Quick idea: in this article, you will learn the location of different organs from the different systems (like skeletal, digestive, respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular, endocrine, nervous, and special sense) of a dog with their important anatomical features. Internal anatomy of a dog: carnivorous domestic mammal raised to perform various tasks for humans. Encephalon: seat of the intelluctual capacities of a gog. Spinal column: important part of the nervous system. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Spleen: hematopoiesis organ that produces lymphocytes.
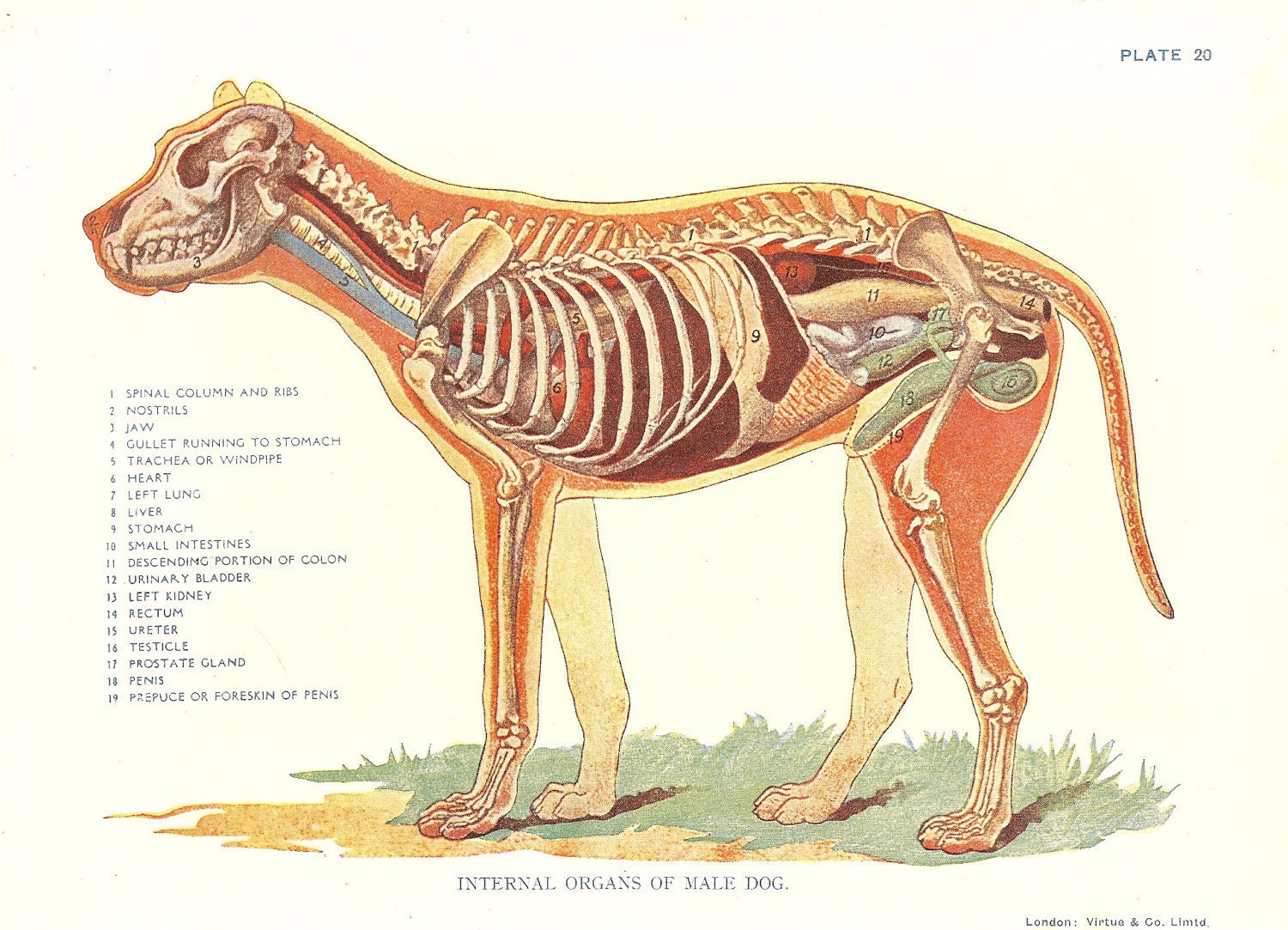
Dog Veterinary Print 1920s "Internal Organs Of Male Dog " Ideal for Framing.
Summary Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Would you be surprised to know that short dogs are more aggressive? Or taller dogs are more affectionate? Internal Anatomy of the Female Dog's Body Female vs. Male Dog Anatomy Comparison Health Considerations Conclusion FAQs External Anatomy of Female Dogs The female dog anatomy bears features both common and unique to her gender. Observing them helps in general care and detecting health abnormalities. Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length. Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated.

Внутренние органы собаки. Вид слева Dog Internal Organs, Anatomy. Left Anatomy Pinterest
External Anatomy Dogs, like all mammals, have eyes, a nose, a forehead, and ears. The only difference is that their noses are cold and wet, and their ears can be either dropped, erect, or cropped, depending on the breed. They also have a throat, a flew (the upper lip), chest, fore and hind legs, back, stomach, buttocks, and a tail. Common anatomical terminology Here are some common veterinary terms and their meanings: Pet senses Pets communicate in a very different way than people do. They have the same basic senses like sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste, but they use them differently to communicate with the world. Canine anatomy Dog skeleton Muscles of the dog Organs of dogs Canine anatomy As we explain above, canine anatomy is far ranging due to the diversity of existing breeds. These different breeds not only differ from each other in size, but in the shape of many body parts. Perhaps the most significant is head shape. Dogs have a third trochanter, which is the attachment site of the superficial gluteal muscle.. The ribs limit overall thoracic spine motion and protect internal organs. Joint Motion. The body segments of the forelimb and hindlimb are illustrated in Figures 5-3 and 5-4, respectively, with the major joints and their flexor and extensor surfaces.

Anatomy of a male dog crosssection, showing the skeleton and internal organs. Colour process
The Anatomage Dog is the first highly detailed dog anatomy atlas that comprehensively features internal organs, including vascular systems and muscular-skeletal structures. Originating from real dog data, the Anatomage Dog exhibits the highest level of anatomical accuracy. On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. You can also view the spinal column and the brain. Laurie O'Keefe Dog Anatomy Organs Right Side
Diaphragm: The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing. When a dog barks, it contracts the diaphragm forcefully to expel air out of its lungs and through its vocal cords. Laryngeal muscles: The laryngeal muscles control the opening and closing of the dog's vocal cords, which are located in the larynx (voice box) in the neck. Demo of the "Glass Dog Anatomy" program. This animation introduces first-year veterinary students to the anatomy of the dog's thorax and abdomen.©UGA

Dog Anatomy With Internal Organs 4k Textures 3D Model lupon.gov.ph
Publication date: Feb 24, 2022 | Last update: Oct 5, 2022 https://doi.org/10.37019/vet-anatomy/898995 ISSN 2534-5087 Introduction Knowledge of cross-sectional anatomy is essential in both medicine and veterinary medicine, particularly for the interpretation of CT and MRI scans. The internal organs of a dog include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, and reproductive organs. These organs work together to keep the dog healthy and functioning properly. For example, the heart pumps blood throughout the body, while the kidneys filter waste products from the blood.




