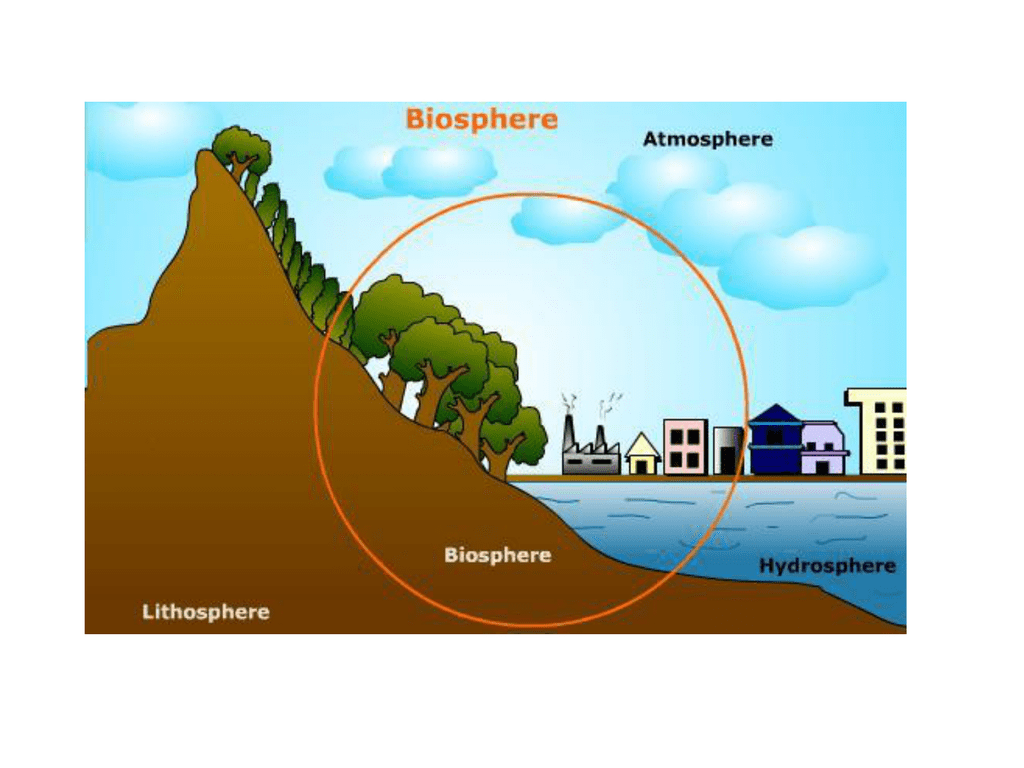
Updated on February 26, 2020 The area near the surface of the earth can be divided into four interconnected spheres: lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere. Think of them as four interconnected parts that make up a complete system; in this case, of life on earth. The hydrosphere is the water sphere of Earth. This includes the total amount of water that can be found on the whole planet, from that on the surface - like in lakes, oceans, rivers etc. as well as water underground, and in the air.
Geographic thoughts Lithosphere
The hydrosphere stretches all the way from the Earth's surface downward numerous miles into the lithosphere and high above the crust into the atmosphere. Most of the water in the atmosphere is in gaseous form and as it rises higher into the atmosphere it condenses to form clouds which fall back on earth as precipitation. Layers of the Atmosphere The Earth's atmosphere has five main layers and a sixth layer, the ionosphere, that overlaps the mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Troposphere: The Densest Layer in the Atmosophere The bottom layer, which is the layer closest to the Earth, is the most dense of the five layers. This layer is known as the troposphere. The last one is atmosphere: the layers of gas surrounding the earth. Key Vocabulary Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, & Atmosphere Earth is made up of three major layers: lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. This activity will teach students about the properties of each layer. This week we are going to look at the interaction between the atmosphere, the lithosphere, and the hydrosphere and how sensible and latent heat transfers drive nearly all motion in the atmosphere and hydrosphere. Hot air is at a lower pressure (less dense) than cold air (think about a hot air balloon where you must heat the air inside the.
