Definition Structure Lysosome in Plant Cells Why are Lysosomes known as Suicidal Bags? How do the Lysosomes Function? Where are Lysosomal Enzymes made? Lysosomal Diseases FAQs on Lysosomes Lysosomes are an important cell organelle found within eukaryotic animal cells. Functions 1)They are called digestive bags.They destroy any foreign material which enter the cell such as bacteria and virus. 2)They remove worn out and poorly working cellular organelles by digesting them to make way for their new replacements.

Diagram of Lysosomes Organelles, School science projects, Cell organelles
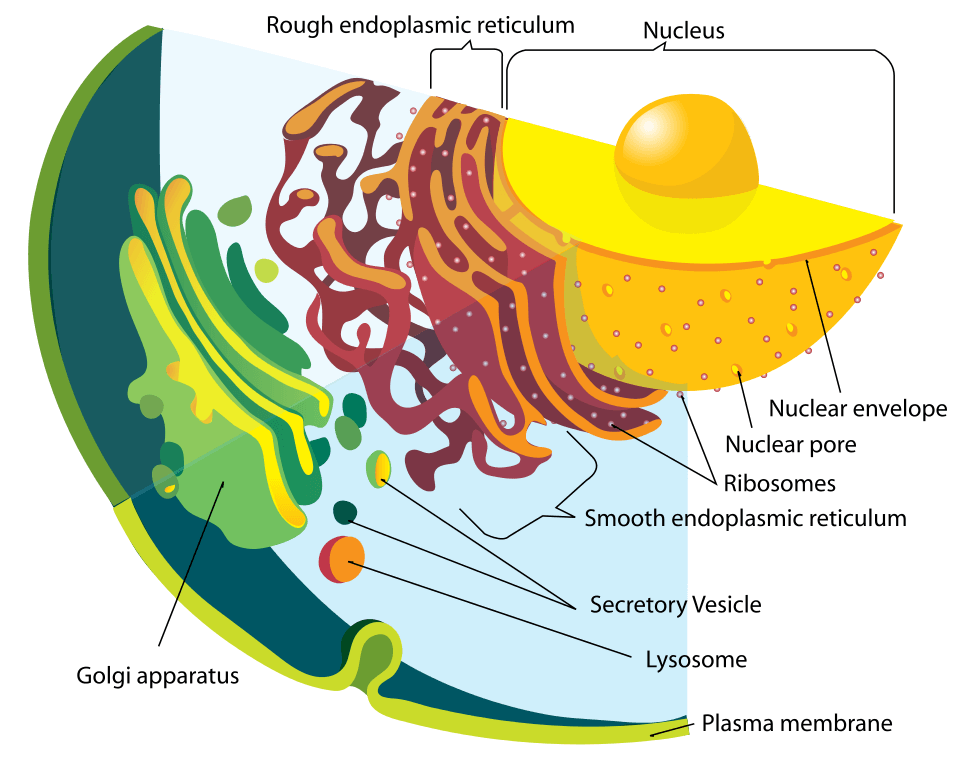
Lysosomes are small cell organelles in nucleus-bearing or eukaryotic cells. They are located in the cytosol of the cells, floating freely within the cells outside the nucleus. They have a simple structure made up of an outer lysosomal membrane surrounding an acidic interior fluid. Edited By: Sagar Aryal Lysosomes are membrane-bound, dense granular structures containing hydrolytic enzymes responsible mainly for intracellular and extracellular digestion. The word "lysosome" is made up of two words "lysis" meaning breakdown and "soma" meaning body. It's an educational video from 9th biology PTB.In this video, you will learn how to draw diagram of formation and functioning of lysosome in cell?Lysosomes,. The endomembrane system ( endo - = "within") is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
10 Characteristics Of Lysosomes
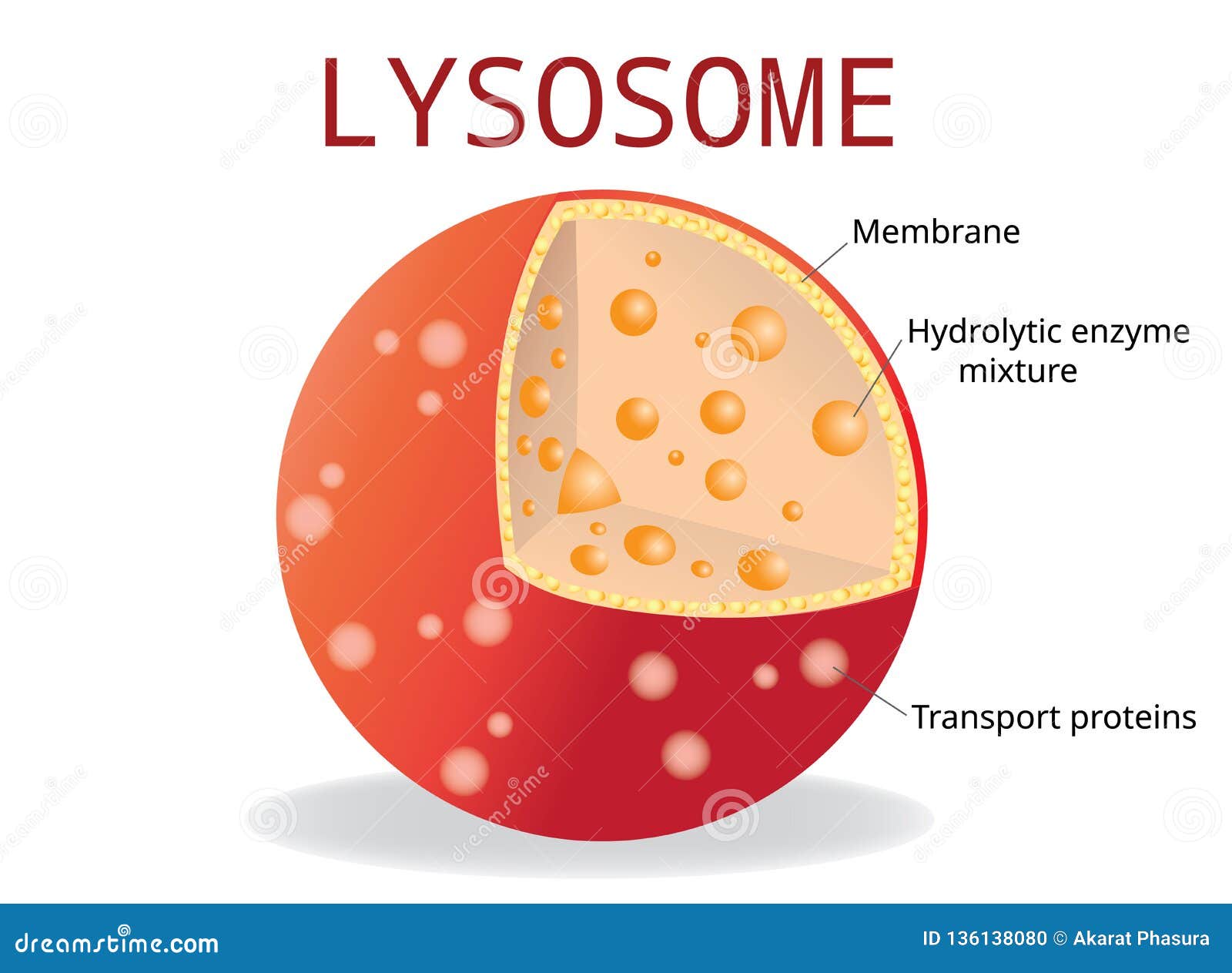
