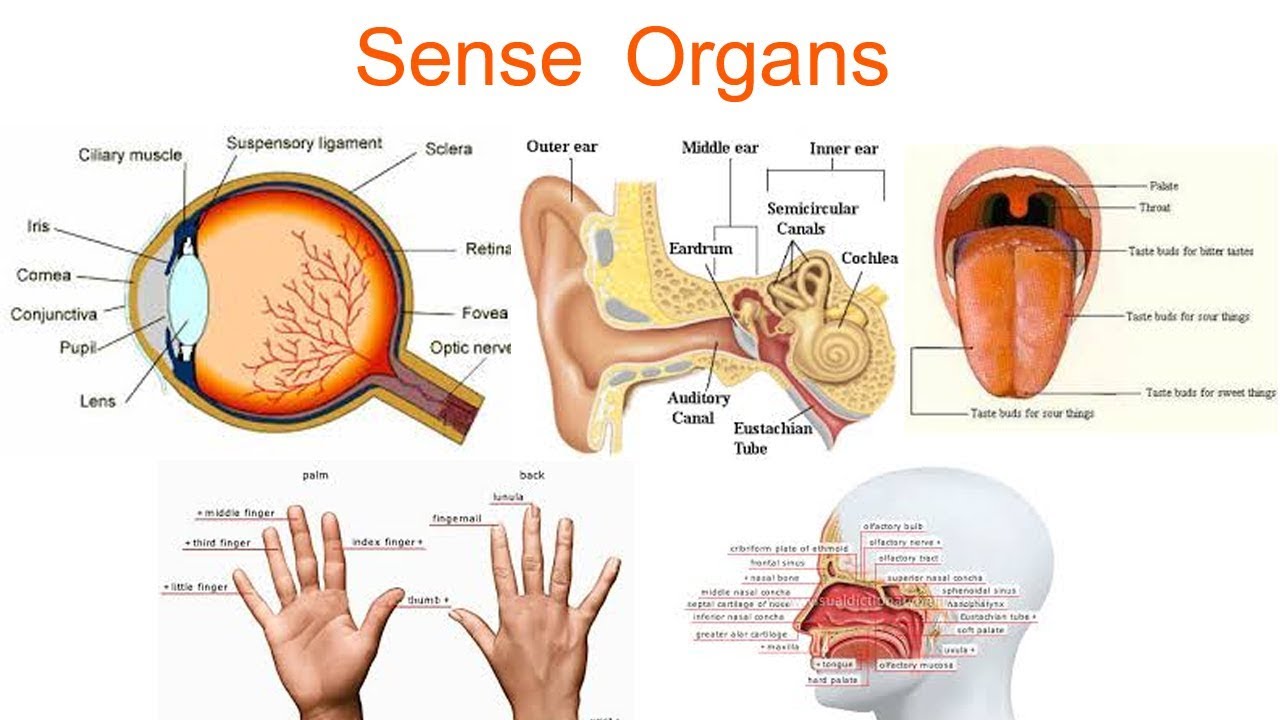
Only the semicircular canals are not involved in hearing. Instead, they sense head position, which is used to monitor balance. Hearing is the ability to sense sound waves, and the ear is the organ that senses sound. Sound waves enter the ear through the ear canal and travel to the eardrum (see the diagram of the ear in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). We have five sense organs, namely: Eyes Ears Nose Tongue Skin These five sense organs contain receptors that relay information through the sensory neurons to the appropriate places within the nervous system. The receptors could be classified into two parts viz. the general and special receptors.
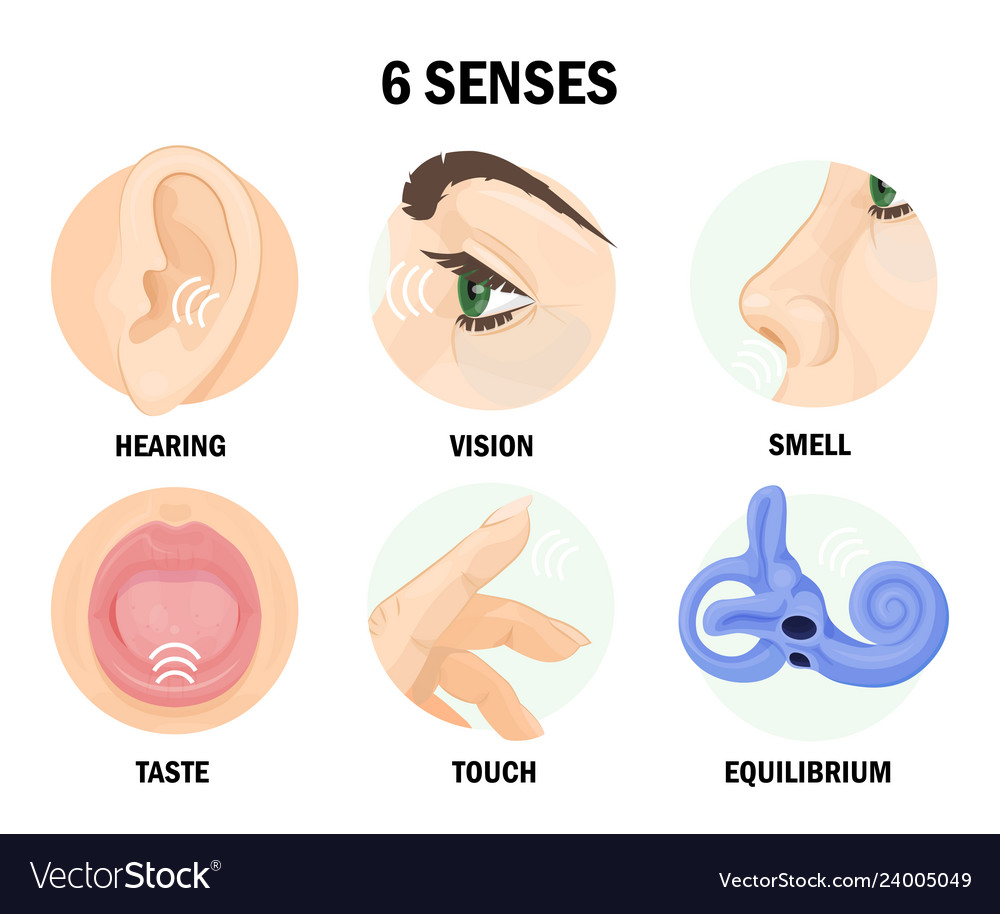
Six sense organs of human body with names Vector Image
1 SENSE ORGANS HANDOUT Sensory Receptors - receive input, generate receptor potentials and with enough summation, generate action potentials in the neurons they are part of or synapse with 5 Types of Sensory Receptors - based on the type of stimuli they detect: 1. Mechanoreceptors - pressure receptors, stretch receptors, and specialized mechanoreceptors involved Sense Organs Organum sensuum Description Traditionally, there are five sense organs that respond to external stimuli and, in turn, relay information to the central nervous system. A sensory receptor is a specialized nerve cell that responds to a stimulus in the internal or external environment by generating a nerve impulse. The nerve impulse then travels along the sensory (afferent) nerve to the central nervous system for processing and to form a response. Nerves relay the signals to the brain, which interprets them as sight (vision), sound (hearing), smell (olfaction), taste (gustation), and touch (tactile perception). 1. The Eyes Translate Light into Image Signals for the Brain to Process. The eyes sit in the orbits of the skull, protected by bone and fat. The white part of the eye is the sclera.
Muscular System Sense Organs Class 6 to 10th Std CBSE Biology
Sense Organs. All of the bodies' many sense organs are components of the nervous system. What are known as the special senses—vision, taste, smell, hearing, and balance—are all detected by specialized organs such as the eyes, taste buds, and olfactory epithelium. Sensory receptors for the general senses like touch, temperature, and pain. What the organs of sense are? The organs of sense include all the anatomical structures that receive energy of the external excitations and transform it into a nervous impulse, which is conducted to the brain. Sensory organs are organs that sense and transduce stimuli. Humans have various sensory organs (i.e. eyes, ears, skin, nose, and mouth) that correspond to a respective visual system (sense of vision), auditory system (sense of hearing), somatosensory system (sense of touch), olfactory system (sense of smell), and gustatory system (sense of taste). Those systems, in turn, contribute to vision. 