The 50 highest summits of India with at least 500 meters of topographic prominence. Rank. Mountain. Height (M) Range. Prominence. State Name. 1. Kangchenjunga. The Transhimalaya is a 1,600-kilometre-long (990 mi) mountain range ,extending in a west-east direction parallel to the main Himalayan range. Located north of Yarlung Tsangpo river on the southern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The Trans-Himalayas, mainly composed of granites and volcanic rocks.

Northern mountains of India map Northern mountain ranges of India map
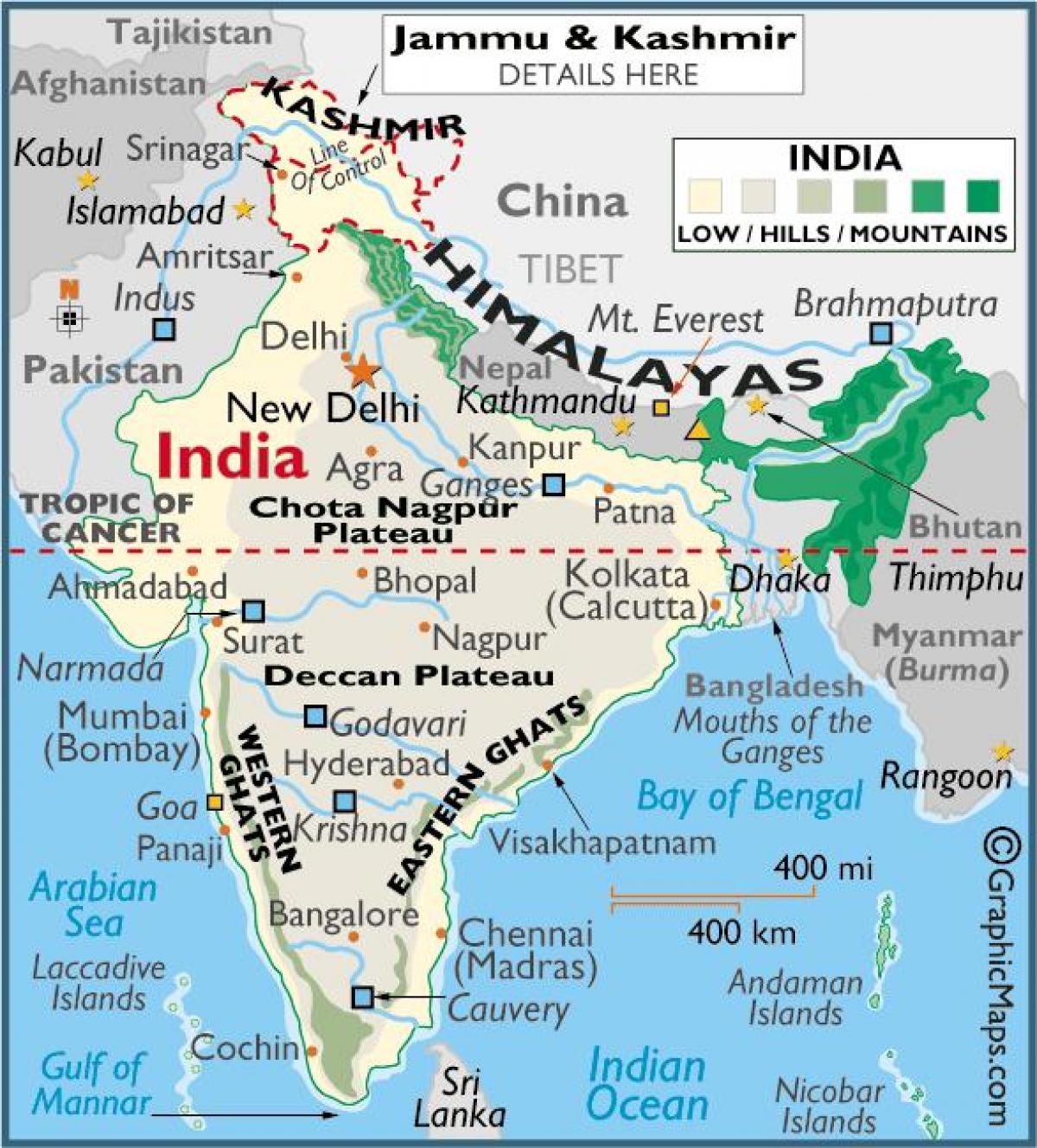
India - Himalayas, Subcontinent, Diversity: The Himalayas (from the Sanskrit words hima, "snow," and alaya, "abode"), the loftiest mountain system in the world, form the northern limit of India. That great, geologically young mountain arc is about 1,550 miles (2,500 km) long, stretching from the peak of Nanga Parbat (26,660 feet [8,126 metres]) in the Pakistani-administered portion of. In India, the Karakoram's highest peak is Saltoro Kangri in the Saltoro mountain range, at 25,400 feet above sea level. The five peaks of Saser Kangri, in the Saser Muztagh range, are not far behind with the tallest having an elevation of 25,171 feet. Mamostong Kangri, in the remote Rimo Mustagh ranges around Siachen Glacier is 24,659 feet. The Northern Mountains (Himalayas) The Himalayan Mountains form the northern mountain region of India. They are the highest mountain ranges in the world. These mountain ranges start from Pamir Knot in the west and extend up to Purvanchal in the east. Youngest & Loftiest Mountain range of the world; Formed by Tectonic Forces & are 2400 Km in Length The parts of India in brown and white, lying above the yellow and green portions of this map, lie in the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) The Indian Himalayan Region (abbreviated to IHR) is the section of the Himalayas within the Republic of India, spanning thirteen Indian states and union territories, namely Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, West Bengal, Manipur.
