Gujarati alphabet Created by Simon Ager, Omniglot.com - the guide to writing systems and languages Vowels and vowel diacritics અ આ ઇ ઈ ઉ ઊ. Microsoft Word - gujarati.doc Author: omniglot Created Date: 20100430164528Z. Download Gujarati alphabet charts in Excel (includes all conjuncts), Word or PDF format Sample text in Gujarātī Transliteration Pratiṣṭhā anē adikhārōnī dr̥ṣṭinē sarvē mānavō janmathī svatantra anē samān hōy chē. Tēmanāmāṁ vicārśakti anē antaḥkaraṇ hōy chē anē tēmaṇē paraspar bandhutvanī vartavuṁ jōiē. Translation

Gujarati Alphabets Chart Gujarati Language Stock Illustration
Gujarati vowel, also called Swar (સ્વર), are the basic part of an alphabet in Gujarati language. Vowels are written as separate letters and combined with consonants to determine the final sound. The Gujarati script ( ગુજરાતી લિપિ, transliterated: Gujǎrātī Lipi) is an abugida for the Gujarati language, Kutchi language, and various other languages. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. Gujarati (Gujar ātī) uses an alphasyllabic script whereby each character represents a syllable rather than one sound. Vowels and diphthongs are marked in two ways: as independent characters (used syllable-initially) and in an abbreviated form, to denote vowels after consonants. The romanization table is unambiguous but the user would have to. This Gujarati alphabet chart ( (barahkhadi) shows the Gujarati letter in black with the pronunciation written out underneath it in blue. This way you will be able to learn the English pronunciation and start to dissect the roots of English to Gujarati translations.

SEG Gujarati alphabet letters
Gujarati/Alphabet. Gujarati has its own writing system, distinct but related to several other Indian languages' writing systems, such as the one used to write Hindi. Strictly speaking, the Gujarati writing system is what is called an abugida (and not an alphabet ), because the consonant characters all contain an inherent vowel, and other vowels. Download now of 1 The Gujarati Alphabet Every language has a different method of writing the script. Gujarati script is derived from Devanagari script to which it bears a considerable resemblance. The difference consists mainly in the omission in Gujarati of the head-line used in joining together most of the Devanagari characters. There are 47 letters in the Gujarati alphabet. The Gujarati script is an abugida which means letters can be made up of a consonant and a vowel. This is different to English where each letter is either a consonant or a vowel. Gujarati does have some stand-alone vowel letter,s but also letters which consist of a consonant and a vowel. The Gujarati alphabet has 47 letters and the script is written from left to right. It is a phonetic script and therefore easier to read than English. There are some sounds in Gujarati which have no equivalent in English. There are no capital letters in Gujarati and no definite or indefinite articles. Every Gujarati noun has a gender.

writing practice of gujarati letters by tracing gujarati alphabet
Trees. jujube-tree bor6I fem. mango tree Aa&bo masc. palm-tree ta6 masc. sandalwood tree c&dnv
created three textbooks: Gujarati Reader 1, 2 and 3. The Reader 1 is devoted to the writing system, while the Reader 2 is devoted to written conversations. The Reader 3 is a collection of Aesop's fables rendered in Gujarati. This dictionary is a part of that project but it has been funded by the Nirman Foundation, Washington DC. Learn GUJARATI Vowels Here you can learn GUJARATI vowels for free. The pictures help you remember the vowel if you already know to speak the language. You can download the GUJARATI alphabets (vowels/consonants) worksheets and alphabet charts from the Indian language Resources downloads section. Click on the alphabets to view it in big font size. 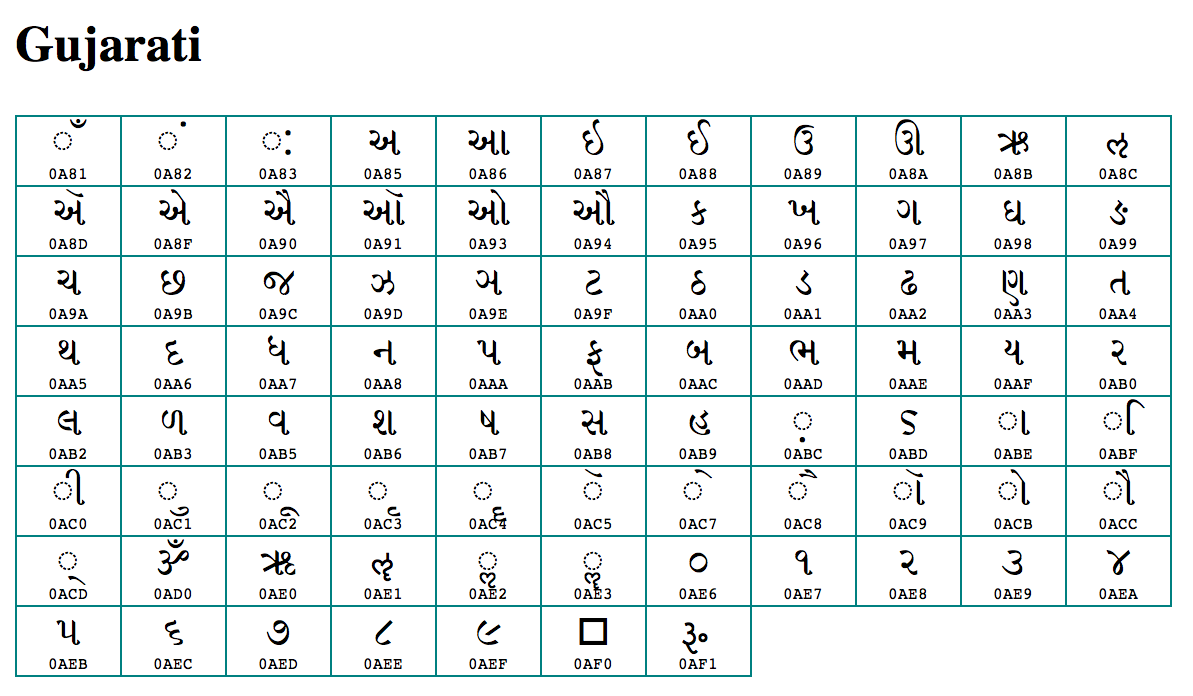
Hand Painted Type Gujarati Information Collection 4 Something
Text here kraoD kama bagaaDInao Aok maaoxa sauQaarI laovaao. sa.gau.gauNaataItaanaMd svaamaIo Prioritize "MOKSHA" over million other errands! હ ha. Only the vowel forms that appear at the beginning of a syllable are listed; the forms used for vowels following a consonant can be found in grammars; no distinction between the two is made in transliteration. when the absence of any vowel is indicated by the subscript symbol ( ্ ) called halanta or virāma. m before labials.




