LED stroboscopes. No bulb changes. Brightest light for crisp, clear detail at high speed. Inspect every detail at full production speed. Extensive sales network. Request a demo. Get deals on bulb incandescent in Industrial products on Amazon. Browse & Discover Thousands of products. Read Customer Reviews and Find Best Sellers

[DIAGRAM] Hid Bulb Diagram
Incandescent lamps work on the principle that when a filament of fine wire is maintained at incandescence (white-hot condition) by the passage of current, it emits sufficient energy in the form of light. (a) (b) (c) Fig.1 : (a) Modern gas filled incandescent lamp, (b) Coiled or helical filament, (c) Coiled-coil filament Incandescent means producing visible light by heating an object. An incandescent lamp works in the same principle. The simplest form of the artificial source of light using electricity is an incandescent lamp. Here we use electric current to flow through a thin and fine filament to produce visible light. The incandescent lamp or light or bulb is an electric light source that works through the incandescence phenomenon that means the light emission can be caused by filament heating. These lamps are available in different sizes with different voltages and wattages. Here, the voltage range of these bulbs ranges from 1.5V to 300V. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia A 230-volt incandescent light bulb with a medium-sized (Edison 27 mm) base. The filament is visible as the mostly horizontal line between the vertical supply wires. scanning electron microscope filament of an incandescent light bulb Elaborate light in Denver, Colorado
