Description of a Maize Plant (With Diagram) Maize or Indian corn (Fig. 221) is a stout annual plant cultivated for the grains during the rainy season. It forms a staple food in some parts of India. Roots are of fibrous adventitious type. Primary root aborts after germination, and is replaced by fibrous adventitious ones from the base of stem. Maize (Zea mays L., 2n = 2x = 20 family Poaceae) is a universal cereal adapted to diverse agro-ecologies of both temperate and tropical regions of the world from 50°N to 40°S, and from sea level.
Parts Of Plant. Morphology Of Corn Maize Plant With Green Leaves, Root System, Fruits And
Maize plant diagram.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 297 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 119 × 240 pixels | 238 × 480 pixels | 380 × 768 pixels | 507 × 1,024 pixels | 1,015 × 2,048 pixels | 394 × 795 pixels. Diagram of a mature maize (Zea mays) plant. Diagram by LadyofHats (Wikimedia Commons, CC0 1.0 Universal/public domain dedication, image relabeled). Germination and vegetative growth Seed germination. Development of the maize plant begins in the embryo, which uses energy stored in the endosperm to fuel its growth. As the seed absorbs moisture. The stem of a maize plant is a long central stalk that supports every part of the plant. The only branches on the stem are those that support the reproductive parts. The strength of the stem allows maize to grow very tall; maize plants can reach as much as 12 feet (4 meters) in height, depending on the variety. Find free pictures, photos, diagrams, images and information related to a wide range of different plants right here at Science Kids. Photo name: Maize (Corn) Plant Diagram Picture category: Plants Image size: 66 KB Dimensions: 436 x 594 Photo description: This maize plant diagram shows both the male and female flowers of what is commonly known as corn.

Corn Labeled Parts Of Plant
Download scientific diagram | Different growth stages of a maize plant, including vegetative (V) and reproductive (R) stages. The V developmental milestones include emergence (VE), in which the. Live plant mitotic studies show a process that occurs over minutes, approximately 45 min in Arabidopsis [32] and 10-15 min in maize and P. patens [30, 31, 34]. In our observations, disassembly of. A Venn diagram shows a comparison of DEGs from the three comparisons. and glycoside hydrolases are critical for degrading host cell walls and disturbing plant immunity. In the maize smut fungus Ustilago maydis, Erc1 binds to host cell wall components and displays 1,3-β-glucanase activity,. Maize gray leaf spot (GLS) is a severe foliar disease that poses a significant threat to maize production and yield [].Maize GLS was initially reported in the United States [], and has since become endemic in several countries, including Brazil, Uganda, South Africa and other countries of South America and Africa [3,4,5,6,7].In China, GLS was first reported in 1991 [].

