An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. It is a special type of microscope having a high resolution of images, able to magnify objects in nanometres, which are formed by controlled use of electrons in a vacuum captured on a phosphorescent screen. 2. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): An SEM creates magnified images of the specimen by probing along a rectangular area of the specimen with a focused electron beam. This process is called the raster scanning.
Scanning Electron Microscope Block Diagram
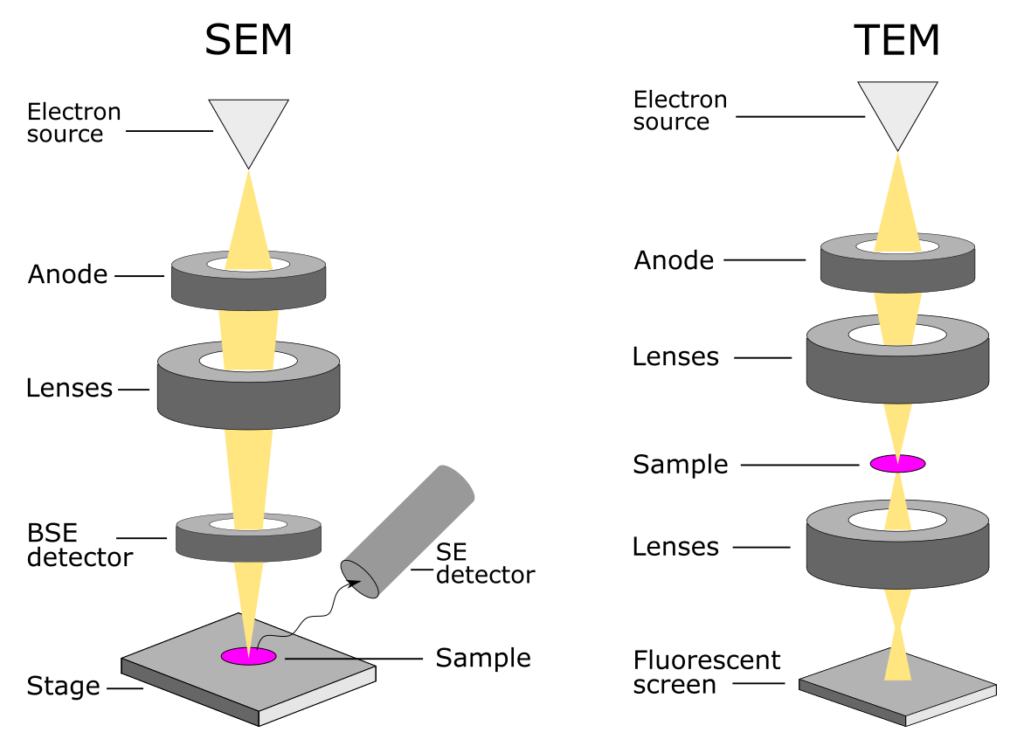
A microscope is an instrument that magnifies objects otherwise too small to be seen, producing an image in which the object appears larger. Most photographs of cells are taken using a microscope, and these pictures can also be called micrographs. From the definition above, it might sound like a microscope is just a kind of magnifying glass. An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. They use electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing them to produce magnified images or electron diffraction patterns. In an electron microscope, a stream of electrons takes the place of a beam of light. An electron has an equivalent wavelength of just over 1 nanometer, which allows us to see things smaller even than light itself (smaller than the wavelength of light's photons). What is Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) A typical SEM instrument, showing the electron column, sample chamber, EDS detector, electronics console, and visual display monitors. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to generate a variety of signals at the surface of solid specimens.

5) Schematic diagram of the scanning electron microscope (SEM) Download Scientific Diagram
Scanning electron microscope is a classification of electron microscope that uses raster scanning to produce the images of a specimen by scanning using a focused electron beam on the surface of the specimen. An SEM creates magnified images of the specimen by probing along a rectangular area of the specimen with a focused electron beam. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) principle, as the name suggests, is to use the transmitted electrons, the electrons that are passing through the sample before they are collected. an electron microscope is an instrument that uses a beam of electrons to magnify a specimen. It has a higher resolution power of up to 100,000X. It is mainly used to observe the internal. The electron microscope uses a beam of electrons and their wave-like characteristics to magnify an object's image, unlike the optical microscope that uses visible light to magnify images. Conventional optical microscopes can magnify between 40 to 2000 times, but recently what are known as "super-resolution" light microscopes have been developed.

