The 50 highest summits of India with at least 500 meters of topographic prominence River map of India West India Rivers Major River Basins in India East India Rivers North India. 15 Comments Mountain Ranges in North India - North to South Mountain Ranges in Central India - West to East Chota Nagpur Plateau - North to South Mountain Ranges in North East India Western Ghats Mountains - North to South Eastern Ghats Mountains - North to South Mountain Ranges in India (with few Details) CARDAMOM HILLS :
IndiaPhysiographyNorthern and Northeastern Mountains
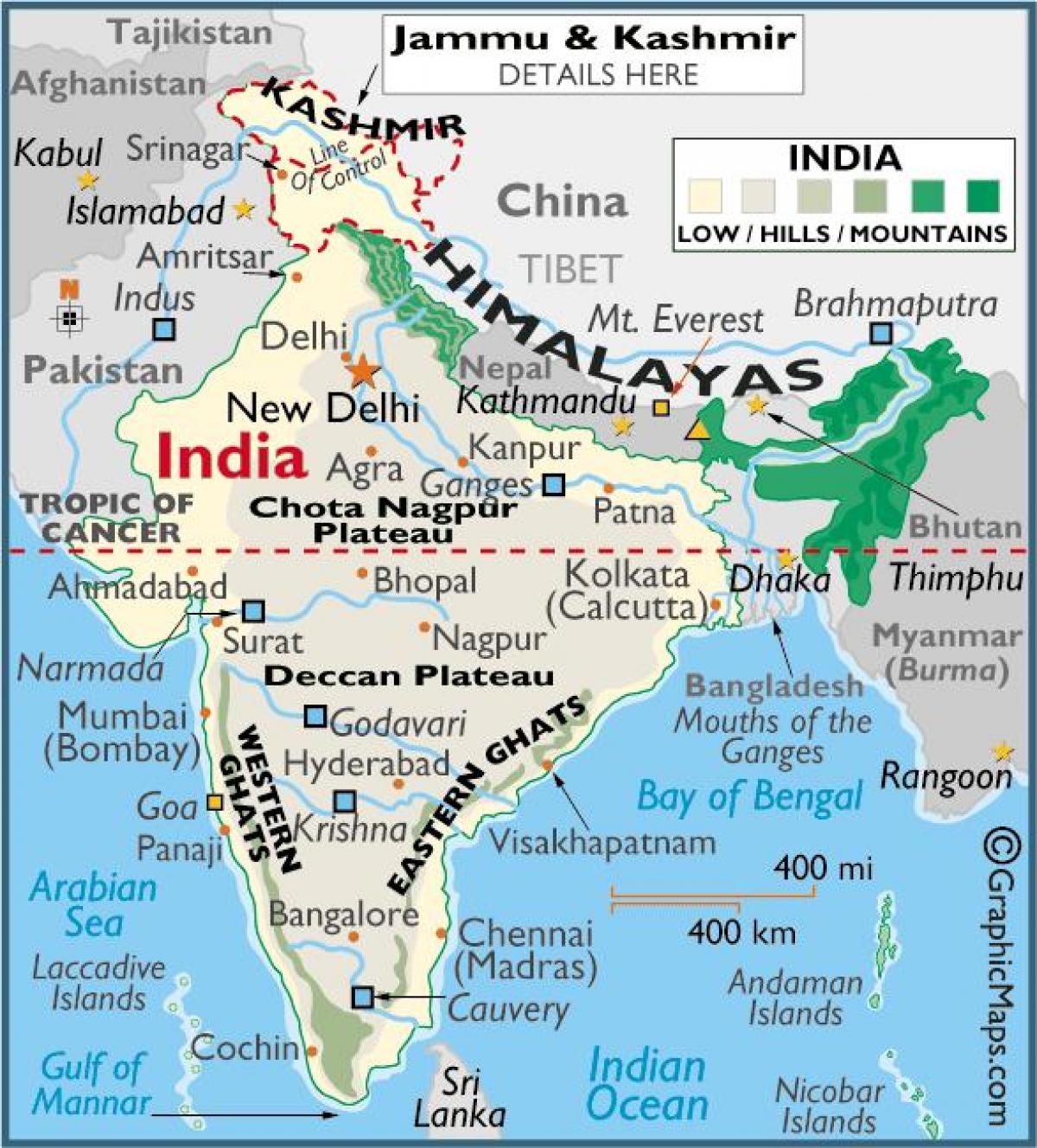
The Aravalli Range. Aravalli Range, also spelled Aravali Range, hill system of northern India, running north-easterly for 350 miles (560 km) through Rajasthan state. Isolated rocky offshoots continue to just south of Delhi. The AravalliRange is the eroded stub of a range of ancient folded mountains. It stretches for over 1,200 miles along India's northern border, all the way from Jammu and Kashmir in the West (where it's bounded by the Indus River) to Arunachal Pradesh in the East. The section in Sikkim has the loftiest peaks, with Mount Kanchenjunga being the third highest peak in the world at 28,169 feet above sea level. Highest Mountain Ranges in India 1. Kangchenjunga Peak India's highest mountain peak is called Kanchenjunga. The mountain is the third tallest in the globe. It is tall, rising to a height of 8,586 metres (28,169 ft). Kanchenjunga's name translates to "The Five Treasures of Snows" (namely gold, silver, gems, grain, and holy books). The Great Mountains of the North: India comprises the Himalayas in the North and North-eastern region, separating the country from the Tibetan plateau. The Himalayan region consists of.
