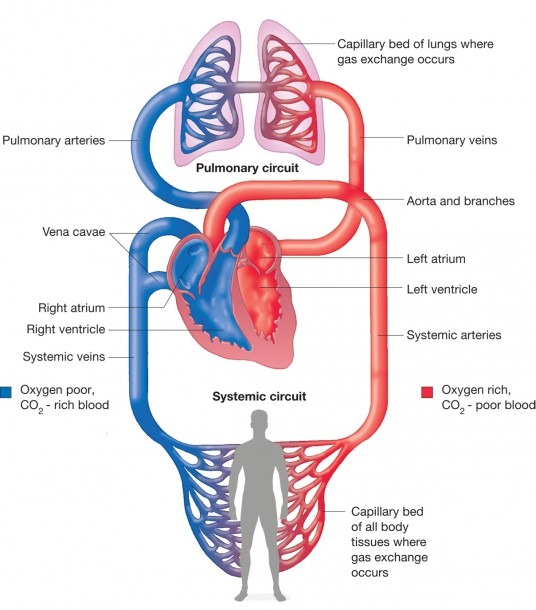
The circulatory system works thanks to constant pressure from the heart and valves throughout the body. This pressure ensures that veins carry blood to the heart and arteries transport it away. systemic circulation: The part of blood circulation that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart, to the body,. Alveoli: A diagram of the alveoli, showing the capillary beds where gas exchange with the blood occurs. Pulmonary circuit: Diagram of pulmonary circulation. Oxygen-rich blood is shown in red; oxygen-depleted blood in blue.

Double Circulation Blood Circulation in Humans BYJU'S
Diagram of the Human Circulatory System (Infographic) Infographics. By Ross Toro. published 29 August 2013. Find out all about the blood, lungs and blood vessels that make up the circulatory system. Step 1 and 6 involve a blood vessel, which makes sense as this is how blood enters and exits that side of the heart. Steps 2-5 involve a chamber, valve, chamber, and valve. So if you remember this general pattern, it will help you recall the order in which blood flows through each side of the heart. The human circulatory system consists of several circuits: The pulmonary circuit provides blood flow between the heart and lungs. The systemic circuit allows blood to flow to and from the rest of the body. The coronary circuit strictly provides blood to the heart (not pictured in the figure below). Image credit: Blood flow from the heart by. 15.3A: Anatomy of Human Circulatory System. The circulatory system is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients (such as amino acids and electrolytes), oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and.
Schematic Diagram Of Blood Circulation In Human Body
Blood then enters the left ventricle to be circulated again. Pulmonary circuit: Diagram of pulmonary circulation. Oxygen-rich blood is shown in red; oxygen-depleted blood in blue. Distribution of blood can be modulated by many factors, including increasing or decreasing heart rate and dilation or constriction of blood vessels. These comprise arteries, veins, and capillaries. The primary function of blood vessels is to transport oxygenated blood and nutrients to all parts of the body. It is also tasked with collecting metabolic wastes to be expelled from the body. Most circulatory system diagrams do not visually represent its sheer length. Schematic cross sectional diagram of the heart. Key anatomical structures are labelled and the flow of electrical activity is illustrated by the white arrows.. This closes the tricuspid valve and opens the pulmonary valve, permitting blood flow across the lungs. Oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins and into the. Figure 1 - Schematic diagram of the brain blood circulation: 1, Aortic Arch; 2, brachiocephalic artery; 3, common carotid artery; 4, posterior inferior cerebellar.

Human Circulatory System GCSE Biology Revision Notes
The cusps are pushed open to allow blood flow in one direction, and then closed to seal the orifices and prevent the backflow of blood. Backward prolapse of the cusps is prevented by the chordae tendineae-also known as the heart strings-fibrous cords that connect the papillary muscles of the ventricular wall to the atrioventricular valves.. There are two sets of valves: atrioventricular. Part 3 (Blood Platelet) — Blood platelets are the initiators of blood clotting. (d) The average life span of a red blood cell (RBC) is about 120 days. (e) Fibrinogen. Question 2. Given below is a highly schematic diagram of the human blood circulatory system.
Download scientific diagram | Schematic diagram of the blood circulatory system. There are three major types of blood vessels: arteries, veins and capillaries. Capillaries are consisted of a layer. Process of blood circulation: Deoxygenated blood from the body cells are carried by the veins to the heart. The right auricle receives the blood and pumps it (through the tricuspid valves) into the right ventricle. From here, pulmonary artery transports it to the lungs where it gets oxygenated. From the lungs the oxygenated blood is carried by.

1 A schematic diagram of the blood circulation system in the human body... Download Scientific
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve. When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. Blood Circulatory System: Types, Diagram, Working, Open vs Closed Circulation, Structure and Functions. Circulatory Systems are bodily systems used to transport nutrients, blood, gases, wastes and other materials of the body to and fro from one part to another part. Circulatory systems are present in the simplest organisms like sea sponges.




