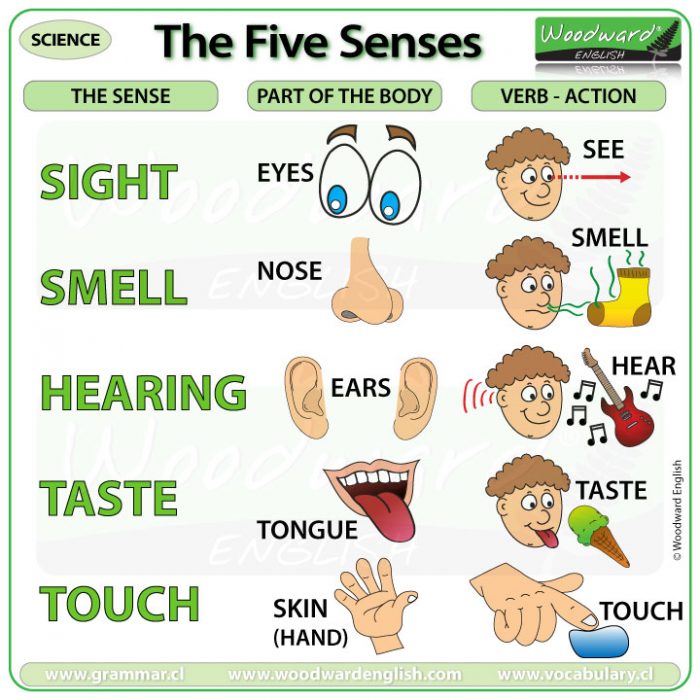
We have five sense organs, namely: Eyes Ears Nose Tongue Skin These five sense organs contain receptors that relay information through the sensory neurons to the appropriate places within the nervous system. The receptors could be classified into two parts viz. the general and special receptors. Special and General Senses. The human body has two basic types of senses, called special senses and general senses. Special senses have specialized sense organs that gather sensory information and change it into nerve impulses. Special senses include the vision for which the eyes are the specialized sense organs, hearing (ears), balance (ears), taste (tongue), and smell (nasal passages).

Sense organs/Function of the sense organs. YouTube
SENSE ORGANS HANDOUT. Sensory Receptors - receive input, generate receptor potentials and with enough summation, generate action potentials in the neurons they are part of or synapse with. 5 Types of Sensory Receptors - based on the type of stimuli they detect: Mechanoreceptors - pressure receptors, stretch receptors, and specialized. Sense Organs Organum sensuum Description Traditionally, there are five sense organs that respond to external stimuli and, in turn, relay information to the central nervous system. Special senses include vision (for which the eyes are the specialized sense organs), hearing (ears), balance (ears), taste (tongue), and smell (nasal passages).. Sound waves enter the ear through the ear canal and travel to the eardrum (see the diagram of the ear Figure 8.7.9). The sound waves strike the eardrum, and make it vibrate. We have five traditional senses known as taste, smell, touch, hearing, and sight. The stimuli from each sensing organ in the body are relayed to different parts of the brain through various pathways. Sensory information is transmitted from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system.
The Five Senses Woodward English
Much of this information comes through the sensory organs: the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Specialized cells and tissues within these organs receive raw stimuli and translate them into signals the nervous system can use. Preparation of a sense organs chart will help understand better about sense organs and their functions. Our Five Sense Organs. As discussed above, our 5 sense organs are capable of receiving and relaying sensory information to the brain. It's necessary for an organism to perceive information with the help of sense organs. There are five basic human senses: touch, sight, hearing, smell and taste. The sensing organs associated with each sense send information to the brain to help us understand and perceive the. The sensory system has two parts: the general sense and the special sense. The general sense has receptors that are present all over the body, whereas the receptors for the special sense are present in specialized organs. General senses include touch, pressure, position, and pain. Special senses include taste, smell, sight, hearing, and balance.
Muscular System Sense Organs Class 6 to 10th Std CBSE Biology Explorer YouTube
The five senses of the body are sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. The five senses of humans are perceived through the use of sensory organs. These sensory organs include eyes for sight, ears. Of course, other materials may be substituted at each station.) Your five senses — seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, and touching — help you notice the world around you. They're pretty powerful! You use your eyes to see, your ears to hear, your nose to smell, your tongue to taste, and your skin to feel.