Mountains in India map Map of mountains in India (Southern Asia Asia)
Northern Mountains - INSIGHTSIAS Home » Indian Geography » Physical Geography of India » Physiographic division of India » Northern Mountains Northern Mountains Origin Himalayas are the outcome of collision between Indian plate and Eurasian plate. During cretaceous period Indian peninsula broke away from Gondwana and started its northward journey. These mountain ranges lies in the central India and runs parallel to right bank of Narmada river and Indians treat it as an informal boundary between north and south India. Vindhyas acted as a major barrier against trade, migration and conquest between north and south in past times. The Aravalli Range (also spelled Aravali) is a mountain range in Northern-Western India, running approximately 670 km (420 mi) in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu at 1,722 m (5,650 ft). The Aravalli Range is arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth. The most dominant mountain ranges in the country are the Himalayan Mountain Ranges. The Northern side of the Indian Subcontinent is defined by the Himalaya Mountains, the Hindukush and the Patkai Ranges. Himalaya Mountains are the highest mountain range in Asia that separates India from the Tibetan plateau. It is known as the King of mountains.

Mountains of India Infographics UPSC Exam Preparation Geography Infographic, Exam preparation
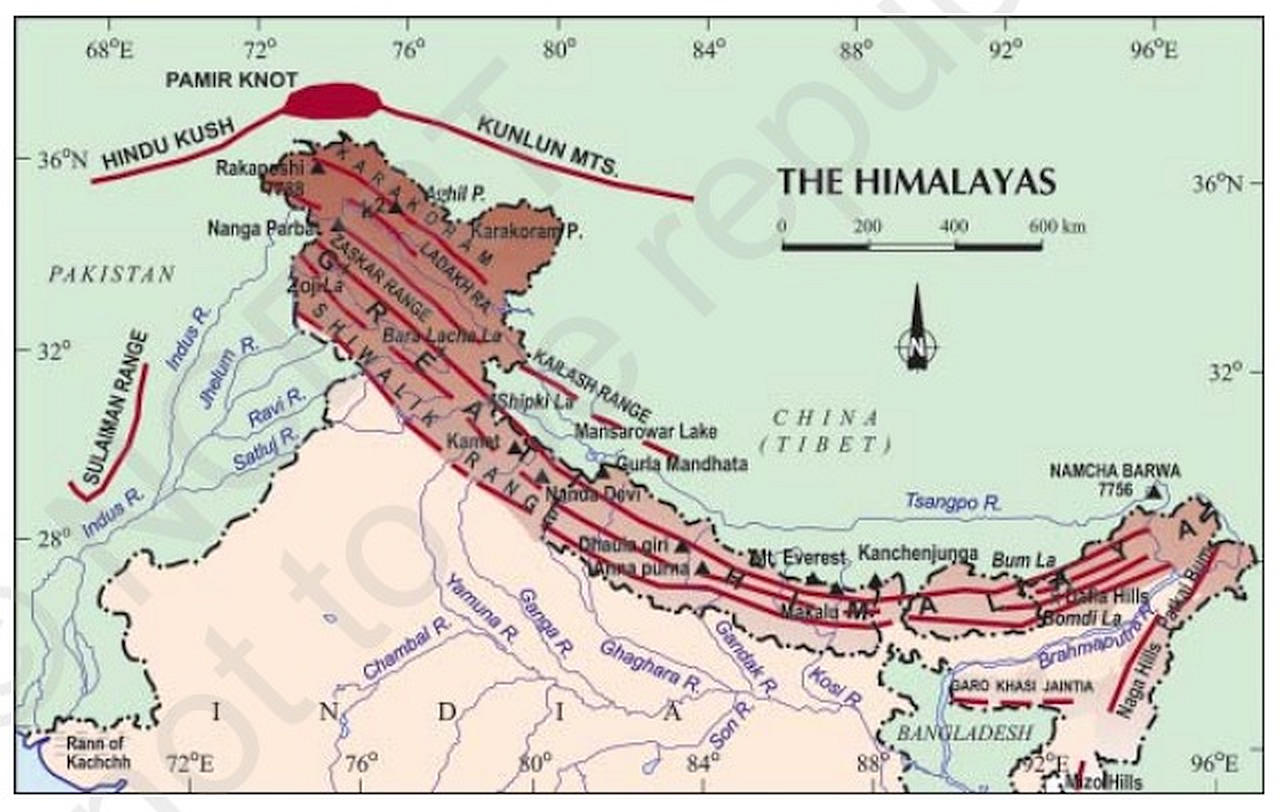
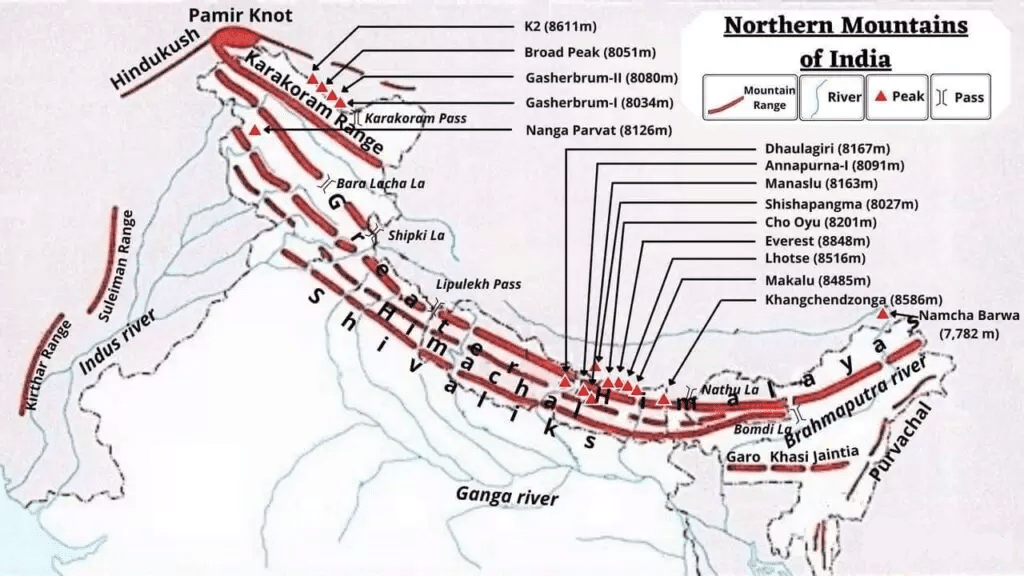
