At the core of every class D amplifier is at least one comparator and one switching power stage. In all but the lowest-cost power amplifiers, a passive LC filter is added. Class-D Vs. Class AB Amplifier Comparison. Block Diagram The class d amplifier block diagram is shown below. The class D amplifier is a switching amplifier because as compared to different amplifiers like class A, B, and AB, the class D amplifier can reach up to 90-95% of efficiency. Class D Type Amplifier Block Diagram What is a Class-D audio amplifier? The simplest answer will be, it's a switching amplifier. But in order to understand its working, we need to learn how it functions and how the switching signal is produced, for that, you can follow the block diagram given below. So why a switching amplifier? The obvious answer to this question is Efficiency.

IRS2092 STEREO CLASS D AMPLIFIER SCHEMATIC CIRCUIT
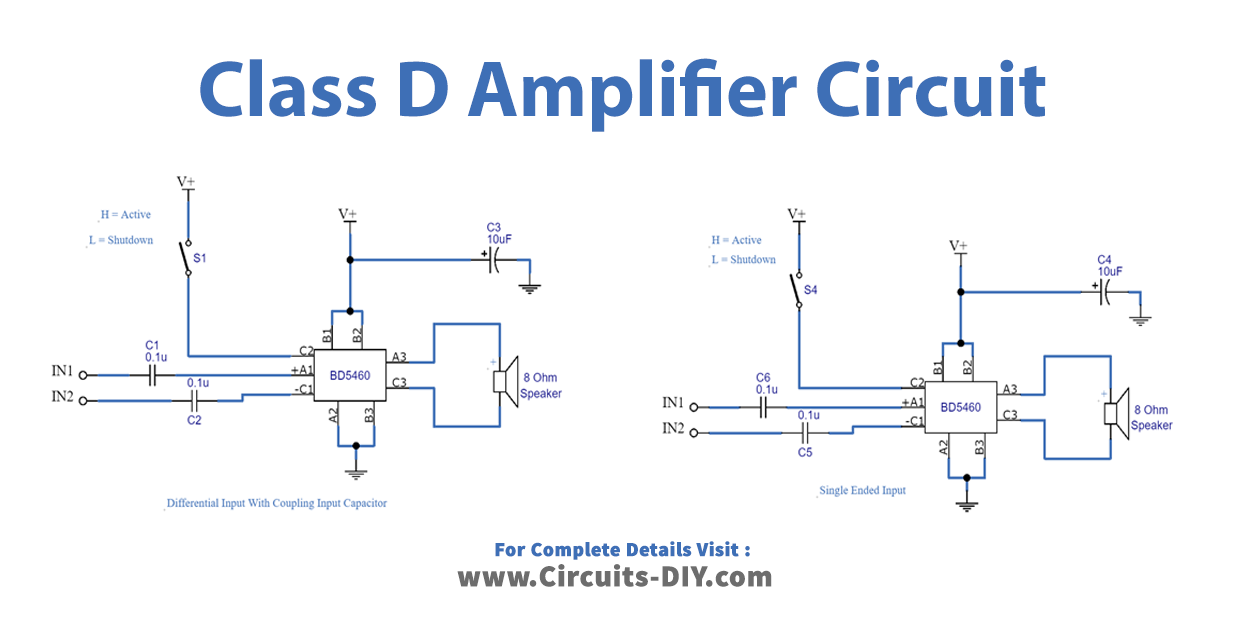
Circuit diagram. Class D amplifier circuit BD5460 Notes. The power supply voltage can be between 2.5 to 6.5V DC. For the circuit shown here, the supply voltage must be 3.6 V DC. Powering the circuit from a battery is the better option because it reduces noise. If you are using a DC power supply, then it must be well regulated and filtered. Class D Amplifier PVDD = 5.6 V to 18 V 3.3 V Second-Order LC Filter Four-Channel BTL Analog Output First-Order RC Filter Four Audio Analog Input Block Diagram www.ti.com 3 Block Diagram Figure 2. Automotive, Four-Channel, Class D Amplifier for Head Unit 3.1 Highlighted Products The TIDA-00573 design uses the following TI products:
