sp 3 d2 Hybridization FAQs What Is Hybridization? Redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms to give orbitals of equivalent energy happens when two atomic orbitals combine to form a hybrid orbital in a molecule. This process is called hybridization . There are no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. To bond six fluorine atoms, the 3 s orbital, the three 3 p orbitals, and two of the 3 d orbitals form six equivalent sp3d2 hybrid orbitals, each directed toward a different corner of an octahedron. Other atoms that exhibit sp3d2 hybridization include the phosphorus atom in PCl6−,PCl6−,

Hybridization Definition, Types, Rules, Examples
Steps to Find Hybridization The chemical process involves the reaction between two or more than two atoms. In chemistry, hybridization is the idea of combining two atomic orbitals to create a brand-new category of hybridized orbitals. Typically, this mixing creates hybrid orbitals with completely distinct energies, morphologies, etc. Hybridization About Transcript In sp³ hybridization, one s orbital and three p orbitals hybridize to form four sp³ orbitals, each consisting of 25% s character and 75% p character. This type of hybridization is required whenever an atom is surrounded by four groups of electrons. Created by Jay. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted The Dreamer 9 years ago Intermixing of one 's', three 'p' and two 'd' orbitals of almost same energy by giving six identical and degenerate hybrid orbitals is called sp 3 d 2 hybridization. These six sp 3 d 2 orbitals are arranged in octahedral symmetry by making 90° angles to each other. Instead of three p orbitals and one s orbital, there are four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. Hybrid orbitals are extremely useful for explaining the characteristics of bonds, as well as predicting the geometry of different molecules. The latter makes use of VSEPR theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion).

