There are good opportunities for Rainwater harvesting in Kerala because Kerala is located in a geographical area with two rainy seasons. Kerala faces severe water scarcity between February and mid May every year. During summer, there are drinking water shortages. During this period drinking water and other water purposes become unavailable. There are several methods that have been traditionally employed in Kerala for water harvesting: Rooftop rainwater collection using clay pots. Surface runoff collection in small reservoirs. Construction of check dams across small streams. Digging pits at regular intervals along hillsides to store rainwater.

Rainwater Harvesting as Government’s Public Policy Decision Legal News / Law News & Articles
rain water harvesting. To harvest the rain water three roof rain water tanks with a total capacity of 75 000 litres has been established at ILDM in the yester years. The surface run off has been controlled by rain water pits which can hold more than 50 000 litres of water. In urban homes, an effective utilization of a system of slabs and grills will allow absorption of rainwater. This system will also avoid puddling up of water. This technique mainly requires one or two slabs and a few pipes. Usually, pipes which are about eight inches wide and one foot tall are used. It is estimated that more than 90 per cent of the rainwater in Kerala is flowing into the sea within a day or two. Kerala has surplus water during the monsoon months but shortage of water during rest of the year. For the entire state, impounding the rainfall for 44 days would be enough to supply 250 lpcd to every person in Kerala for an entire. Rainwater is collected from a roof-like surface and redirected to a tank, cistern, deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), aquifer, or a reservoir with percolation, so that it seeps down and restores the ground water. Dew and fog can also be collected with nets or other tools. Rainwater harvesting differs from storm water harvesting as the runoff.

Rainwater harvesting How long can India afford to ignore it?
The rules governing rain water harvesting in Kerala emphasize the need for appropriate design, construction, and maintenance of rainwater harvesting systems. The state government encourages individuals, households, schools, offices, hospitals and other institutions to implement rainwater harvesting techniques through incentives such as. Harvesting The Rain: How One Kerala District Is Solving Its Water Problem. Well water availability has been falling across India, and in Kerala, it fell by 10 percentage points to 62% in the decade ending 2011. In 2008, the district administration of Thrissur initiated Mazhapolima, a scheme to recharge wells through rooftop rainwater harvesting. Madakas are one of the fast disappearing traditional rainwater harvesting structures found in the laterite belts of Karnataka and Kerala. They are naturally occuring depressions with high terrain on the three sides where water from the surrounding laterite slopes, mainly runoff from the rains, is accumulated. These have been traditionally used. Mazhapolima is an open well recharge programme based on rainwater harvesting in Kerala. Facts and figures indicate that Mazhapolima was initiated in 2009 by the Thrissur district administration in collaboration with Panchayati Raj institutions to ensure water security to households. In the first 3.5 years, around 8500 open wells were recharged.

Rainwater Harvesting Project in Nepal 2015 YouTube
Rainwater harvesting is the collecting and storing of rainwater that can be used for a variety of purposes such as drinking, irrigation, and even laundry. Rooftop rainwater harvesting can be an effective and sustainable method to conserve water and reduce water bills. The benefits of rooftop rainwater harvesting are plentiful. JB Group headed by Bijomon provides best RWH consultation in Kerala. Get expert advice on the design and implementation of your rainwater harvesting system.
This despite the state government giving top priority for rain water harvesting and well recharging..Rain water harvesting in Kerala. monsoon in Kerala. water scarcity. well recharging in Kerala. summer. Mazhapolima. Palathulli Rooftops That Recharge 4.5 Lakh Wells: How Kerala's Thrissur Solved Its Water Scarcity! Awarded the Danish Water Air Food Award 2018 for offering an effective sustainable solution, Thrissur's 'Mazhapolima' initiative could teach cities like Bengaluru and Chennai a thing or two about protecting their groundwater.
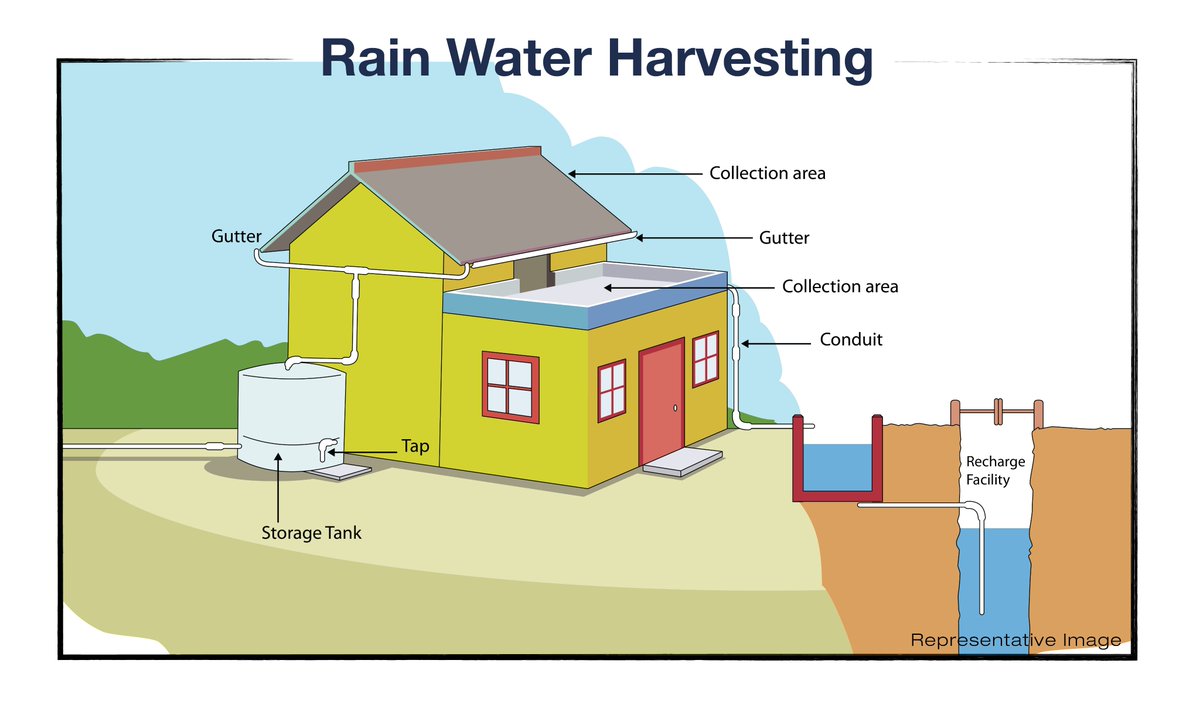
8 Important Rainwater Harvesting Components With Their Uses
Short title and commencement:- (1) These rules may be called the Kerala Municipality Building (Amendment) Rules, 2004. They shall come into force at once. 2. Amendment of the Rules.-. In the Kerala Municipality Building Rules, 1999 after Chapter XVI, the following Chapter shall be inserted, namely:-. "Chapter XVI-A. 8 Principles Of Successful Rainwater Harvesting System. 1. Be a root with keen and careful observation. For a proper Rainwater Harvesting System we have to be so careful in our observations. For a strong building we need a strong base,for a strong tree there have to be a great root searching for minerals and water.