Scanning electron microscope (SEM) Definition, Images, Uses, Advantages, & Facts Britannica
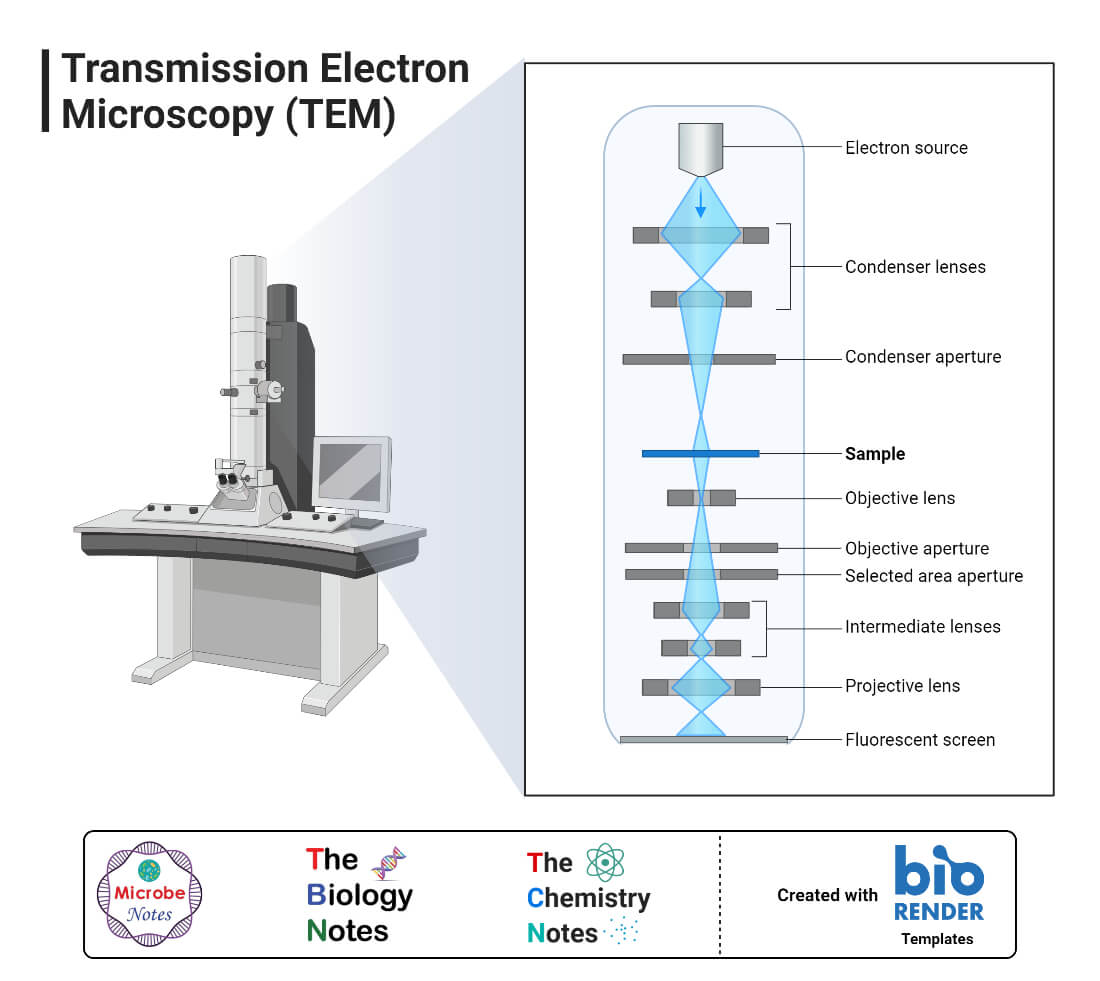
An electron microscope (EM) uses a high energy electron beam aa s probe instead of visible light. The electrons have a shorter wavelength and provide a very high-resolution capacity (0.1 nm) and 500,000 times magnification power. It is also easy to manipulate the electron beams. Instead of glass as a lens, the electron microscope uses an. TEM: An Overview. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a form of microscopy which in which a beam of electrons transmits through an extremely thin specimen, and then interacts with the specimen when passing through it. The formation of images in a TEM can be explained by an optical electron beam diagram in Figure 8.2.1.
Electron microscope (EM) uses high-energy electron beam as probe instead of visible light. The electrons have shorter wavelength and provides very high-resolution capacity (0.1 nm) and 500,000 times magnification power. It is also easy to manipulate the electron beams. Instead of glass as lens, the electron microscope uses electromagnetic coil. What is electron microscopy? What is the diference between scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM)? How can you choose a microscope that best fits your research process? CHAPTER 2 Challenges in microscopic analysis
Electron Microscopy AnaPath
tissues the scanning electron microscope (SEM) has a large depth of field so can be used to examine the surface structure of specimens TEMs have a maximum magnification of around ×1,000,000,. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) can image specimens up to 1 micrometre in thickness. High-voltage electron microscopes are similar to TEMs but work at much higher voltages. The scanning electron microscope (SEM), in which a beam of electrons is scanned over the surface of a solid object, is used to build up an image of the details of the surface structure.




