This guide will provide a description and example of how to draw the human respiratory system. First by outlining the lungs, bronchi, and trachea, then detailing additional components and accessory structures. By the end of this wikiHow, you will be proficient in drawing a medically accurate human respiratory system and be ready to ace your exams! Edexcel Respiratory system - Edexcel Respiratory system structure and function The respiratory system transports oxygen from the air we breathe, through a system of tubes, into our.

The Respiratory System Anatomy Sketch
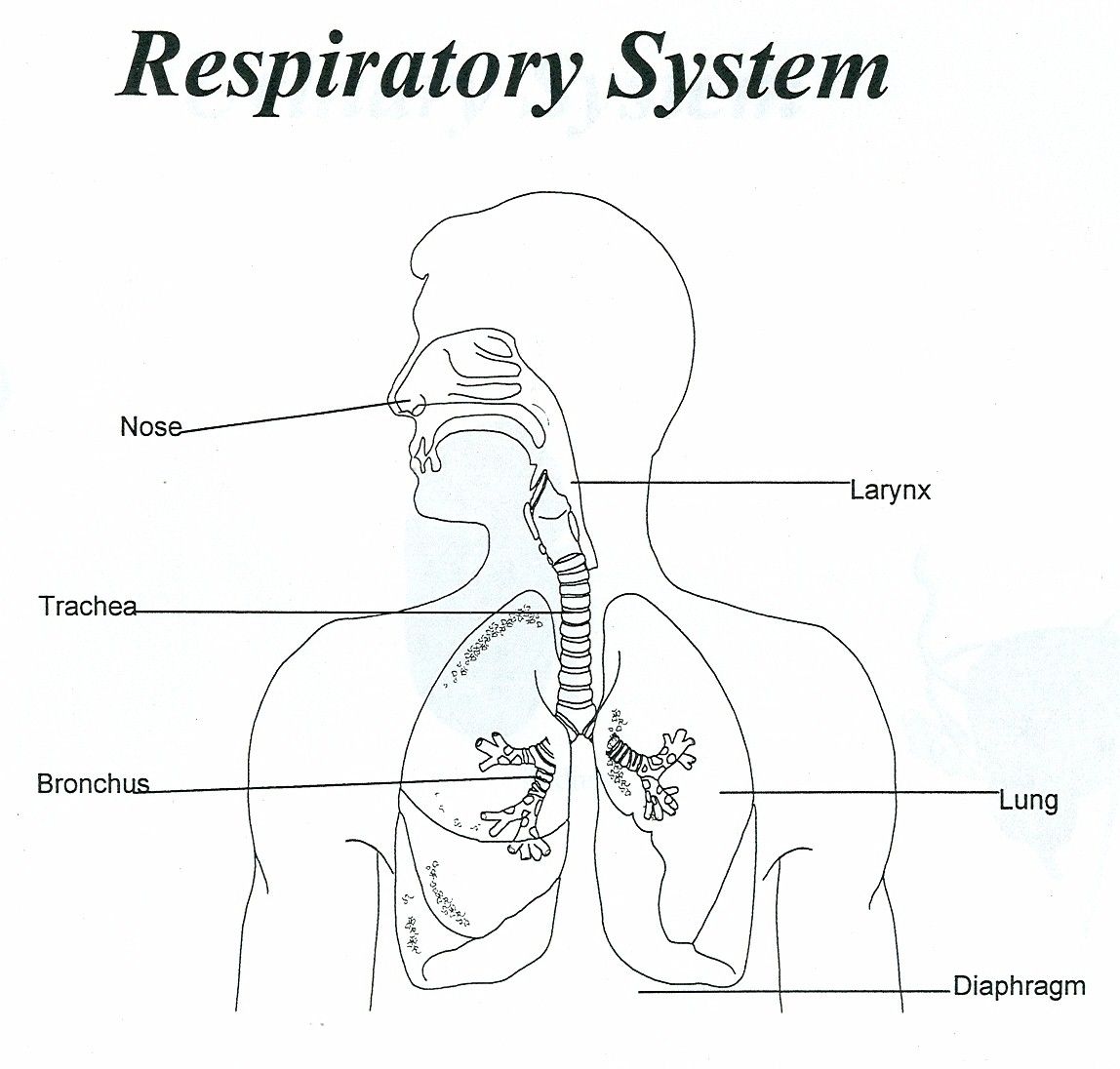
The respiratory system includes the organs, tissues, and muscles that help you breathe. It helps distribute oxygen throughout your body while filtering out carbon dioxide and other waste. human respiratory system, the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. The design of the respiratory system Passage of air through the respiratory tract explained The respiratory tract conveys air from the mouth and nose to the lungs, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the alveoli and the capillaries. The upper respiratory tract refers to the parts of the respiratory system that lie outside the thorax, more specifically above the cricoid cartilage and vocal cords. It includes the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx and the superior portion of the larynx. The human respiratory system has the following main structures - Nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Explore in detail. Table of Contents Definition What Is Respiratory System Diagram Features Parts Respiratory Tract Functions Respiratory System Definition
Respiratory System With Label Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
In the respiratory portion of the tract is connected to the bronchioles by alveolar ducts which in turn connect to alveoli. These are lined with simple squamosal epithelial. Unlike other epithelial tissue, the basement membrane of the tissue is connected to other squamosal epithelial cells; either other alveoli or capillaries. Figure 20.6. 20.6. Chapter 67 Respiratory Physiology: Anatomy & Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY Nose Function: humidifies, warms, filters inspired air; voice resonance chamber; houses olfactory receptors Nasal vibrissae (hairs) coated with mucus → traps large particles (e.g. dust, pollen) Nasal cavity Nasal cavity division Midline nasal septum: composed of septal cartilage, anteriorly Vomer bone. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle below the lungs that controls breathing. The diaphragm flattens out and pulls forward, drawing air into the lungs for inhalation. During exhalation the. Alveoli are connected to their neighbors by alveolar pores, which help maintain equal air pressure throughout the alveoli and lung ( Figure 22.11 ). Figure 22.11 Structures of the Respiratory Zone (a) The alveolus is responsible for gas exchange. (b) A micrograph shows the alveolar structures within lung tissue.