Mountains in India map Map of mountains in India (Southern Asia Asia)
Summits of India with at least 500 meters of topographic prominence; Rank India Rank (world) Name Height (m) Height (ft) Range Prominence (m) Coordinates State 1 3 Kangchenjunga: 8,586 28,169 Himalayas: 3,922 Sikkim: 2 23 Nanda Devi: 7,816 25,643 Garhwal Himalaya The Aravalli Range. Aravalli Range, also spelled Aravali Range, hill system of northern India, running north-easterly for 350 miles (560 km) through Rajasthan state. Isolated rocky offshoots continue to just south of Delhi. The AravalliRange is the eroded stub of a range of ancient folded mountains. Himalayan mountain ranges. Himalayas, great mountain system of Asia forming a barrier between the Plateau of Tibet to the north and the alluvial plains of the Indian subcontinent to the south. The Himalayas include the highest mountains in the world, with more than 110 peaks rising to elevations of 24,000 feet (7,300 metres) or more above sea. Great Himalayas, highest and northernmost section of the Himalayan mountain ranges. It extends southeastward across northern Pakistan, northern India, and Nepal before trending eastward across Sikkim state (India) and Bhutan and finally turning northeastward across northern Arunachal Pradesh state (India); throughout nearly all of its length it adjoins to the north the southern Tibet.
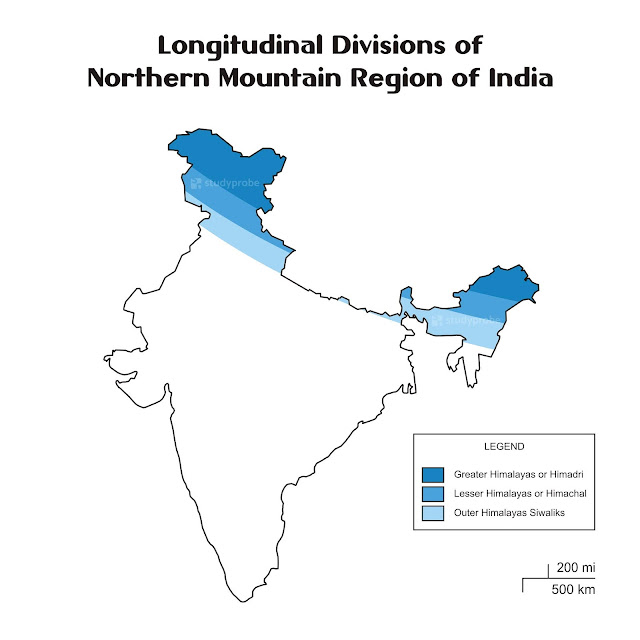
Indian Physiography Northern Mountains of India
India can physiographically be divided into the Northern Mountains, the Northern Plains, the Peninsular Plateau and the Coastal Plains and Islands. Northern Mountains of India are made up of Himalayan mountain complex extending from Pamir Knot in the west to Purvanchal in the east. The location of the Northern mountain ranges mostly lie between India and China. The most dominant mountain ranges in the country are the Himalayan Mountain Ranges. The Northern side of the Indian Subcontinent is defined by the Himalaya Mountains, the Hindukush and the Patkai Ranges. Himalaya Mountains are the highest mountain range in Asia that separates India from the Tibetan plateau. It is known as the King of mountains.
Dhaula Dhar Range - It lies south of Pir Panjal range and is characterized by snow-tipped mountains forming Beas, Ravi Chenab and Tawi valleys. East Karakoram Range - Characterized by its vastness, it separates India with Central Asia and connects Leh, Yarkand and Kashgar. Here, the highest peaks are Rimo, Saltoro Kangri and Teram Kargari. Here let's take a look at physical map of India and the other primary physical geography of India. India is a geographically rich and diverse country. Our country has all the features that one expects from a country. It has deserts, coastal areas, mountains and plateaus.. The Great Mountain of North. The key mountain of the North is the.

Physiographic Divisions of India The Himalaya Geography Frontier IAS
The Northern Mountain Ranges are one of the most beautiful places in India. It is also one of the most popular tourists' destinations in the whole India. The Northern Mountain Ranges of India has many highest mountain peaks and Mt. Everest, the tallest mountain in the whole world is also situated here. The northern mountain system in India is divided into three parts: The Himalayas, The trans-Himalayas, and The Purvanchal Hills; Himalayas. Himalayas run from the west (Indus) to the east (Brahmaputra) direction along the northern boundary of India; They cover a distance of 2500 km. Their width varies from 400 km. in the west and 150 km. in the.