What is Hybridization? sp3, sp2, Examples and Formula
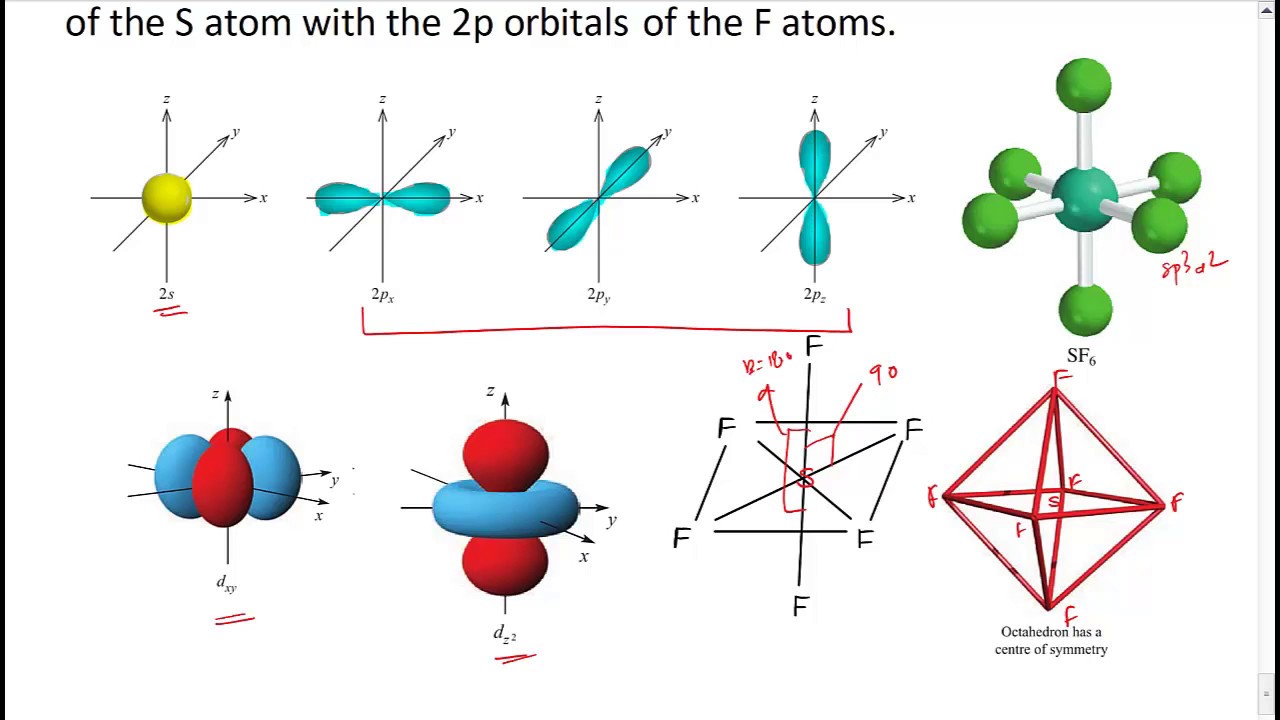
July 30, 2019 sp 3 d Hybridization sp 3 d hybridization is shown in phosphorus penta chloride (PCl 5 ). The grounds state and the excited state outer electronic configurations of phosphorus (Z=15) are represented below. sp hybridization examples (Beryllium chloride, BeCl 2; Acetylene, C 2 H 2) sp 2 (Boron trichoride, BCl 3; Ethylene, C 2 H 4) sp 3 (Methane, CH 4; Ethane, C 2 H 6) sp 3 d (phosphorus pentachloride, PCl 5) sp 3 d 2 (sulfur hexafluoride, SF 6) sp 3 d 3 (Iodine heptafluoride, IF 7) Once again, a linear geometry with a bond angles of 180 degrees. Let's do one more example using steric number to analyze the molecule. Let's do carbon dioxide. If we wanted to figure out the hybridization of the carbon there. Let's go ahead and do that. Using steric number. The hybridization of this carbon. The sulfur atom in sulfur hexafluoride, SF 6, exhibits sp3d 2 hybridization. A molecule of sulfur hexafluoride has six bonding pairs of electrons connecting six fluorine atoms to a single sulfur atom. There are no lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. To bond six fluorine atoms, the 3 s orbital, the three 3 p orbitals, and two of the 3 d.
sp3d and sp3d2 hybriisation chemical bonding chemistry Neeraj dubey YouTube
0:00 / 5:47 Part 5: sp3d Hybridization with Examples (Animation) Dr. Puspendra Classes 321K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 592 views 1 year ago Hybridization - An Edu Series Complete. Trigonal hybridization in carbon: the double bond. Carbon and hydrogen can also form a compound ethylene (ethene) in which each carbon atom is linked to only three other atoms. Here, we can regard carbon as being trivalent. We can explain this trivalence by supposing that the orbital hybridization in carbon is in this case not sp 3, but is sp 2 instead; in other words, only two of the three.
Introduction. The term "sp 3 hybridization" refers to the mixing character of one 2s-orbital and three 2p-orbitals to create four hybrid orbitals with similar characteristics. In order for an atom to be sp 3 hybridized, it must have an s orbital and three p orbitals.. From wave function to the visual representation: Four equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals, resulting from the combination of one. sp Hybridization. The beryllium atom in a gaseous BeCl 2 molecule is an example of a central atom with no lone pairs of electrons in a linear arrangement of three atoms. There are two regions of valence electron density in the BeCl 2 molecule that correspond to the two covalent Be-Cl bonds. To accommodate these two electron domains, two of the Be atom's four valence orbitals will mix to.

Hybridization sp3d2 examples YouTube
sp hybridisation, usually known as diagonal hybridisation, occurs when two s & one p orbitals belonging to the same primary shell of an atom combine to generate two new identical hybrid orbitals. The molecule generated due to this hybridisation has a linear shape with an angle of 180 degrees. In this lecture discuss about the Sp3d2 hybridization will all examples. Sp3d2 Hybridization sigma and pi bond. Sp3d2 hybridization in SF6, XeF4, IF5 Gemotry.