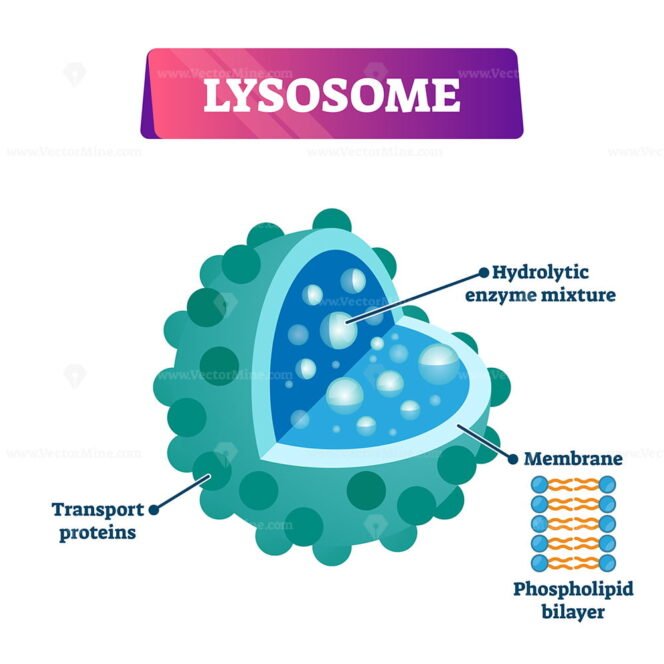
They are membrane-bound vesicles formed in the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes are also called 'suicidal bags' since they are rich in hydrolytic enzymes such as l. 0:00 / 6:46 Lysosome | Structure and Function | Cells | Class 9 | CBSE | NCERT | ICSE DeltaStep 924K subscribers 812 53K views 7 years ago Biology: Cells Understand the Structure of. Structure. Lysosomes are acidic membrane-bound organelles found within cells, usually around 1 micrometre in length. Lysosomes contain numerous hydrolytic enzymes which catalyse hydrolysis reactions. The membrane surrounding the lysosome is vital to ensure these enzymes do not leak out into the cytoplasm and damage the cell from within. Bookshelf ID: NBK9953. Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Lysosomes function as the digestive system of the cell, serving both to degrade material taken up from outside the cell and to digest.
Animal Cell Diagram Lysosome / Anatomy Of The Lysosome Hydrolytic Enzymes, Membrane And
Lysosome Definition. Lysosomes are specialized vesicles within cells that digest large molecules through the use of hydrolytic enzymes. Vesicles are small spheres of fluid surrounded by a lipid bilayer membrane, and they have roles in transporting molecules within the cell. Lysosomes are only found in animal cells; a human cell contains around. lysosome, subcellular organelle that is found in nearly all types of eukaryotic cells (cells with a clearly defined nucleus) and that is responsible