Summary Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Would you be surprised to know that short dogs are more aggressive? Or taller dogs are more affectionate? Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.
Body parts of Beagle dog The Animals
Updated: 10-08-2021 From The Book: Dog Grooming For Dummies Dog Grooming For Dummies Explore Book Buy On Amazon Some canine anatomical names may be familiar to you — dogs have elbows and ears and eyes — but other names may be downright foreign. Many anatomical terms used to describe parts of a dog are similar to the ones used for horses. Your Dog's Body Explained (A Simple Guide To Your Dog's Anatomy) By K9 Magazine April 17, 2023 In Dog Health Anyone who has ever run their hands over dogs of various breeds, ages and sizes will know that dogs are, despite being man's best friend, built entirely differently to humans. ANATOMICAL PARTS Abdomen Abdominal aorta Abdominal mammary gland Abdominal mammary region Accessory carpal bone Acromion Adductor muscle Ala of ilium; Wing of ilium Ala of nose Anconeus muscle Antebrachial region Aortic arch Apex of nose; Tip of nose Arm On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. You can also view the spinal column and the brain. Laurie O'Keefe Dog Anatomy Organs Right Side

Parts of a Dog Vocabulary English Study Here
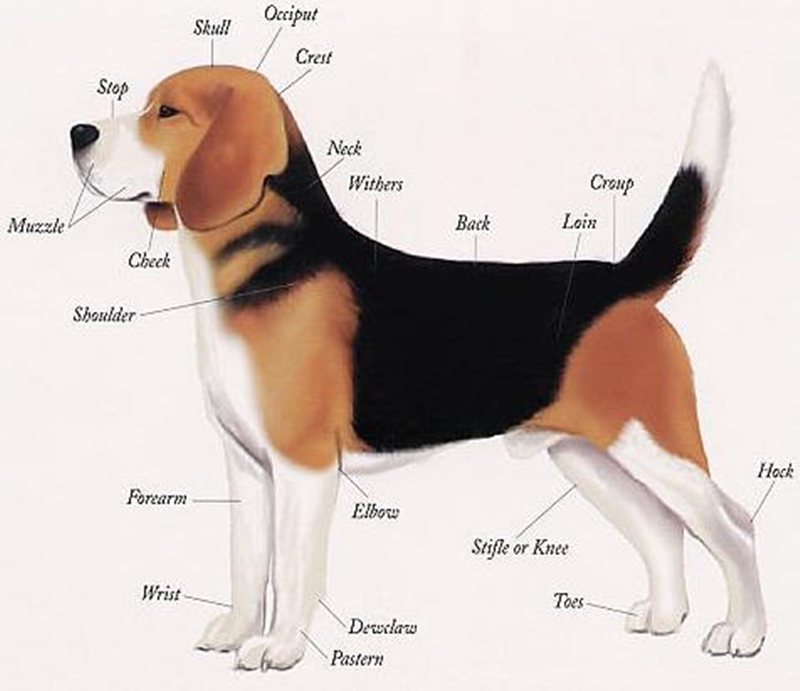
Animal Body Parts Vocabulary Frequently Asked Questions Parts of a Dog Vocabulary Practice Dog Anatomy Learn these dog body parts to enhance your English vocabulary words about animal anatomy. Parts of a Dog Eye Cheek Tongue Neck Shoulder Chest Elbow Forearm Claw Paw Toes Hock Tail Abdomen (belly) Thigh Withers Back Nose Muzzle We will be covering the most commonly used body parts of a dog, including the abdomen, throat, back, nape, belly, brisket, wrist, chest, prosternum, croup, claw, ear, elbow, and many more. Our aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the different parts of a dog's anatomy. Heart: Responsible for pumping blood throughout the body Lungs: Play a crucial role in the respiratory system, allowing dogs to breathe and take in oxygen Liver: Essential for metabolism and detoxification Kidneys: Filter and eliminate waste from the body through urine production These internal organs, along with others such as the stomach, intestines, and brain, work together to ensure a dog. Canine anatomy Dog skeleton Muscles of the dog Organs of dogs Canine anatomy As we explain above, canine anatomy is far ranging due to the diversity of existing breeds. These different breeds not only differ from each other in size, but in the shape of many body parts. Perhaps the most significant is head shape.

"Animal Body Parts" Vocabulary in English ESLBuzz Learning English
Parts of a dog body or barrel Topline of the dog body Different parts of a dog's forelimb Types of dog's forelimb and feet Different parts of the dog hind limb Hock point and Achilles tendon of the dog The body regions of a dog The cranium regions of a dog Regions of the face of a dog Regions of the dorsum of a dog This module of vet-Anatomy is a basic atlas of normal imaging anatomy of the dog on radiographs. 51 sampled x-ray images of healthy dogs performed by Susanne AEB Borofka (PhD - dipl. ECVDI, Utrecht, Netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx, thorax and abdomen/pelvis).
A dog's bark expresses different emotions like pleasure, fun, loneliness, fear, or stress. Smell: Smell is the dogs' primary sense. Dogs have nearly 220 million olfactory (smelling) cells, compared to 5 million in people. August 1, 2023 by George Nathan Welcome to "A Comprehensive Guide to Dog Body Parts Names." In this comprehensive article, we will take an in-depth look at the various body parts and systems of dogs, providing you with a detailed understanding of your furry friend's anatomy.

dog Role in human societies Britannica
External Anatomy Dogs, like all mammals, have eyes, a nose, a forehead, and ears. The only difference is that their noses are cold and wet, and their ears can be either dropped, erect, or cropped, depending on the breed. They also have a throat, a flew (the upper lip), chest, fore and hind legs, back, stomach, buttocks, and a tail. Anatomic Planes. The main planes of motion for dogs are as follows (see Figure 5-1): • The sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. • The dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions.