The Class E [15, 17] amplifier builds on the Class D amplifier concept of using a transistor as a switch rather than as a linear amplifier. An RF Class E amplifier is shown in Figure 4.3.4 4.3. 4. The circuit shown uses two MOSFETS with M1 M 1 being the switching transistor and M2 M 2 acting in part as an active load. What are Class D amplifiers? How do they compare with other kinds of amplifiers? Why is Class D of interest for audio? What is needed to make a "good" audio Class D amplifier? What are the features of ADI's Class D amplifier products? Find the answers to all these questions in the following pages. Audio Amplifier Background
Simple Class D Amplifier Circuit
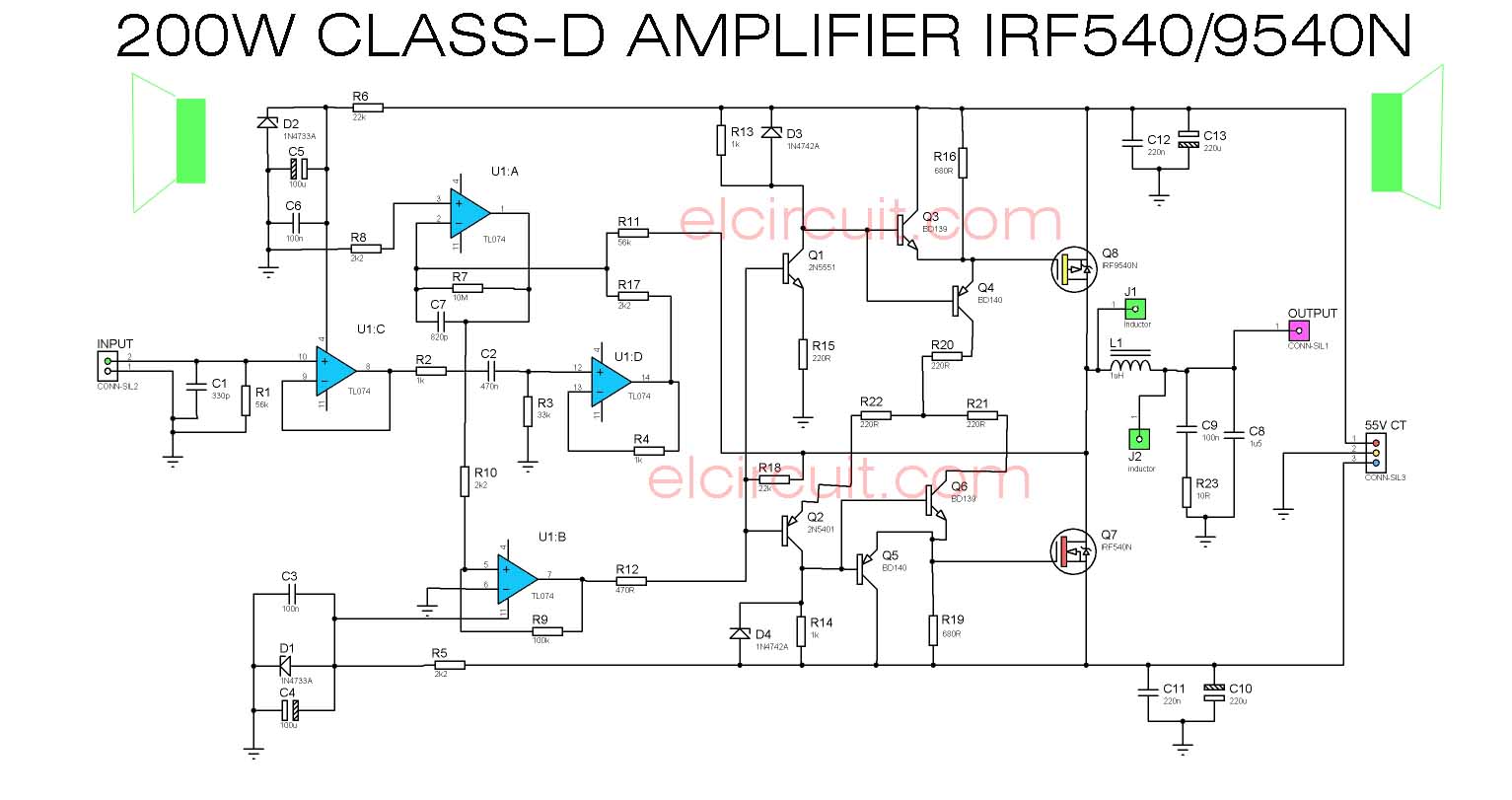
Class D Amplifier is Compact, Powerful, Low Cost, High Efficient. This Complete making of Class D Amplifier circuit that can produce 200W output power, very powerful, high efficient amplifier. See the circuit diagram, PCB Layout, wiring circuits, and tested amplifier video here. The amplifier will only consume power during the on/off transitions if leakage currents are not taken into account. Class D amplifier consisting of the following stages: PMW modulator; Switching circuit; Output lowpass filter; Block Diagram of Class D Amplifier PMW Modulator. We need a circuit building block known as a comparator.




