Design Desirability, feasibility and viability diagram: What does it mean? In this post we'll define desirability, viability and feasibility and provide examples to illustrate how these criteria keep you on the right track when designing any product. Cynthia Vinney 6 October 2022 6 min read Free course: Introduction to UX Design What is UX? Table of Contents 1) What is Desirability in Design Thinking? 2) Viability in Design Thinking 3) Feasibility in Design Thinking 4) Benefits of DVF Framework 5) Conclusion What is Desirability in Design Thinking? Customers or users need or want a product that satisfies the Desirability criteria.
Move Over Design Thinking Desirability, Viability, Feasibility Time for a Better Approach
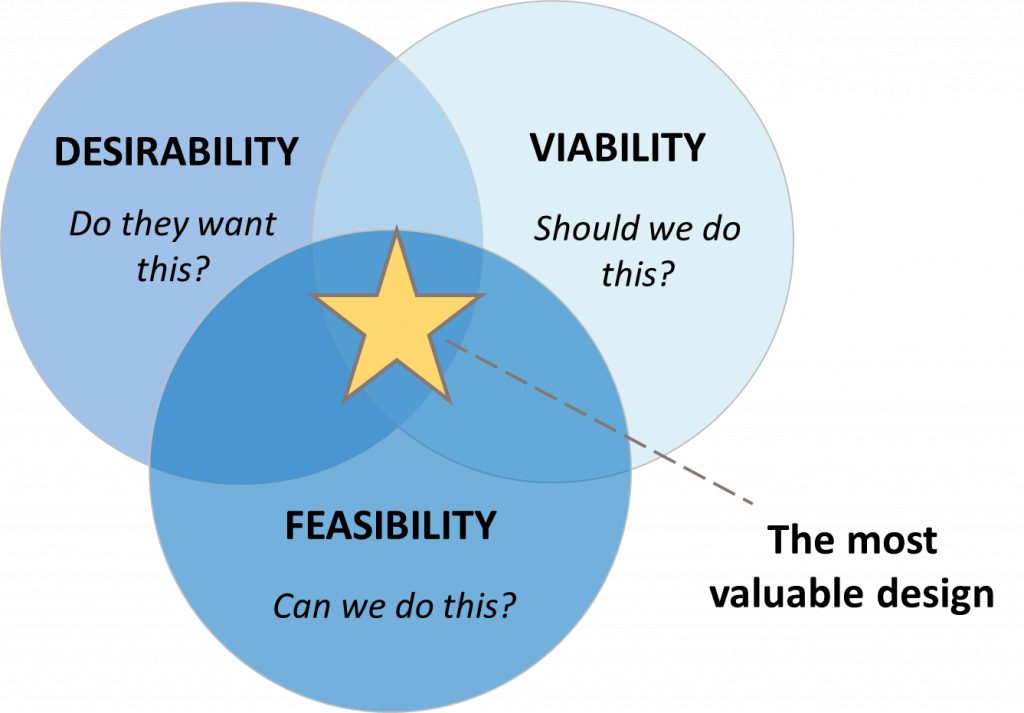
Desirability, viability, and feasibility is a design thinking methodology to test ideas, concepts, and hypotheses to determine if you have a unique value proposition (aka unique selling point) and whether it's worth pursuing. Without checking all three boxes, you increase the risks, costs, and potential for failure. The 5 phases of design thinking Empathizing with your target audience, your end users, whether B2C or B2B. Discovering, exploring, learning and putting yourself in your end users' shoes. Being user-centric. Defining the problem space, its scope and the opportunity areas that you can innovate around. Being specific. In design thinking, the concept of desirability is to assess whether the product or service the company is providing is considered essential to the user or merely a "nice to have." As part of the assessment, a UX design team considers carefully how exactly the product assists users in reaching their goals and what success looks like to the. Desirability is an important level of user experience that gauges how much a product or brand is wanted by a consumer. Sometimes, high desirability may be expressed through a premium. Increased prices sometimes evoke desirability—for example, as seen with a sleek BMW car design.

Design Thinking; Feasibility, Viability, Desirability Model. (HPI... Download Scientific Diagram
T he desirability, viability, feasibility diagram was originally developed to help explain the design thinking approach, which is primarily concerned with putting the customer or user at the center of the innovation process. The end goal of a design thinking process is to create a solution that is desirable, feasible and viable. This means that your product should satisfy the needs of a user, be feasible to implement and have a financial model as well. The design thinking process doesn't follow a fixed sequence of steps, but it has an ideal end point. The end goal of every design thinking project is a solution that is desirable, feasible and viable. Desirability focuses on people. It's what puts the "human" in human-centered design. Your solution is desirable if it appeals to the. Design Thinking is a customer-centric development process that creates desirable products that are profitable and sustainable over their lifecycle.. By definition, a prototype is cheaper and faster to produce than a complete solution. This enables faster feedback from users and customers, increased understanding of solution requirements, and.

Move Over Design Thinking Desirability, Viability, Feasibility Time for a Better Approach
IDEO's Desirability, Viability and Feasibility (DVF) framework is a powerful tool that helps teams create successful products by evaluating three key factors separately and bringing them together. By considering desirability, viability, and feasibility at each stage of the development process, product design teams can reduce uncertainty and. 6 The ideal innovation process is the trifecta of desirability, feasibility and viability, an idea that originated from IDEO in the early '00s (.
Desirability refers to the degree to which a design concept meets the needs, wants, and expectations of the target audience. This includes factors such as aesthetics, usability, and emotional. The answer is possibly a big no! Take the case of Tata Nano, the car that was supposed to shake up the auto industry. Tata motors demonstrated that it was feasible to produce a car at that low price point, at a fairly consistent quality and reliability level. Unfortunately, there was no convergence of desirability, feasibility and viability.
QUANTIFIED DESIGN™ Solving the Monty Hall Problem of Innovation Strategy Newry Corp
A. Definition and Significance of Desirability in Design Thinking. At the heart of Design Thinking lies desirability, a critical dimension encompassing the user's wants, needs, and aspirations. Desirability focuses on creating solutions that resonate deeply with users, sparking emotional connections and fulfilling unmet desires.. The Desirability, Viability and Feasibility (DVF) framework has traditionally been used within design thinking and innovation approaches. It endeavours to balance what is desirable from a customer point of view with what is technologically feasible and economically viable. Prioritizr provides the ability to score issues in Jira across each key.