2 The sense organs 3 Touch And Pressure 4 Pain 5 Temperature 6 Awareness Of Limb Position 7 Smell 8 Taste 9 Sight 9.1 Structure of the Eye 9.2 How The Eye Sees 9.3 Colour Vision In Animals 9.4 Binocular Vision 10 Hearing 10.1 Structure of the Ear 10.2 How The Ear Hears 11 Balance 12 Summary 13 Worksheet 14 Test Yourself 15 Websites 16 Glossary

Five Senses Of Human Perception Poster Icons Taste And Hear Stock
Of course, other materials may be substituted at each station.) Your five senses — seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, and touching — help you notice the world around you. They're pretty powerful! You use your eyes to see, your ears to hear, your nose to smell, your tongue to taste, and your skin to feel. Overview Test Series Sense is the ability to understand the surroundings. Humans have a set of sensory organs. In this article, we will learn about the structure of the five sensory organs, eyes, ear, skin, nose and tongue with neatly labelled diagrams, working and functions. Set of Human Sensory Organs
A collection of sensory receptors in a specialised organ or part of the body that is sensitive to a particular stimulus/stimuli. s Sensory receptor cells respond to changes in the conditions around them. This may be the internal environment of the body itself, or the wider environment in which an organism lives. Ears. Eyes. Nose. Tongue. Skin. These classic five sensory organs help in perceiving sound, light, smell, taste, and touch, respectively. Receptors present in the sense organs can transmit a signal to a sensory nerve, and these are classified into two, namely- general receptors and special receptors.

Sense organs/Function of the sense organs. YouTube
The inner layer is dermis which is made up of connective tissue. Dermis contains hair follicle and erector muscles. Dermis contains blood supply and nerve endings. The nerve endings and sense organs here are concerned with sensations of touch and pain. Dermis part of skin contains sebaceous glands and sweat glands. Humans have five special senses corresponding to specialized sense organs which are responsible for detecting and conveying sensory information to the brain for processing. Special senses include vision, olfaction (smell), audition (hearing), equilibrioception (balance) and gustation (taste).