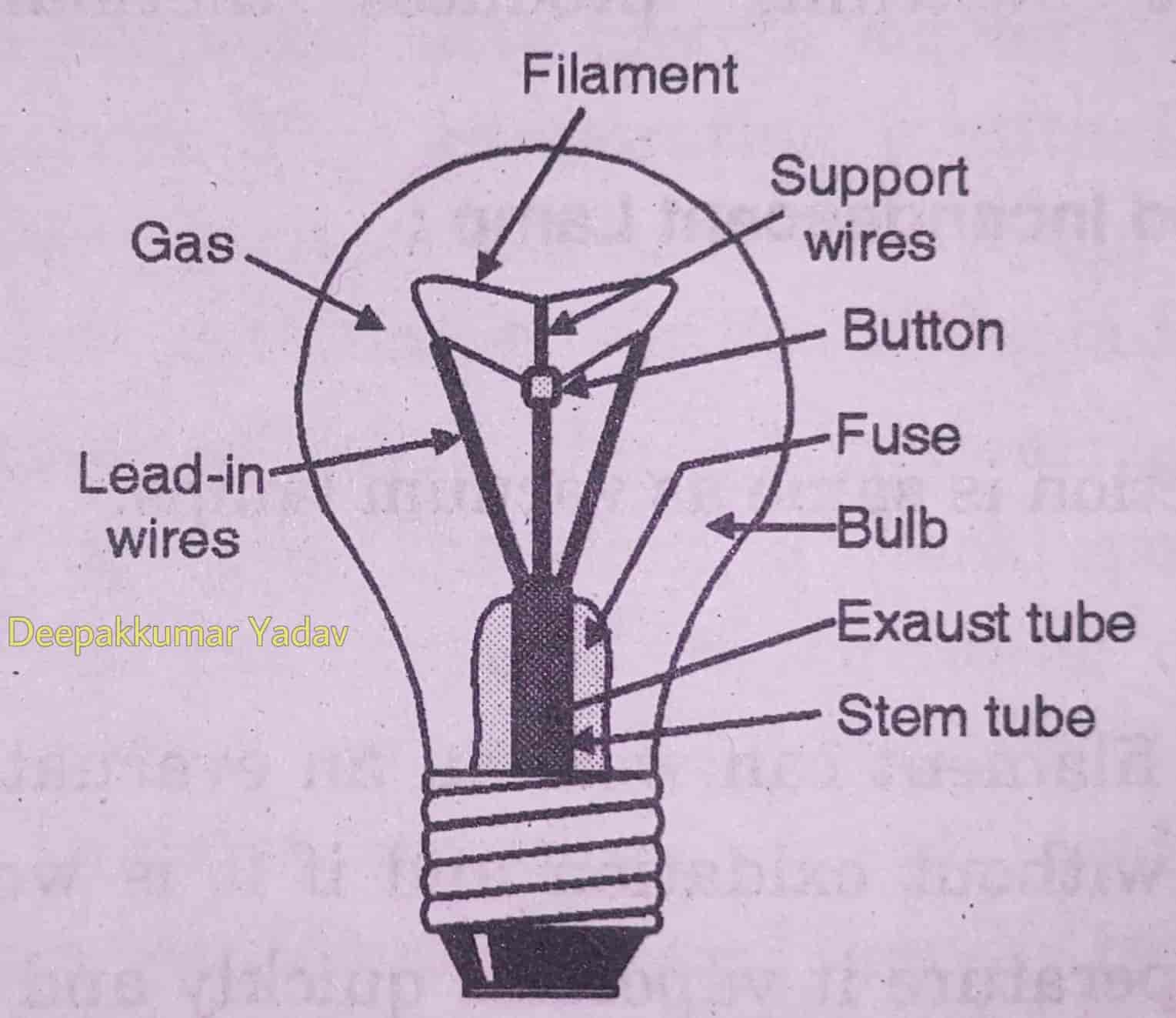
Incandescent Lamp Working and Bulb Construction
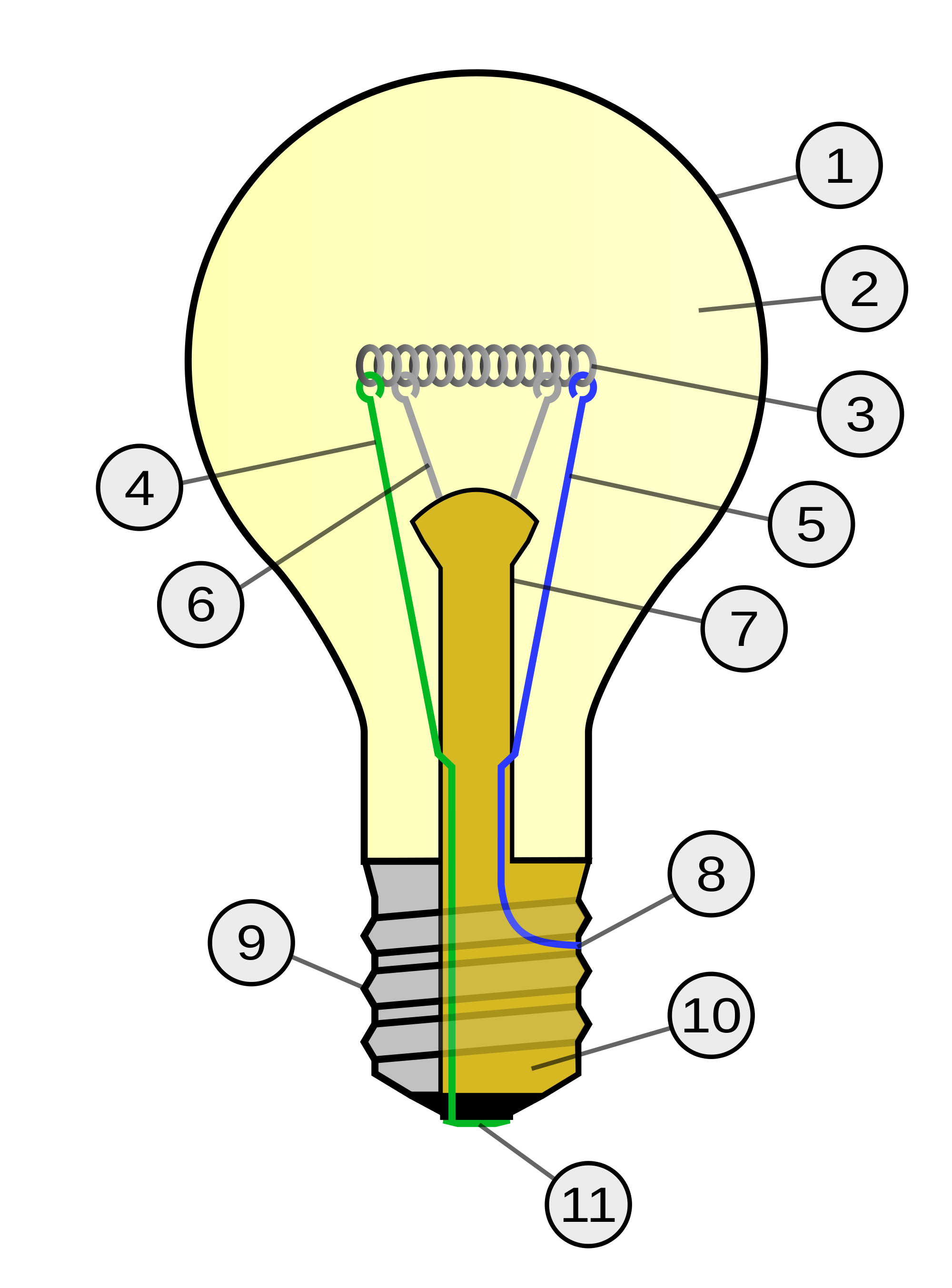
Diagram showing the major parts of a modern incandescent light bulb. Glass bulb Inert gas Tungsten filament Contact wire (goes to foot) Contact wire (goes to base) Support wires Glass mount/support Base contact wire Screw threads Insulation Electrical foot contact Where are they used? An electric light bulb or lamp that produces light by heating a filament wire to a high temperature until it glows is known as incandescent bulb. The incandescent bulb was invented by an American inventor, named Thomas Alva Edison. Incandescent lamps (ones that make light by making heat) are getting something of a bad press these days because they waste so much energy, but they've long been considered among the greatest inventions of all time and a burning-bright light bulb is still widely used as the symbol of a great idea. Incandescence occurs when electrical resistive heating creates thermally excited atoms. Some of the thermal kinetic energy is transferred to electronic excitations within the solid. The excited states are relieved by ph- o tonic emission.
Free Images Of A Light Bulb, Download Free Images Of A Light Bulb png images, Free ClipArts on
The conventional circuit diagram (on the left) shows the filament bulb lighting brightly when the switch is turned on. The current flows through the filament, causing light to be emitted. In the pictorial circuit diagram on the right the components are shown as pictures rather than symbols. Introduction The incandescent lamp is the oldest type of electric lamp still in general use. Its practical form was invented simultaneously in 1879 by Sir Joseph Swan in England, and by Thomas Edison in America.
