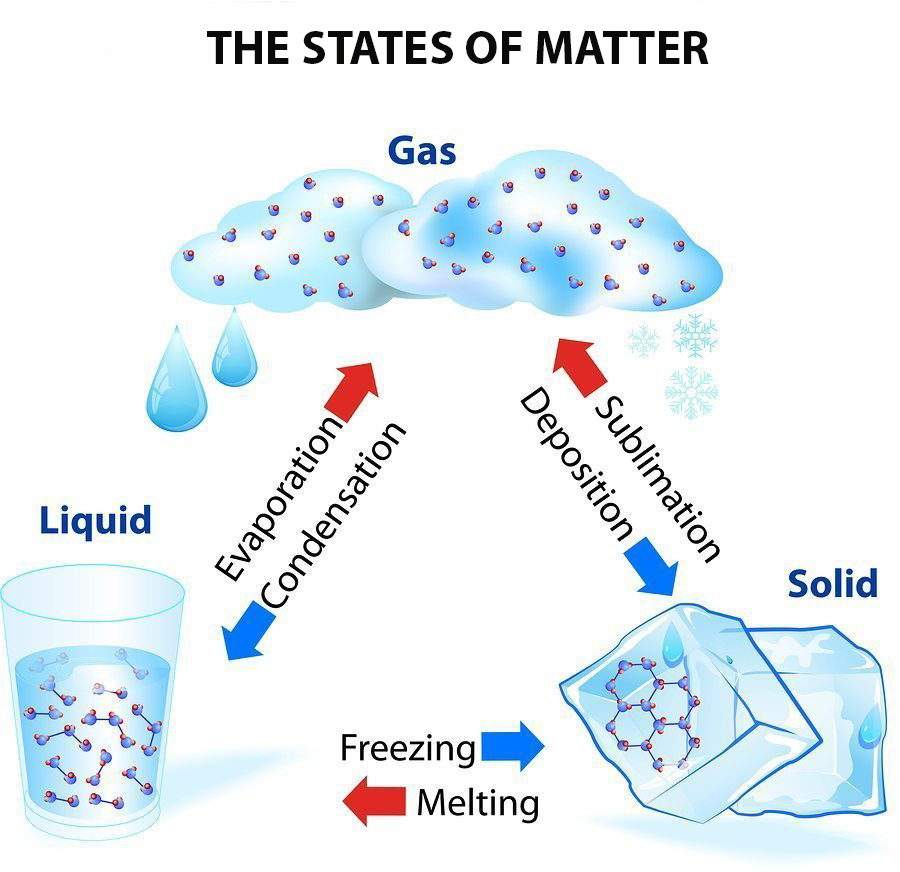
The change from solid to liquid usually does not significantly change the volume of a substance. However, the change from a liquid to a gas significantly increases the volume of a substance, by a factor of 1,000 or more. Figures \(\PageIndex{3}\) and \(\PageIndex{4}\) show the differences among solids, liquids, and gases at the molecular level. 12: Intermolecular Forces: Liquids And Solids

Premium Vector Different states of matter solid, liquid, gas vector diagram
The solid liquid line is "normal" (meaning positive sloping). For this, complete the following: 1. Roughly sketch the phase diagram, using units of atmosphere and Kelvin. Answer. 1-solid, 2-liquid, 3-gas, 4-supercritical fluid, point O-triple point, C-critical point -78.5 °C (The phase of dry ice changes from solid to gas at -78.5 °C) 2. This diagram shows the nomenclature for the different phase transitions. In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma. Liquids and Solids Phase Diagrams OpenStaxCollege [latexpage] Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the construction and use of a typical phase diagram Use phase diagrams to identify stable phases at given temperatures and pressures, and to describe phase transitions resulting from changes in these properties As we increase the temperature, the pressure of the water vapor increases, as described by the liquid-gas curve in the phase diagram for water ( Figure 10.31 ), and a two-phase equilibrium of liquid and gaseous phases remains. At a temperature of 374 °C, the vapor pressure has risen to 218 atm, and any further increase in temperature results.
Solid Liquid Gas Venn Diagram IAN by Shawn Boggs issuu
Phase Change - when a substance changes from one state of matter to another (e.g. solid to liquid, or liquid to gas) What are Phase Chase Diagrams? A phase transition occurs when a substance changes from one state of matter to another state. There are three primary states of matter: liquid, solid, and gas. A phase diagram is a plot that. States of matter include solid, liquid or gas phases. At high pressures and low temperatures, the substance is in the solid phase. At low pressure and high temperature, the substance is in the gas phase. The liquid phase appears between the two regions. In this diagram, Point A is in the solid region. PhET Global DEIB in STEM Ed Donate Watch different types of molecules form a solid, liquid, or gas. Add or remove heat and watch the phase change. Change the temperature or volume of a container and see a pressure-temperature diagram respond in real time. Relate the interaction potential to the forces between molecules. Particles in a: gas vibrate and move freely at high speeds. liquid vibrate, move about, and slide past each other. solid vibrate (jiggle) but generally do not move from place to place. Liquids and solids are often referred to as condensed phases because the particles are very close together.

Solids Liquids And Gases Images and Photos finder
What are models? Working scientifically Variables Test your knowledge Key points Almost everything is made of particles. Particles can be atoms, molecules or ions. Particles behave differently in. Suppose you have a pure substance at three different sets of conditions of temperature and pressure corresponding to 1, 2 and 3 in the next diagram. Under the set of conditions at 1 in the diagram, the substance would be a solid because it falls into that area of the phase diagram. At 2, it would be a liquid; and at 3, it would be a vapor (a gas).
physical chemistry mineralogy, and is a type of used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct (such as solid, liquid or gaseous states) occur and coexist at equilibrium AboutTranscript. In this video, we'll learn how to represent solids, liquids, and gases using particulate models. The particles in a solid are either highly ordered (if the solid is crystalline) or have no regular arrangement (if the solid is amorphous). In both cases, the motion of the particles is limited. The particles in a liquid are close.
Itinerant Mission 3 Physical States of Matter Solid Liquid Gas
Solids, liquids and gases — Science Learning Hub Article Solids, liquids and gases Resource Related topics & concepts Add to collection Water is the only common substance that is naturally found as a solid, liquid or gas. Solids, liquids and gases are known as states of matter. For example, state, melting point, conductivity, etc. of solids, liquids and gases.. The particles in the diagrams could be atoms close atom The smallest part of an element that can exist.,.




