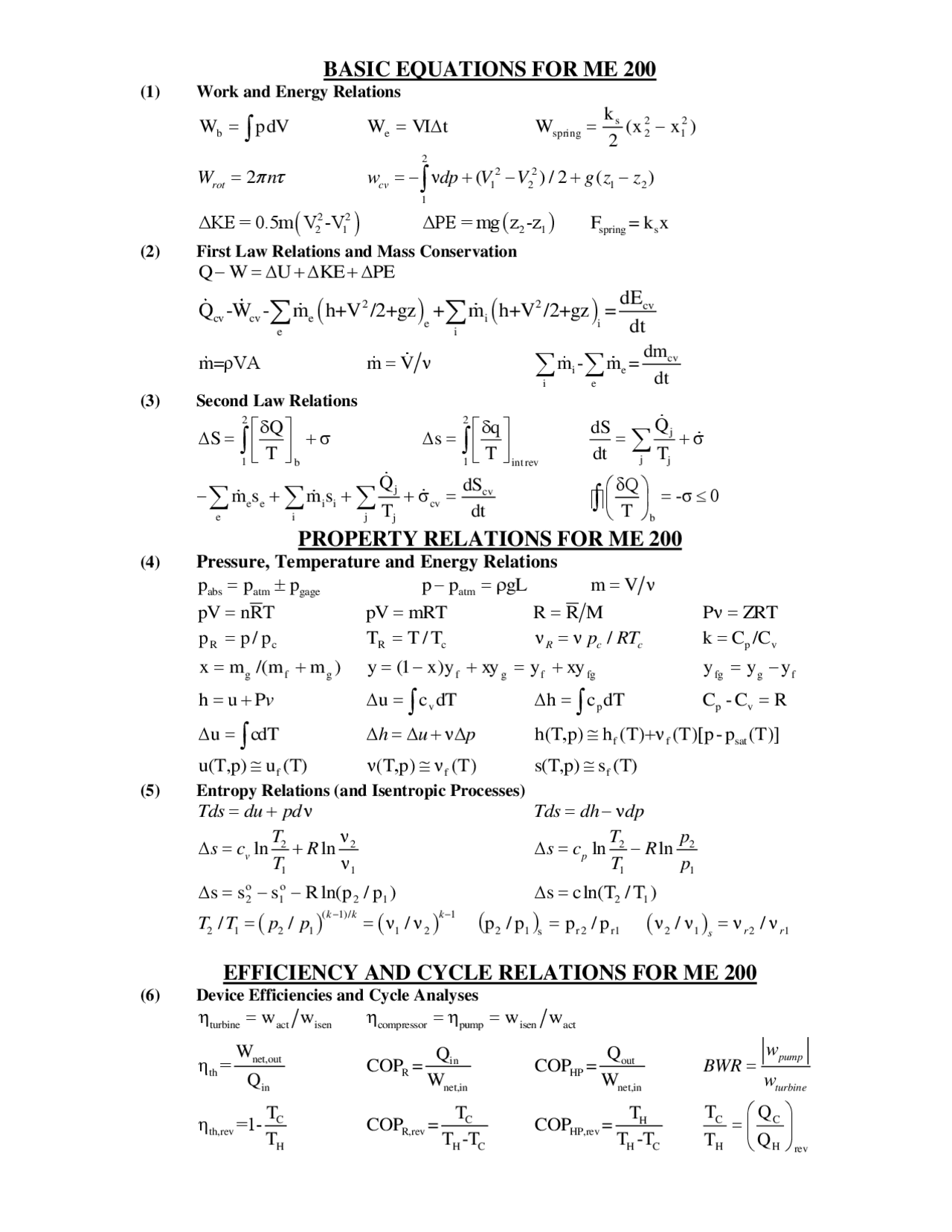
Basic Thermodynamic Formulas (Exam Equation Sheet) Control Mass (no mass flow across system boundaries) Conservation of mass: 𝑚= 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐. Conservation of energy (1st Law): 𝑄−𝑊= ∆𝐸 = ∆𝑈+ ∆𝐾𝐸+ ∆𝑃𝐸 = 𝑚 ∆𝑢+ 𝑣2 2−𝑣 1 2 2 + 𝑔(𝑧2−𝑧1) Thermodynamics Cheat Sheet Universal Gas Law The First Law Always true: For cycles: For constant volume (no work done): Work Done Always true: True for constant : True for constant : (PV is constant) True when adiabatic & reversible: (Isentropic) Shaft Work Constant Pressure Constant Volume Perfect, Adiabatic & Reversible (Isentropic) is constant:
Equation sheet for Thermodynamics ME 2334 Docsity
Common thermodynamic equations and quantities in thermodynamics, using mathematical notation, are as follows: Definitions Many of the definitions below are also used in the thermodynamics of chemical reactions . General basic quantities General derived quantities Thermal properties of matter Thermal transfer Equations Thermodynamics equation h , = Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration , = 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) ENERGY TRANSFER BY WORK: Electrical Work: When N Coulombs of electrical charge move through a potential difference V = In the rate form, = = 2 = Where 2 ( ) Chapter 1 Formula Sheet - Thermodynamics. Chapter 3. Chapter 4. Chapter 6. Thermodynamics sounds intimidating, and it can be. However, if you focus on the most important thermodynamic formulas and equations, get comfortable converting from one unit of physical measurement to another, and become familiar with the physical constants related to thermodynamics, you'll be at the head of the class.