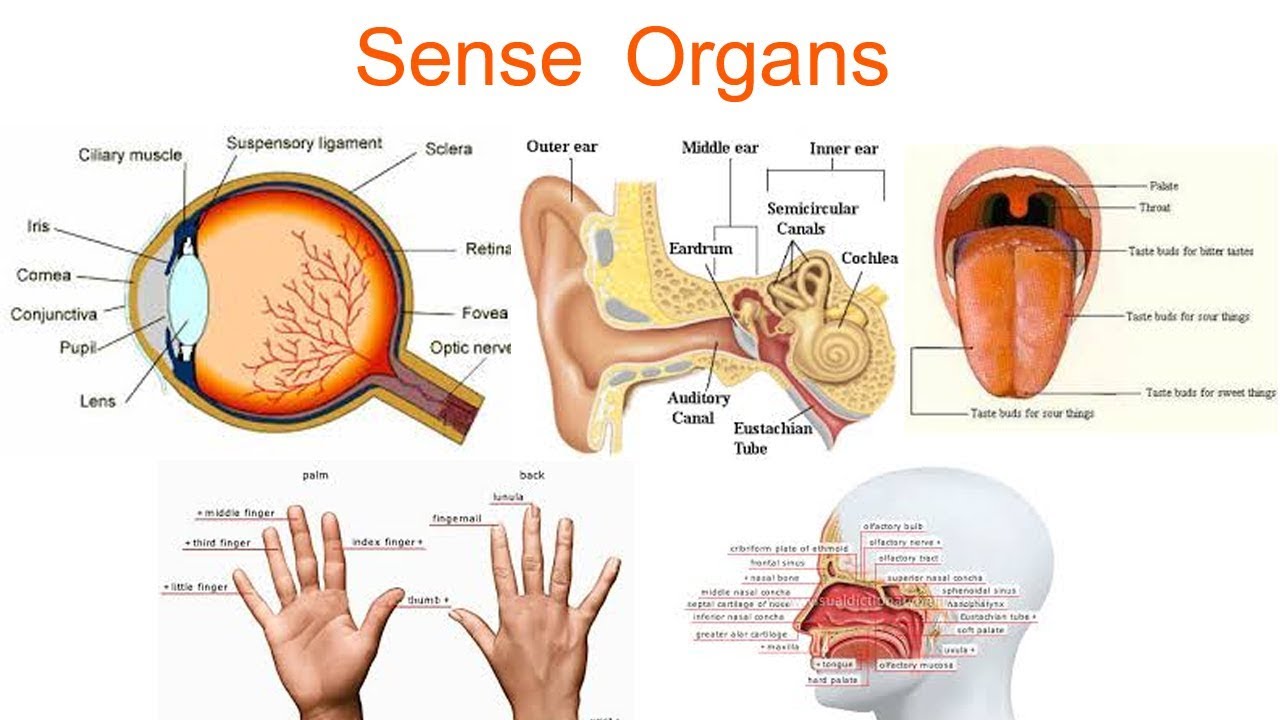
2 The sense organs 3 Touch And Pressure 4 Pain 5 Temperature 6 Awareness Of Limb Position 7 Smell 8 Taste 9 Sight 9.1 Structure of the Eye 9.2 How The Eye Sees 9.3 Colour Vision In Animals 9.4 Binocular Vision 10 Hearing 10.1 Structure of the Ear 10.2 How The Ear Hears 11 Balance 12 Summary 13 Worksheet 14 Test Yourself 15 Websites 16 Glossary Sense is the ability to understand the surroundings. Humans have a set of sensory organs. In this article, we will learn about the structure of the five sensory organs, eyes, ear, skin, nose and tongue with neatly labelled diagrams, working and functions. Set of Human Sensory Organs
Five Senses Concept With Human Organs 2391216 Vector Art at Vecteezy
GCSE WJEC The nervous system - WJEC Detecting and responding Our nervous system allows us to detect and react to changes in the environment. Sense organs, like the eyes, detect changes and. Typical of mammalian structure, the human body shows such characteristics as hair, mammary glands, and highly developed sense organs. Beyond these similarities, however, lie some profound differences. Among the mammals, only humans have a predominantly two-legged posture, a fact that has greatly modified the general mammalian body plan.




