EV Charging Block Diagram Full Product Recommendation Table Solution Description Interactive Block Diagram (onsemi.com) 3-Phase Rectifier / PFC Topology 1 - Less components, higher efficiency, 1200 V diodes, requires 6 switches. Topology 2 - Cost effective, 600 V diodes, requires only 3 switches but diodes are in series, hence the lower efficiency. Fig. 1: EV charger block diagram Designers can choose an appropriate MCU from the HT45F5Q-X series according to their application requirements. Specifications of the battery charger flash MCU HT45F5Q-X series are shown in Fig. 2. Fig. 2: HT45F5Q-X specifications

Block Diagram (SBD) EV HEV Charger level 1 & 2 Electronic Products
Figure 2-1 shows the system level block diagram of a EV charging station power module captured from TI's EV charging station power module, web page. On the input side it has three-phase AC mains which are connected to the AC/DC power stage. This block converts the incoming AC voltage into a fixed DC voltage of around 800 V. Block Diagram (SBD) EV HEV Charger: level 1 & 2 Posted on November 6, 2013 by Electronic Products Design Considerations Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) and Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) are two quickly emerging technologies which use powerful electric motors and high voltage battery packs as the propulsion and energy sources. An Electric Vehicle (EV) charging station supplies power for recharging electric vehicles. Typical EV charging stations are made up of at least one smart controller board and one power socket board. The smart controller manages security, services and connectivity to a remote server and the power socket board distributes and measures energy. A typical block diagram of an EV on-board battery charger is shown in Fig. 1 which illustrates the two converters; AC-DC converter with Power Factor Correction (PFC) [15,16] followed by an.
Bidirectional Designs to Reduce Carbon Footprint in EV
View the TI DC fast charging station block diagram, product recommendations, reference designs and start designing. Below is a block diagram for an EV Charging station, with a Vienna rectifier for the PFC front end and a full bridge resonant LLC DC-DC stage. The green blocks show all the subsystem solutions which are offered by ON Semiconductor. Applications Related Products EV Charging EV-CHARGING Last Updated: Oct 26, 2023 An Electric Vehicle (EV) charging station supplies power for recharging electric vehicles. Typical EV charging stations are made up of at least one smart controller board and one power socket board. The smart controller manages security, services and connectivity to a remote server and . block diagram of a typical inductive EV wireless charging system is shown in Figure 1, following the standardized stationary wireless EV chargers model presented in the SAE J2954.

Servotech Power to expand product portfolio to EV chargers Your Gateway to Power Transmission
2 ELECTRIC VEHICLE COMPONENTS. A typical block diagram of the EV is shown in Figure 1. Each block is designed for specification and topology suitable for its required applications. The existing battery charging topologies are listed subsequently in Table 1. An EVSE is designed and engineered to charge a battery pack by using the grid for Power Delivery; these battery packs might be present in an Electric Vehicle (EV) or in a Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV). The power, connector and protocol for these EVSE will vary based on it design which we will discuss in this article.
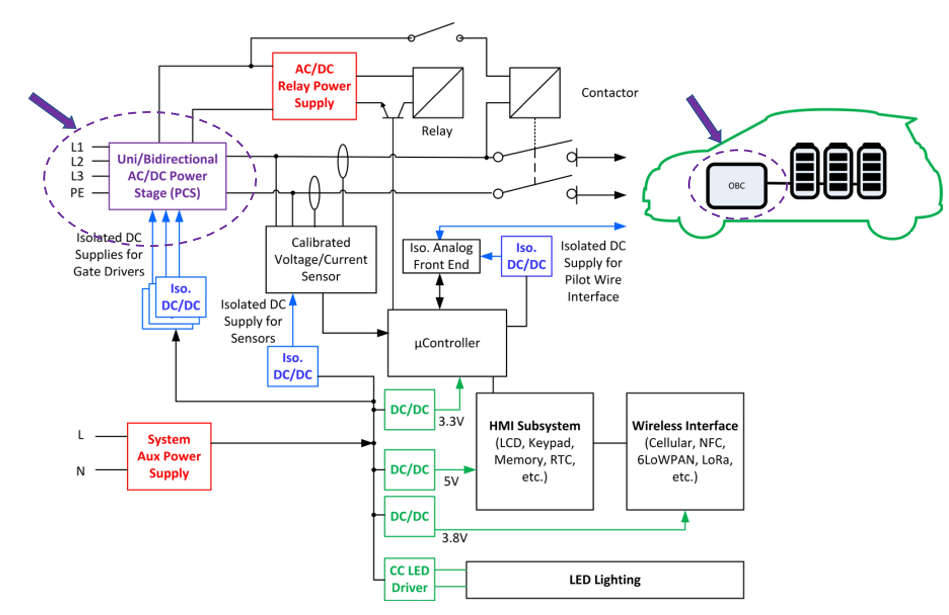
An Electric Vehicle (EV) charging station supplies power for recharging electric vehicles. Typical EV charging stations are made up of at least one smart controller board and one power socket board. The smart controller manages security, services and connectivity to a remote server and the power socket board distributes and measures energy. Figure 3: A Block diagram of a typical on-board charger. Because the OBC is permanently mounted, the weight must be minimised, to reduce its impact on the range of the vehicle. Efficiency is also important, and there are other benefits to efficiency too, such as requiring less thermal management which will reduce the size, weight and cost of.

Design Essentials for Smart EV Charging System Control Free Online PCB CAD Library
System level control is another important area and the 25 kW fast charger features multiple closed-loop controllers within the PFC and DAB to control parameters such as transformer active flux balancing and primary to secondary phase shifts to control output voltage and current. One challenge here is selecting the gain for each loop, so that. Charging for EVSE level 3 is different from levels 1 and 2 because the charger is located inside the EVSE. Figure 4 shows a typical level 3 block diagram. Click image to enlarge. Figure 4: Typical level 3 EVSE block diagram . The level 3 EVSE in Figure 4 uses 24 V instead of 12 V for the main power rail.




