Radiation physics Jan 5, 2014 223 likes • 34,470 views Education Technology D Recommended Radiation physics 8.5K • 116 slides Line focus principle. 21.5K views • 10 slides TLD Fatma AL-Gafri 52.1K views • 40 slides Radiation Biology IAU Dent 47.3K views • 45 slides radiology-image-characteristics Parth Thakkar 46.4K views • 44 slides Objective: To familiarize the student with the basic principles of radiation physics and modern physics used in radiotherapy. Slide set prepared in 2006 by E.B. Podgorsak (Montreal, McGill University) Comments to S. Vatnitsky:
[email protected] 1.1.3 Physical quantities and units

PPT RA 220 RADIATION PHYSICS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1101144
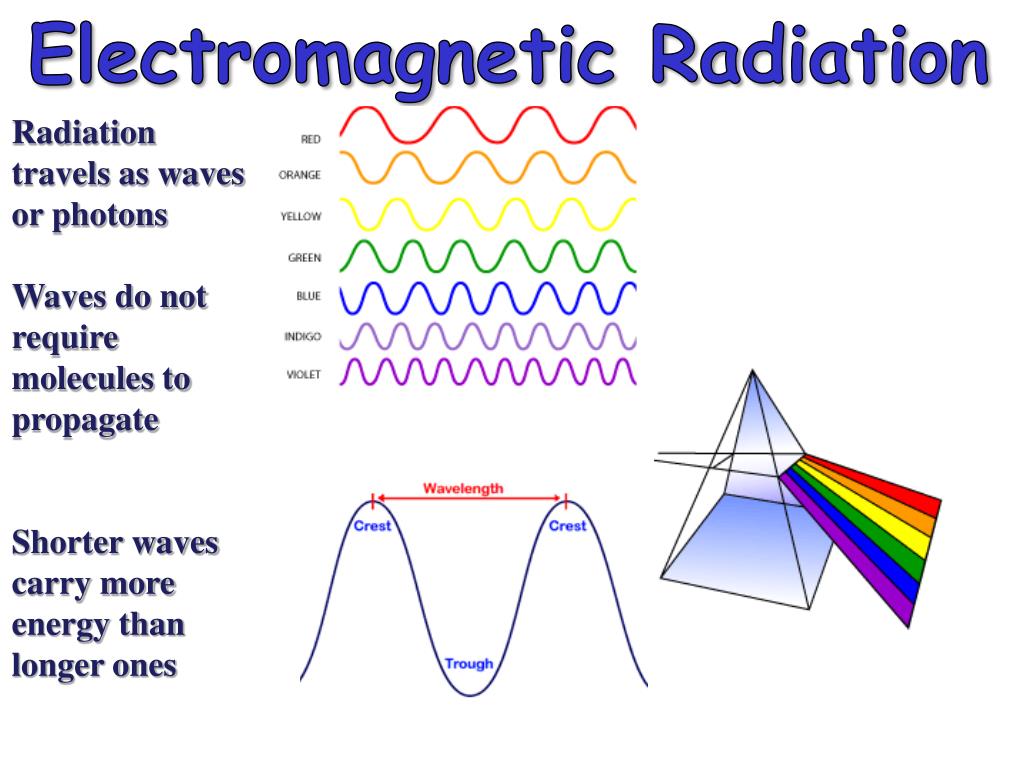
The 24 chapters include a broad coverage of topics relevant to diagnostic radiology physics, including the radiation physics, dosimetry and instrumentation, image quality and image perception, imaging modality specific topics, recent advances in digital techniques and radiation biology and protection. Radiation physics Radiation physics 1 of 116 Download Now Save slide Save slide Recommended Radiation physics DR.URVASHI NIKTE 34.5K views • 86 slides Collimation & filtration POOJAKUMARI277 20.9K views • 19 slides radiology-image-characteristics Parth Thakkar 46.5K views • 44 slides Processing of x ray film shilakandel 36.7K views • 89 slides 23. The leaded-glass housing leaded-glass vacuum tube that prevents x-rays from escaping in all directions. One central area of the leaded-glass tube has a "window" that permits the x-ray beam to exit the tube and directs the x-ray beam toward the aluminum disks, lead collimator Filtration: The sheets of 0.5 mm thick aluminum is placed in the path of the X-ray beam. Electromagnetic (non particulate) radiation is the movement of energy through space or matter as a combination of electric and magnetic fields that travel at right angles to each other. [e.g. heat; radar; radio waves, TV waves; microwaves; visible light infra red; ultra violet; cosmic rays, x-rays, gamma rays].
PPT Radiation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1417138
EL582 Radiation Physics Yao Wang, Polytechnic U., Brooklyn 7 Ionization and Excitation • Ionization is "knocking" an electron out of an atom - Creates a free electron + ion (an atom with +1 charge) - Occurs when radiated with energy above the electron binding energy • Excitation is "knocking" an electron to a higher orbit - ÐÏ à¡± á> þÿ y þÿÿÿþÿÿÿ` a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x. Types of Radiation: there are three type of radiation that can be radiated by a radioactive substance: alpha (α) particles - these are helium nuclei 4 2He. beta (β) particles - these are electron (e-) or positrons (e+) gamma (γ) particles - these are high energy photons. radiation can ionize molecules, including those in your body. Chapter 1: Basic Radiation Physics Slide set of 194 slides based on the chapter authored by E.B. Podgorsak of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students Objective: To familiarize the student with the basic principles of radiation

PPT RA 220 RADIATION PHYSICS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1102721
2 × 2 pixels and 4 × 4 pixels. 3 × 3 mm2 each. Pitch of 4 mm. A 16 × 16 pixel array of 50 × 50 mm2 (recently introduced) Blue sensitive SiPMs have detection efficiency of 25% at 400 nm, including a 60% fill factor. 6.4.3.1. Inorganic scintillators. Inorganic scintillator bandgap has to be relatively large so as to: hThe basic understanding of radiation physics is important when dealing with radiation and explaining its associated health effects. Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. A chemical element holds the same number of protons, which corresponds to its atomic number. However, depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus, the.
The IAEA has published " Radiation Oncology Physics: a handbook for teachers and students " aiming at providing the minimum level of knowledge expected of a medical physicist specializing in radiation therapy. As a complement to the publication, a set of slides following closely the material in the book has been developed. Radioactivity : It is the act of emitting radiation spontaneously from the unstable atoms. Unstable atoms differ from stable atoms because they have an excess of energy or mass or both. Unstable atoms are known as radioactive atoms. E.g. Carbon 14, Uranium 238 5.

PPT What is Radiation? PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID640474
Diapositiva 1 Chapter 3: Radiation Protection Set of 103 slides based on the chapter authored by S.T. Carlsson and J.C. Le Heron of the IAEA publication (ISBN 978-92--143810-2): Nuclear Medicine Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students Objective: To familiarize with radiation protection aspects in nuclear medicine. Radiation Physics Ppt by mohamed. Topics Radiology 1 ACU Collection opensource. Radiology 1 ACU Addeddate 2023-10-26 16:43:44 Identifier radiation-physics-ppt Identifier-ark ark:/13960/s29h1jmhzw6 Ocr tesseract 5.3.0-3-g9920 Ocr_autonomous true Ocr_detected_lang en Ocr_detected_lang_conf 1.0000 Ocr_detected_script Latin




