A Free Online Certificate Course On Plant Cell Technology And Plant Tissue Culture. Thousands Of Free Certificate Courses. Study Online Anytime, Anywhere & At Your Own Pace. 75 of The Top 100 Retailers Can Be Found on eBay. Find Great Deals from the Top Retailers. eBay Is Here For You with Money Back Guarantee and Easy Return. Get Your Plants Today!
4 Plant Tissue Concept Map Map Gambaran
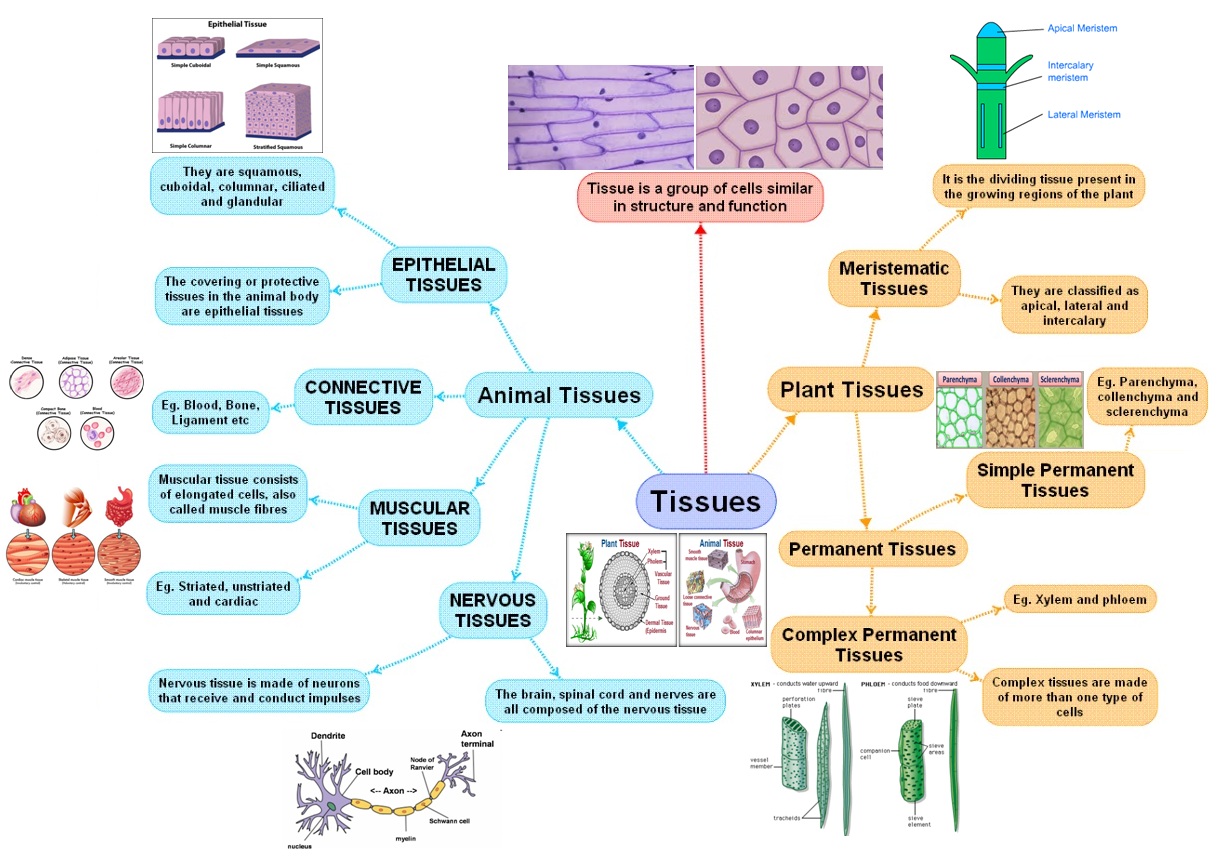
Plant tissue concept map helps students to thoroughly learn about different types of tissues in plants. This concept map makes learning more interactive. Moreover, concept mapping assists students in visualizing the relationships between various concepts and helps in understanding complex subjects. Explain Plant Tissue by Creating a Concept Map Biology is divided into different categories, like ecology, genetics, anatomy, botany, and more. Botany specifically studies plants scientifically in detail. Understanding plant types, functions, and benefits is not as simple as it sounds. Plant tissue is a collection of similar cells performing an organized function for the plant. Each plant tissue is specialized for a unique purpose, and can be combined with other tissues to create organs such as leaves, flowers, stems and roots. The following is a brief outline of plant tissues, and their functions within the plant. Figure 3.1.3.1 3.1.3. 1: Openings called stomata (singular: stoma) allow a plant to take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen and water vapor. The (a) colorized scanning-electron micrograph shows a closed stoma of a eudicot. Each stoma is flanked by two guard cells that regulate its (b) opening and closing.

biology Get Biology Science Concept Map Background
A concept map about plant tissues can significantly enhance a student's understanding of plant biology. By presenting information in an interactive, visual format, concept maps make it easier for students to grasp the connections between different concepts and simplify the learning process for complex subjects. Apply this concept to plants, and explain why plants have different types of cells and tissues. This page titled 9.12: Plant Tissues is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. Plant Tissues As for all animals, your body is made of four types of tissue: epithelial, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues. Plants, too, are built of tissues, but not surprisingly, their very different lifestyles derive from different kinds of tissues. All three types of plant cells are found in most plant tissues. The root system, which supports the plants and absorbs water and minerals, is usually underground. Figure 35.1.1.1 35.1.1. 1: Example plant organ systems: The shoot system of a plant consists of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. The root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil.

Tissue Concept Map Epithelium Tissue (Biology)
Use the dissecting needle to lift off a small piece of the soft banana tissue. Put the sample onto a petri dish or watch glass and mash it slightly using the dissecting needle (and a pencil if you want). Lift a small sample of the tissue onto a microscope slide on which you already have placed a drop of iodine solution. Put the cover slip on. A tissue is a cluster of cells, that are alike in configuration and work together to attain a specific function. Different types of plant tissues include permanent and meristematic tissues. Also Read: Tissues Meristematic tissue: These tissues have the capability to develop by swift division. They assist in the major growth of the vegetation.
Content Addressed: Specialized Plant Tissue: Primary Focus: Plants contain several types of tissues that function for growth, food and nutrient transport and storage, and protection. Concept Map. Inspiration version . GIF Image . Flashpaper; Standards. National Standards Addressed . State Standards Addressed page 75 1 0 Resource summary Plant Tissue Meristematic Tissue Apical Meristem (Growing Tip) - Tissue is present on the tips of stems and roots. - Function is to trigger the growth of new cells in young seedling at the tips of roots and shoots and forming buds. - Allows the plant to develop special structures as flowers and leaves.

Green Plant Biology Concept Map Template Concept map template, Concept map, Mind map design
A vascular tissue composed of living cells called Companion cells and Sieve cells which regulates the function of the phloem and execute this function respectively. Phloem Tissue is responsible for transporting the sugars produced through photosynthesis in the leaves of all the other parts of the plants. plant tissue is a group of cells of similar structur existed in association with one another to perform one or more specific functions Meristematic tissue permanent tissue large cells ,large vacuoles boundary or dermal tissue ground tissue vascular tissue small cells, large nucleus and have dense cytoplasm primary meristematic tissue secondary m.




