What is a Plant Cell? Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that vary in several fundamental factors from other eukaryotic organisms. Both plant and animal cells contain a nucleus along with similar organelles. One of the distinctive aspects of a plant cell is the presence of a cell wall outside the cell membrane. Read more: Cells Plant Cell Diagram A chloroplast is a type of plastid (a saclike organelle with a double membrane) that serves as the site of photosynthesis, the process by which energy from the Sun is converted into chemical energy for growth. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll to absorb light energy.
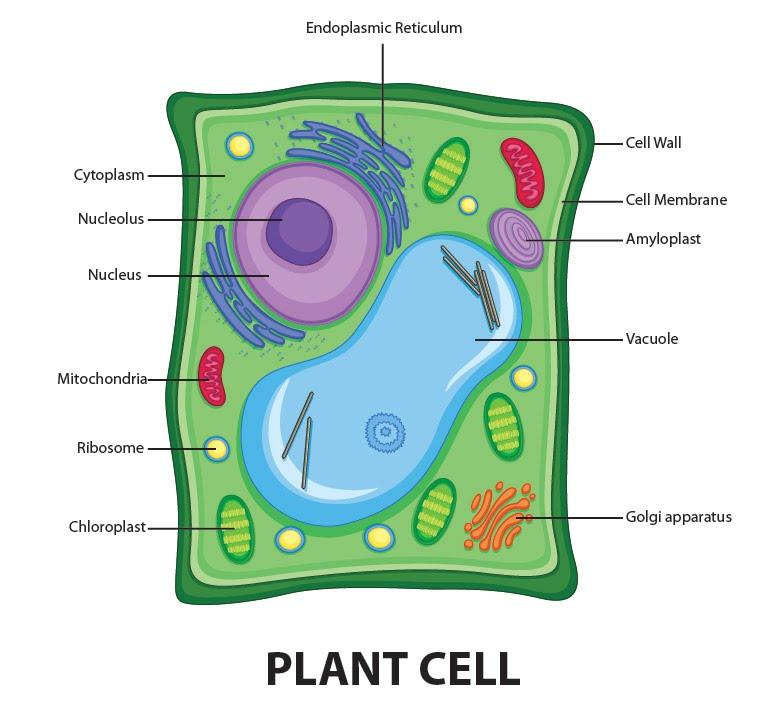
Draw a welllabelled diagram of a plant cell.
Structure of the plant cell (plasma) membrane Functions of the plant cell (plasma) membrane Plasmodesmata Structure of plasmodesmata of plant cells Functions of the plasmodesmata Cytoplasm Plastids Development of plastids General functions of plastids Types of Plastids Chloroplast Structure of the plant cell chloroplast A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Plant Cell Characteristics Plant cells are eukaryotic. 3. DNA, the heredity information of cells, which can be found in a nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the a nucleoid region of prokaryotic cell. 4. ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures composed of ribosomes and proteins. These structures can be found on the image of the plant cell (Figure 3.1.2.1 3.1.2. 1 ). The central vacuole is a large organelle that often fills most of the plant cell. It is filled with liquid and surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast. Plants can alter the solute concentration in the central vacuole to influence cell structure and movement of water. It is also a place to store pigments, such as anthocyanins, or other.

Vector Illustration Of The Plant Cell Anatomy Structure Educational Infographic Stock
Plant Cell: Parts and Structure With Functions Plant cells are the basic unit and building blocks of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They are cells that have a distinct nucleus and other cellular organelles enclosed within a membrane and thus are eukaryotic in origin. The plant cell will store water in the central vacuole, which expands the vacuole into the sides of the cell. The cell wall then pushes against the walls of other cells, creating a force known as turgor pressure. While animals rely on a skeleton for structure, turgor pressure in plant cells allows plants to grow tall and reach more sunlight. Plant Cell Structure Plants are unique among the eukaryotes, organisms whose cells have membrane-enclosed nuclei and organelles, because they can manufacture their own food. The structures are not necessarily drawn to scale but in enough detail to aid recognition and to help students re-draw this diagram by hand to include in study notes or homework. The structure of plant cells has similarities and differences compared with the structure of animal cells. The following table lists the parts of plant cells shown in.

Ultrastructure of a eukaryotic cell a plant cell (palisade mesophyll). Plant and animal cells
Animal and plant cells share common elements like plasma membranes, cytoskeletons, and mitochondria. However, they differ in certain aspects. For example, plant cells have a cell wall and a central vacuole, while animal cells contain centrosomes. The understanding of these cellular structures continues to evolve through ongoing research. This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below - the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal and plant cells.