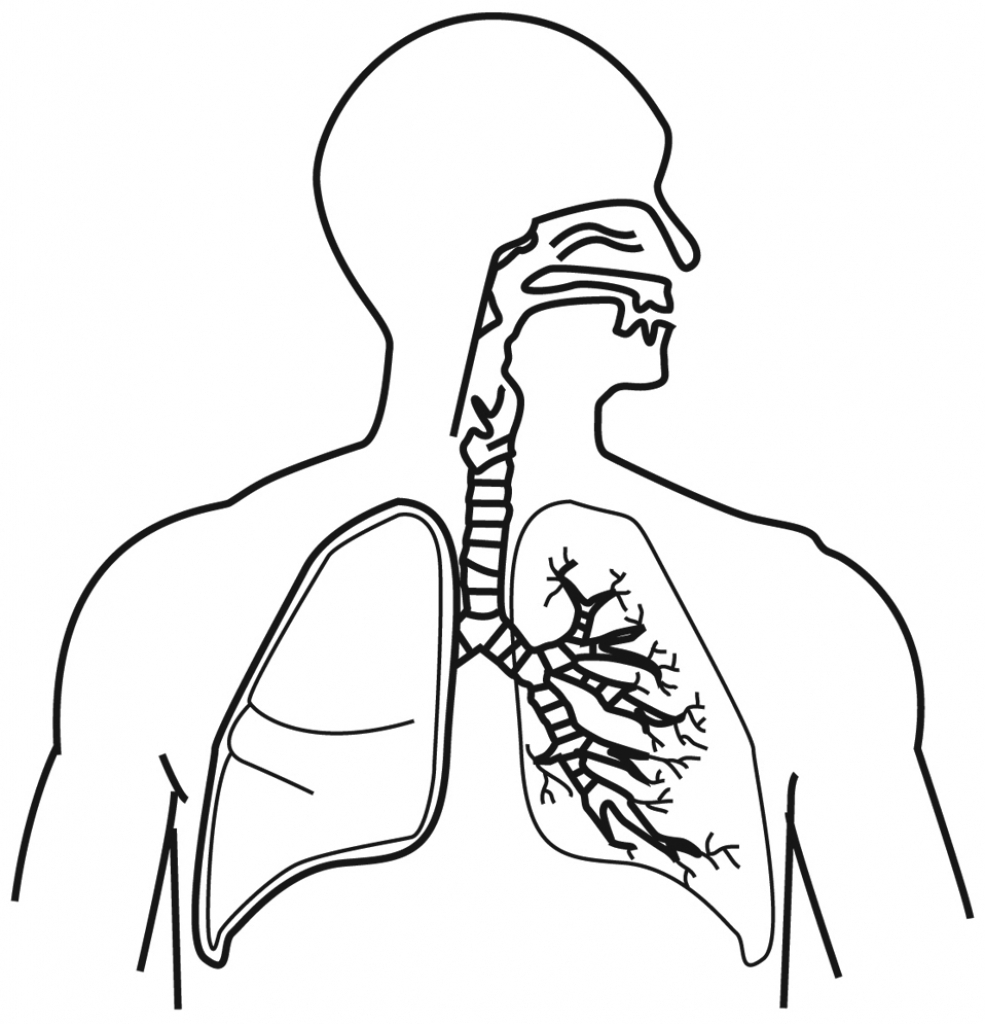
Respiratory System Coloring Page CC3 Classical Homeschooling for Nursing/school
The respiratory system. The process of physiological respiration includes two major parts: external respiration and internal respiration. External respiration, also known as breathing, involves both bringing air into the lungs (inhalation) and releasing air to the atmosphere (exhalation). During internal respiration, oxygen and carbon dioxide. The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages called the respiratory tract, through which air flows into and out of the body. The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The organs in each division are shown in Figure 16.2.2 16.2.
In the 4-week-old human embryo the beginnings of the respiratory system are first seen as an outpouching, the laryngotracheal bud, on the ventral surface of the endoderm of the digestive tract (Fig. 2.16). As the bud elongates the proximal portion forms the trachea and the distal end bifurcates to form first the two main bronchi and then the more distal parts of the bronchial tree, eventually. The respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe. It includes your airways, lungs and blood vessels. The muscles that power your lungs are also part of the respiratory system. These parts work together to move oxygen throughout the body and clean out waste gases like carbon dioxide. Advertisement.
Respiratory System Coloring Page Coloring Home
How to draw diagram of human Respiratory system easily - step by step Perhaps Bidesh 61.8K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 12K 1.1M views 4 years ago Biology diagram Hi guys.. Today I will. Respiratory zone. The respiratory zone, which includes the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli, is the only site of gas exchange. Conducting zone structures. All other respiratory passages are conducting zone structures that serve as conduits to and from the respiratory zone. Stroma.