The Northern Mountains (Himalayas) The Himalayan Mountains form the northern mountain region of India. They are the highest mountain ranges in the world. These mountain ranges start from Pamir Knot in the west and extend up to Purvanchal in the east. Youngest & Loftiest Mountain range of the world Formed by Tectonic Forces & are 2400 Km in Length River Indus originates from the northern slopes of the Kailas range. The northern most range of the Trans-Himalayan Ranges in India is the Great Karakoram Range also known as the Krishnagiri range. Karakoram Range extends eastwards from the Pamir for about 800 km. It is a range with lofty peaks [elevation 5,500 m and above].
Maps of India - India's No. 1. Stretching for more than 2,500 km from the East to West, and 250 km to 400 km from South to North, the Himalayan Mountain Ranges are one of the natural wonders of. The northern Indian subcontinent is surrounded by a great arc of mountains, consisting of the Himalayas, Hindu Kush and Patkai ranges. Mountains in these ranges include some of the world's tallest mountains and they also act as a natural barriers to cold polar winds and facilitate the monsoon winds, both having a significant impact on the climate of India.
Important Mountain Peaks In India UPSC
List of mountains in India - Wikipedia List of mountains in India Map all coordinates using: OpenStreetMap Highest major summits in India Other significant mountains Agastyamalai Anamudi Anginda Apharwat Peak Bamba Dhura Bandarpunch Betlingchhip Blue Mountain Brammah Burphu Dhura Chandrashila Changuch Chaudhara Chiring We Churdhar Deo Tibba Deomali Lesser Himalayas of the Himalayan mountain ranges in North India are formed 2-5 million years back. The average height of these mountains range from 3700 m to 4500 m and their average width is 50 km. These mountains are covered with snow only during winter. In summer, they have cool and pleasant climate.