Free IGCSE Bio practice questions:igcsebio.sciencesauceonline.comCells are the smallest unit of living organisms. Here I walk through how to draw a simple pl. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. Cell wall A thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. This layer of cellulose fiber gives the cell most of its support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant. Centrosome (The.
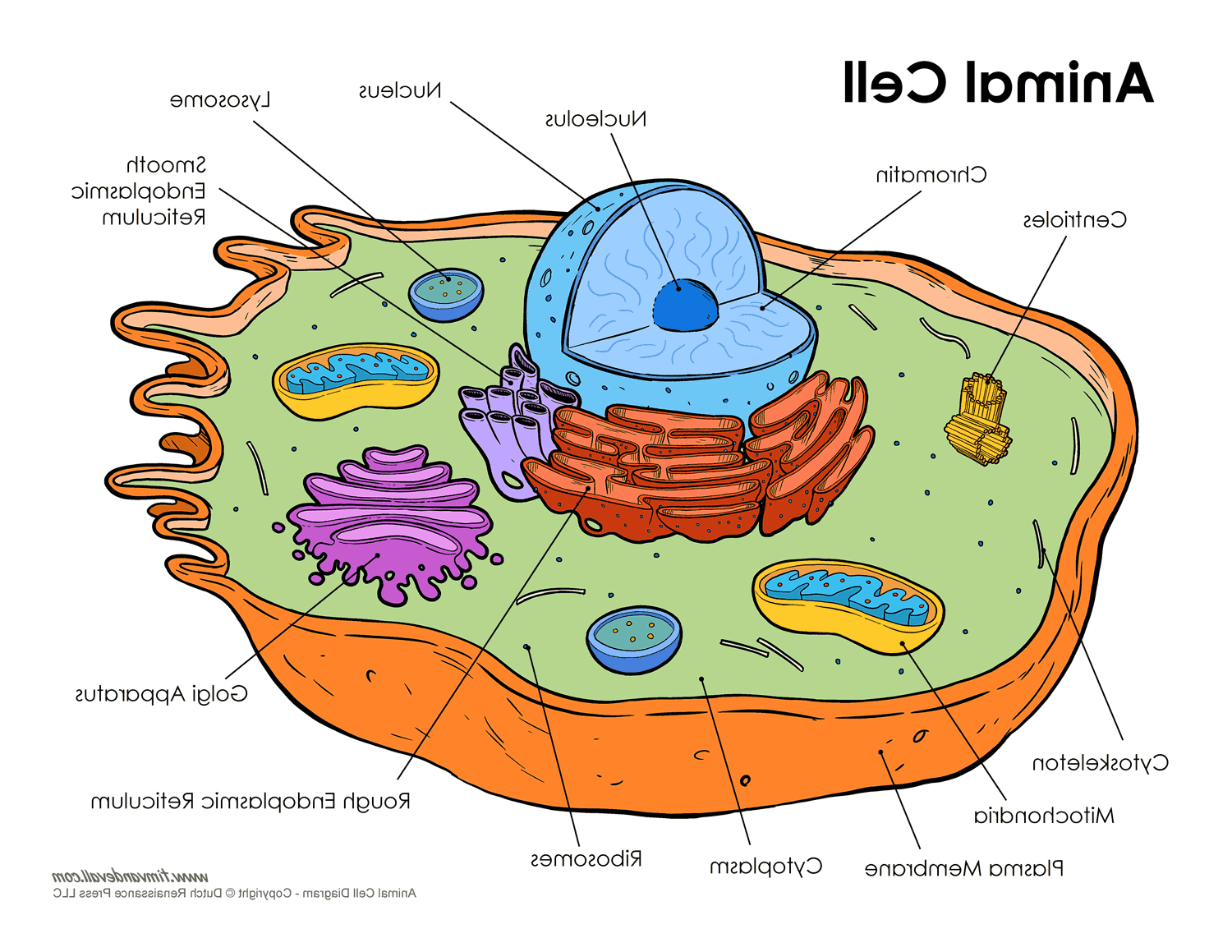
Draw A Labelled Diagram Of Animal Cell Describe The Structure And Gambaran
A typical plant cell structure includes organelles, cytoplasmic structures, cytosol, cell membrane (also called plasma membrane), and cell wall.Plant cell organelles include plastids, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.. The nucleus is the organelle that modulates the metabolic activities of the cell. Different Parts of a Plant Cell. Plant cells are classified into three types, based on the structure and function, viz. parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. The parenchyma cells are living, thin-walled and undergo repeated cell division for growth of the plant. They are mostly present in the leaf epidermis, stem pith, root and fruit pulp.