All Formulas Of Thermodynamics Physics Class 11 Physics Formula
Q = heat. Q = heat transferred during the process between state 1 and state 2. Q = rate of heat transfer. W = work. = work done during the change from state 1 to state 2. W = rate of work = power. 1w = 1 J/s. K = specific hear ratio. Thermodynamics - Equations. internal energy:Δ, is also shown as in many books and often on Quest) First Law of Thermodynamics(this is a mathematical version of the first law) Substances not changing phase: ==. Substances that are changing phase (transition): = =. "trans" will be one of the following: fusion, freezing, evaporation, condensation. Chapter 6 Formula Sheet. Reversible Adiabatic (Isentropic Process): Entropy decrease in process 3-4 = the entropy increase in process 1-2. Q = heat transferred during the process between state 1 and state 2. Q = rate of heat transfer. W = work. = work done during the change from state 1 to state 2. W = rate of work = power. 1w = 1 J/s. K = specific hear ratio. = constant pressure.

W Formula Thermodynamics ISPIT
Chapter 1 Formula Sheet; Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Formula Sheet; Chapter 3. Chapter 3 Formula Sheet; Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Formula Sheet; Chapter 5; Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Formula Sheet; Steam Property Tables Chapter 3 Formula Sheet - Thermodynamics. Chapter 1. Chapter 2. Chapter 3. Chapter 4. Chapter 6.
K = mv2/2 = p2/2m. WNET = K. Potential Energy. Ugrav = mgy (near earth surface) Ugrav = -GMm/r (in general) Uspring = kx2/2. E = K + U = Wnc. 1 Heat and Temperature Temp. scales: F = 32 + 9 5C; K = C + 273:16 Ideal gas equation: pV = nRT, n : number of moles van der Waals equation: p + a 2 (V b) V = nRT Thermal expansion: L = L0(1 + A = A0(1 + T); V = V0(1 + = 3
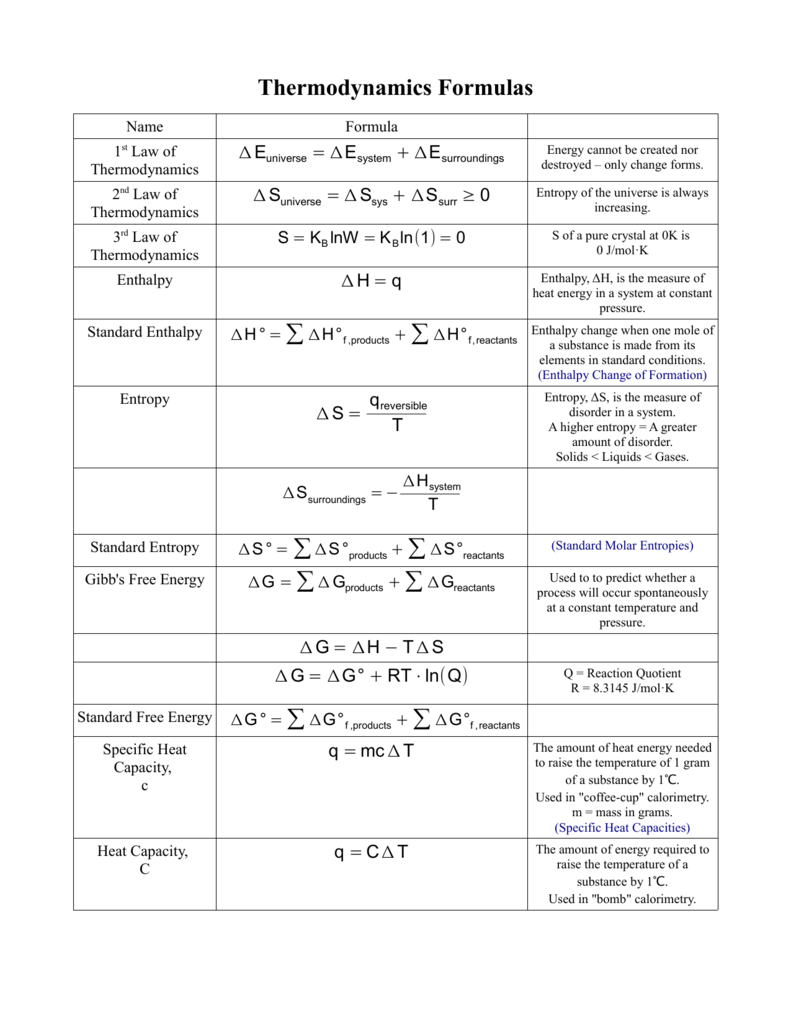
Thermodynamics Formulas
Forms of the First Law of Thermodynamics Most general forms = Q - W, e = q - w, dE = Q - W, and de = q - w Neglecting changes in kinetic and potential energy = Q - W u = q - w, dU = Q - W, and du = q - w Neglecting changes in kinetic and potential energy, in terms of enthalpy = U + pV therefore dH = dU + pdV + Vdp so dH = - W + pdV + Vdp Example: 1,000,000 Pa = 1 MPa. Newton's Second Law . Sometimes, the questions indicate weight (W) Temperature Conversion . Pressure Measurement