The operating principle of the incandescent lamp is extremely simple. An electric current is passed through a thin wire of comparatively high resistance so as to heat this to incandescence. The wire is usually heated to a temperature of between 2700 K and 2800 K, at which temperature it emits warm-white light. The incandescent lamp is based on the principle of temperature radiation - in that objects emit light when they are heated to high temperatures. It is a well known phenomenon observed everyday, for instance from the glow of coals in a fire or the bright yellow radiation of molten steel being cast into a mould.. The energy balance diagram in.

Electrical Engineering MCQ Questions and Answers Electrical Mcq Electrical Mcq Pdf
According to Brons the optimum fill pressure for a standard incandescent lamp filled with a 95 % Ar/ 5 % N 2 mix is around 80 mbar. In practice the cold fill pressure is usually around 0.8-0.9 bar so as to reduce the risk of arcing (Moore 1958 ), and the pressure in smaller lamps can be as high as 5 bars. Incandescent lamps are quasi-blackbody thermal radiators. A true blackbody radiator would generate light according to Planck's Law, as shown in eqn [1] and Figure 1, for various temperatures.Most incandescent lamps use tungsten filaments, and the emissivity of tungsten, the ratio of its radiative output to that of a blackbody at the same temperature, is about 0.44 in the visible region of the.




