The Northern Plains of India span an area of over 7 lakh square kilometers. Because of the abundant water supply, agreeable climate, and fertile alluvial soil, there is a large population. The river has a mild slope, which causes the water to flow through it slowly. Coordinates: 27.25°N 80.5°E Indo-Gangetic Plain Clusters of yellow lights on the Indo-Gangetic Plain reveal numerous cities large and small in this photograph of northern India and northern Pakistan, seen from the northwest. The orange line is the India-Pakistan border.
Indian Physiography Northern Plains of India Indo Gangetic Plain
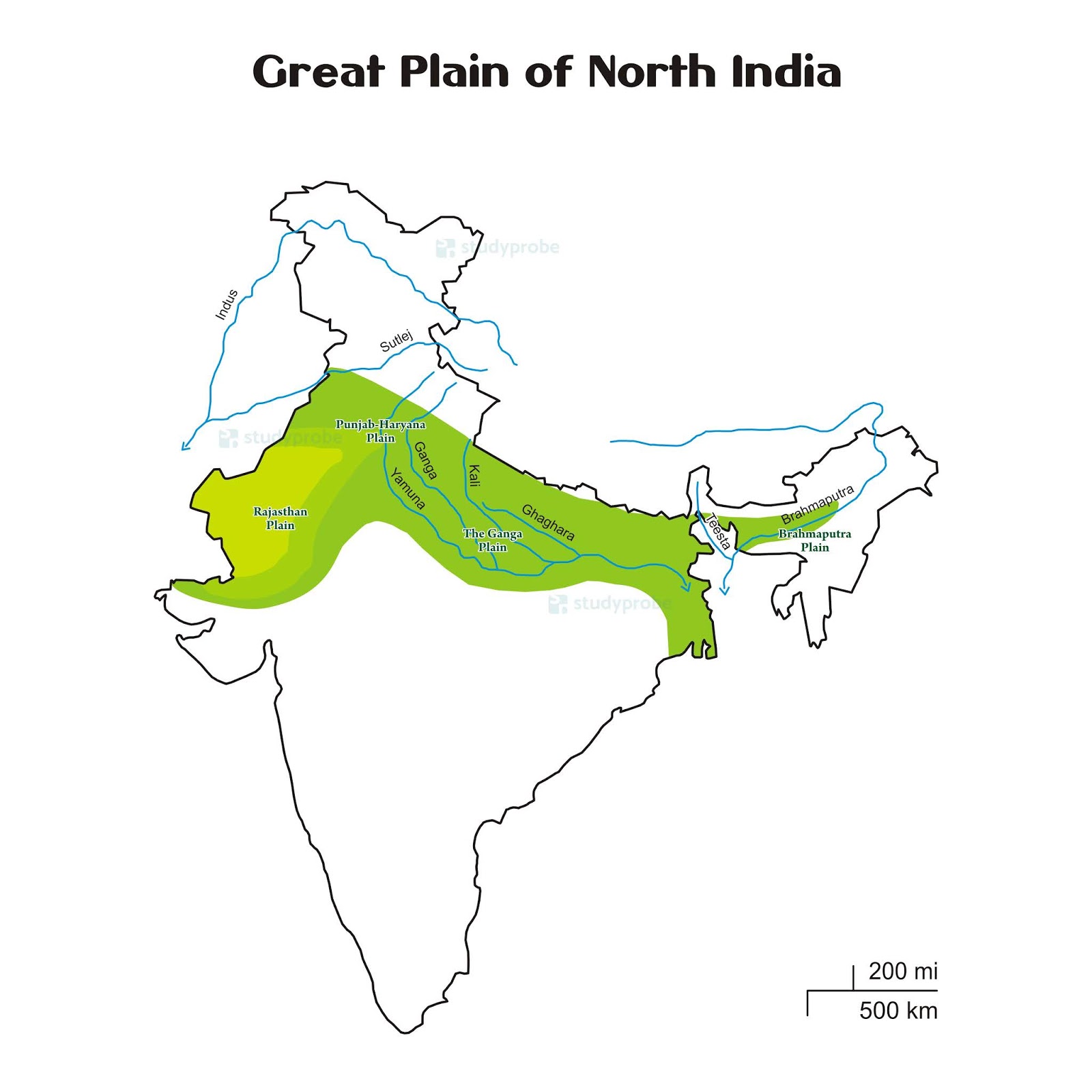
Indo-Gangetic Plain, extensive north-central section of the Indian subcontinent, stretching westward from (and including) the combined delta of the Brahmaputra and Ganges (Ganga) rivers to the Indus River valley. The region contains the subcontinent's richest and most densely populated areas. North India is a well-defined region of the northern part of India. The Indus-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas are the important geographical features of this region and delimitate it from. Northern plains of India or Indo-Gangetic plains form the second largest physiological division of India with an approximate area of 21 percent of the total geographic area of India. The Ganga, Indus and Brahmaputra flow through these plains and provide plenty of water for irrigation. North India, also called Northern India or simply the North, is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia.

North Indian Plain Map
North Indian Plain - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia North Indian Plain The North Gangetic Plains of India, Bangladesh and Nepal. The Ganges River is in the middle of the plains. Northern Plains of India Importance, Features, Maps And States Madhavi Gaur September 05, 2023 12:02 2277 0 Blogs The Northern Plains of India are made by the mud and sand carried by rivers like Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra. If you want to know more about the Northern Plains of India, check out this article. Table of Contents The great plains of northern India, also known as Ganga-Satlej Plains, are, in fact, transitional belt between the Himalayas and Peninsular India. The great plains cover an area 7,74,000 km 2 (3,00,000 square miles) having west-east length of 2400 km and north- south width of 144 km. Except Aravallis in the Rajas than plains no part of these. Plains of Northern India, also known as the Gangetic Plains, is situated in the southern Himalayan Region. The Northern Plains spreading from Assam to Punjab has a length of around 2400 km and the width ranges between 150 km to 300 km, varying in different regions. It can be found in Bihar, Punjab, Assam, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, parts of.

Give an account of the Northern Plains of India? CBSE Class Notes Online Classnotes123
The Northern Plains are developed by alluvial sediments carried by the rivers Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra. These plains stretch for around 3,200 kilometres from east to west. The typical. A significant physical division of India, the Great North Indian Plains plays a pivotal role in Indian geography and competitive exams like UPSC, IAS etc. Featuring as one of the most fertile landmasses on the Indian territory, these plains are suitable for farming, cultivation, crop production, and other agricultural activities.
Home » Indian Geography » Physical Geography of India » Northern Plain Northern Plain The great plains are the outcome of alluvial deposits brought from rivers originating in Himalayan and Peninsular regions.These plains extend approximately 3,200 km from the east to the west. These plains extend from the western regions of Jammu and Kashmir and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the eastern state of Assam, encompassing a significant portion of Northern and Eastern India. These plains serve as the primary drainage area for the rivers, playing a crucial role in the region's hydrology.

Learn about Indian Plains. Memorize the division of Indian plains using visualization. in 2020
Northern plains are the youngest physiographic feature in India. They lie to the south of the Shivaliks, separated by the Himalayan Frontal Fault (HFF). The southern boundary is a wavy irregular line along the northern edge of the Peninsular India. On the eastern side, the plains are bordered by the Purvanchal hills. The Northern Plains | Part 1 1 Comment The northern plains have been formed by the interplay of the three major river systems, namely the Indus, the Ganga, and the Brahmaputra along with their tributaries. This plain spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 Km long and 240 to 320 Km broad, is a densely populated physiographic division.