Parts Of A Corn Plant
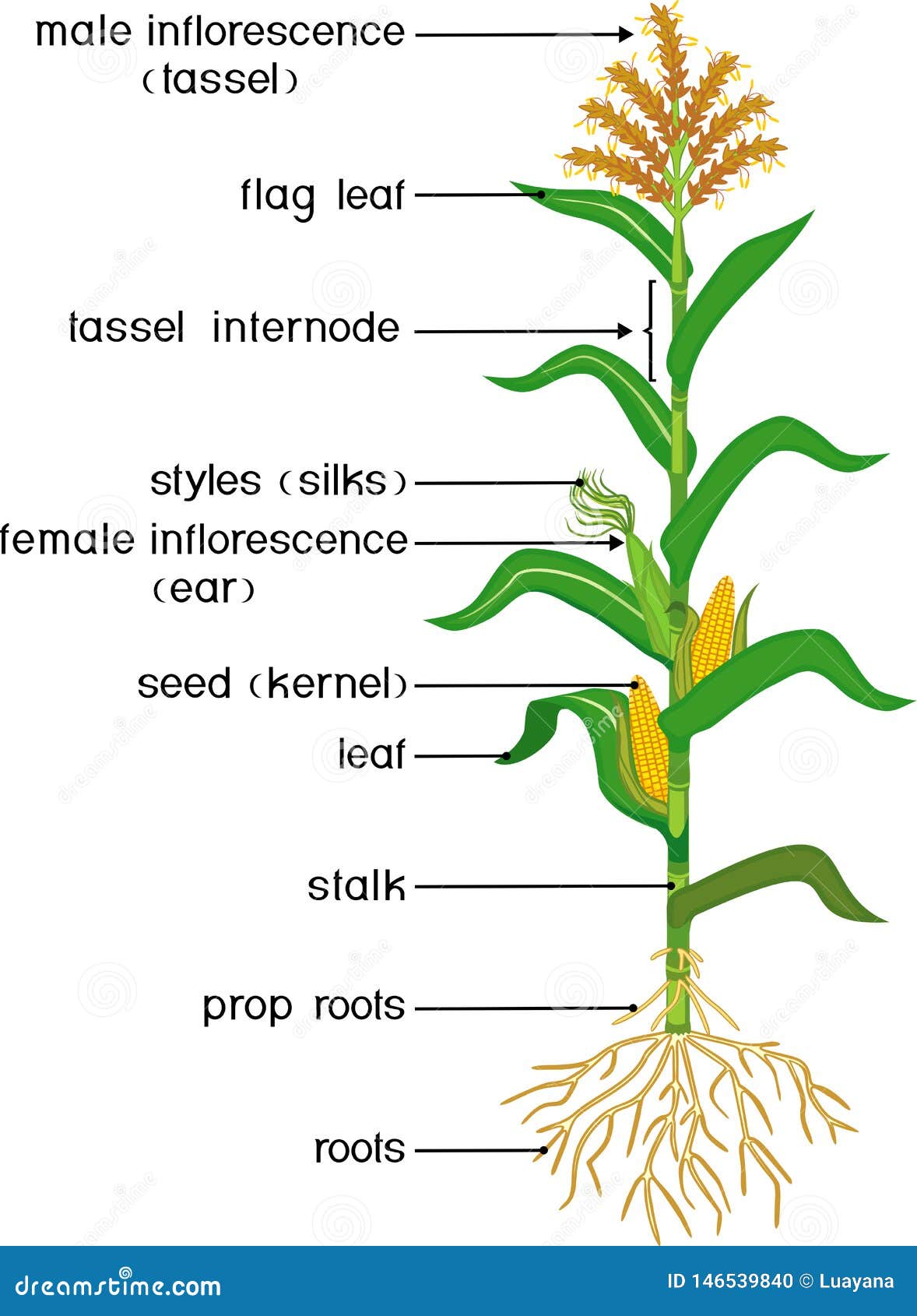
Maize (/ m eɪ z / MAYZ); Zea mays subsp. mays, also known as corn in North American and Australian English, is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences (or "tassels") which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears which yield kernels or "seeds". Receptor-like kinases (RLKs) are evolved for plant cell-cell communications. The typical RLK protein contains an extracellular and hypervariable N-terminus to perceive various signals, a transmembrane domain to anchor into plasma membrane, and a cytoplasmic, highly conserved kinase domain to phosphorylate target proteins.
The typical maize plant is a tall (1-4 m), determinate annual grass (monocot) which forms a seasonal root system bearing a single erect stem (culm) made up of nodes and internodes, although some cultivars may develop elongated lateral branches (tillers). Among the characteristics maize shares with other grasses are the conspicuous nodes and. Key message ZmMRPA6 was cloned and characterized as the first ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter in maize to be proven to participate in cold and salt tolerance. Homologous genes AtABCC4 and AtABCC14 of ZmMRPA6 also responded to salt stress. Abstract ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins are major transmembrane transporters that play significant roles in plant development against various.

The maize plant and its flowering parts. Download Scientific Diagram
1) The development of the maize plant, from germination to the maturation of the seed, is divided into the vegetative, transitional, reproductive, and seed stages. The ear and tassel differentiate and develop in the reproductive stage. 2) The mature tassel is a terminal, staminate inflorescence consisting of a symmetrical, many-rowed central. Maize plant diagram, infographic elements with the parts of corn plant, anthers, tassel, corn ears, cobs, roots, stalks, silk, flowering, seeds fruits Vector encyclopedic illustration flat design. Download a free preview or high-quality Adobe Illustrator (ai), EPS, PDF, SVG vectors and high-res JPEG and PNG images.