for the digestion of macromolecules, old cell parts, and microorganisms. Each lysosome is surrounded by a membrane that maintains an acidic environment within the interior via a proton pump. Lysosomes contain a wide variety of hydrolytic enzymes.
Read a lysosome definition, and learn about lysosome functions, structure, and roles in the cell. See info on lysosomal storage diseases. Updated: 11/21/2023 Lysosomes are very small cell organelles. They are found in the nucleus-bearing or eukaryotic cells. Furthermore, they are found in the cytosol of the cells. Ones that float freely inside the cells outside the nucleus. Lysosome function is of utmost importance for cells. Their structure is quite simple.
Lysosome cell organelle vector illustration labeled cross section diagram VectorMine
Lysosome positioning and motility. Lysosomes are broadly distributed throughout the cytoplasm (Fig. 2).In non-polarized cells, they are most concentrated in a central region surrounding the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) (the 'perinuclear cloud') (Jongsma et al., 2016), although there are also many peripheral lysosomes, some reaching as far as the plasma membrane and cell protrusions. Few lysosomes occur in muscle cells or in acinar cells of the pancreas. Lysosomes are produced by certain cells in tissue culture (HeLa cells, monocytes, lymphoctyes, etc.). Although it has a number of functions not shared by lysosomes of animal cells, the large vacuole of many plant cells is a modified lysosome.