Biosphere, Atmosphere, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere Stock Vector Illustration of lithosphere, soil
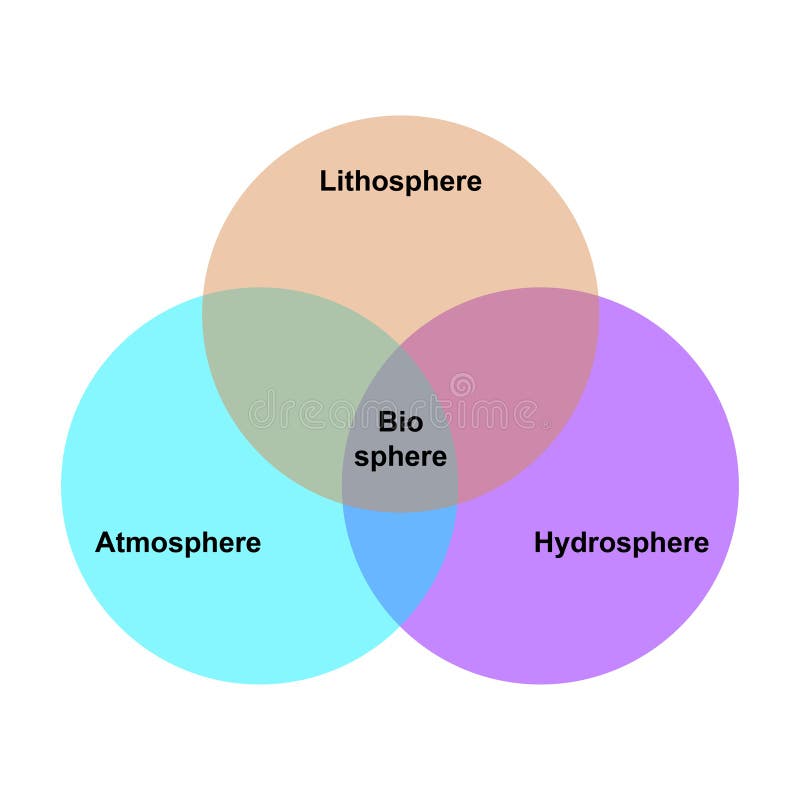
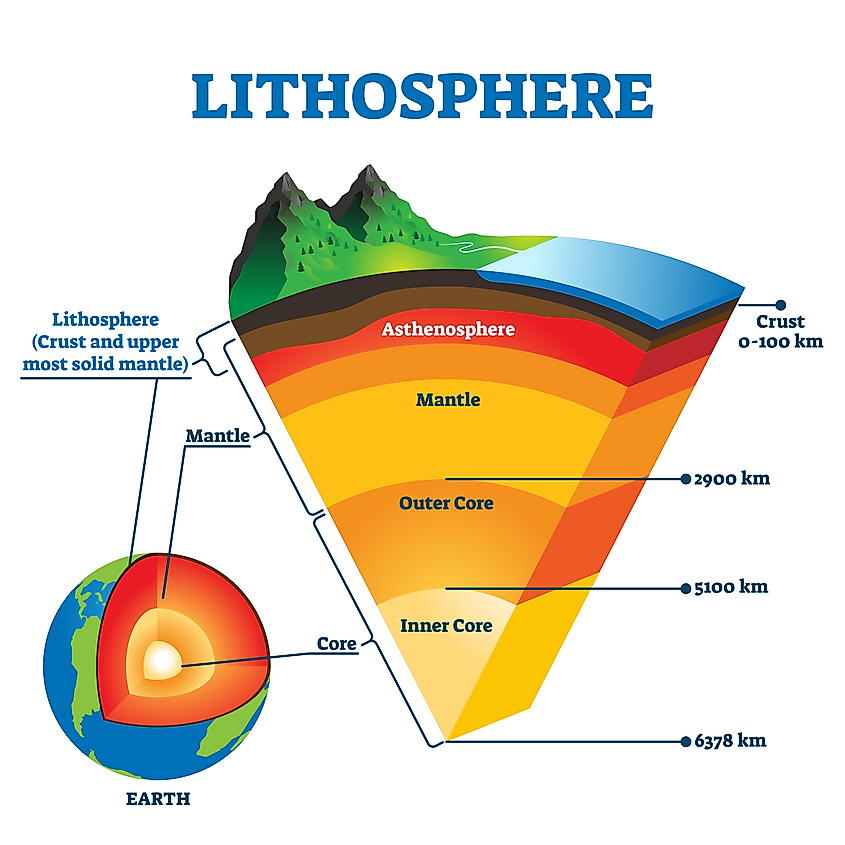
The five components of the climate system all interact. They are the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, the cryosphere, the lithosphere and the biosphere.. Earth's climate system is a complex system with five interacting components: the atmosphere (air), the hydrosphere (water), the cryosphere (ice and permafrost), the lithosphere (earth's upper rocky layer) and the biosphere (living things). ARTICLE Earth's Systems The five systems of Earth (geosphere, biosphere, cryosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere) interact to produce the environments we are familiar with. Grades 5 - 8 Subjects Biology, Ecology, Earth Science, Climatology, Geology, Oceanography Image Great Bear Rainforest The lithosphere is the solid, outer part of Earth. The lithosphere includes the brittle upper portion of the mantle and the crust, the outermost layers of Earth's structure. It is bounded by the atmosphere above and the asthenosphere (another part of the upper mantle) below. The biosphere includes all living things on the planet. The lithosphere is the rocky outer shell of the earth. All these spheres — the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere — are linked through flows of mass, energy, and life. Their interactions have affected the development of our planet.

Atmosphere, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, and Biosphere Fully Defence
(i) Atmosphere: The atmosphere is the gaseous mantle, which envelops the hydrosphere and the lithosphere. There are no characteristic or permanent inhabitants of the atmosphere, although the air is traversed by many kinds of animals and plant propagules. (ii) Lithosphere: The Earth system covers complex and continuous interaction between lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere , and biosphere. The two main energy sources that operate this system are: 1. Solar energy, which is forcing the external processes that occur on or above Earth's surface. 2.
Earth's atmosphere is composed of a series of layers, each with its own specific traits. Moving upward from ground level, these layers are called the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. The exosphere gradually fades away into the realm of interplanetary space. The layers of the atmosphere: the troposphere. The geosphere, also called the lithosphere, includes all Earth's rock, soil and sand in all its forms from mountains to its rocky stream beds, mudflats, ocean trenches, sandy beaches and lava flows. It even includes the very ground that is made up of tectonic plates forming our islands and continents. The hydrosphere includes Earth's water.
The Four Spheres Of The Earth WorldAtlas
Hydrosphere is a domain that contains water or water bodies. If we take the earth into consideration. If we take the earth into consideration. Only 1/4th (29%) of the earth is covered in soil /land while the rest 3/4th (71%) portion is covered in water. 97% of the earth's water is found in oceans and is not suitable for use as it is saltwater. The hydrosphere (from Ancient Greek ὕδωρ (húdōr) 'water', and σφαῖρα (sphaîra) 'sphere') [1] [2] is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth 's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, [3] [4] it continues to change in shape.




