Home / Concrete Technology Reading time: 4 minutes Bar bending schedule (BBS) of an concrete footing provides the reinforcement details and the total steel quantity required for the footing construction. The BBS and quantity of steel reinforcement required for a simply isolated footing are calculated and explained by means of a workout example. The material of rafts is reinforcement concrete that has the following parameters: Width of the section to be designed Section thickness Concrete cover + 1/2 bar diameter Effective depth of the section Steel bar diameter b = 1.0 t = 0.60 c = 5 d = t - c = 0.55 Φ = 25 [m] [m] [cm] [m] [mm] 3 Analysis of the footing
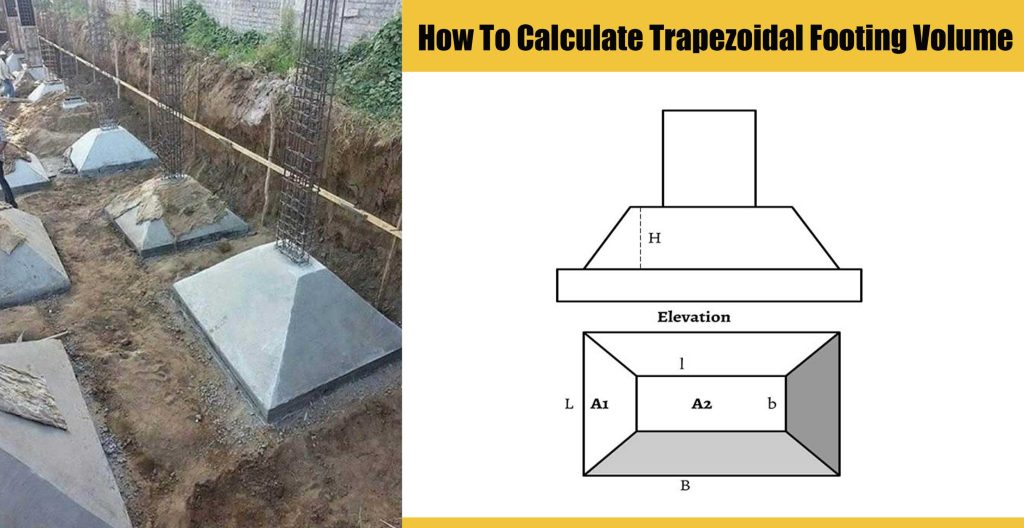
How To Calculate Trapezoidal Footing Volume Engineering Discoveries
This video explains what is a trapezoidal footing and the terminology used, the reinforcement details and the stresses acting on a trapezoidal footing. This article presents a simplified analytical model for designing irregular shaped reinforced concrete (RC) footings supporting square column and subjected to eccentric loading, that is, axial load P and biaxial moments, Mx in (x-x) axis and My in (y-y) axis, respectively. Trapezoidal footing is provided when one column load is much more than the other. As a result, the both projections of footing beyond the faces of the columns will be restricted. Rectangular footing is provided when one of the projections of the footing is restricted or the width of the footing is restricted. Rectangular combined footing trapezoidal slab type with or without a beam connecting the columns, and isolated footings connected by a beam (strap footing). Objectives

Usually, it should be examined when the footings are arranged for concreting i.e. reinforcement
A1 - Area of the lower shape A2 - Area of the upper shape Trapezoidal Footing Volume - Example Calculation Let's take this example and solve, Calculation We know the formula, Here, we have assumed square footing, V = h/3 (A1+A2+√ (A1 x A2)) { Where, A1 = 1.6 x 1.6 = 2.56 m 2 ; A2 = 0.8 x 0.8 = 0.64 m 2 } = 0.3/3 ( 2.56 + 0.64 + √ (2.56 x 0.64)) design of the trapezoidal combined footings , considering the total cost of the footing as an objective function . The cost. U Reinforcement ratio S Unit mass of steel X Poisson's ratio INTRODUCTION The combined footing is a footing that supports two or more columns. It is the most practical solution for some Save In this civil engineering video tutorial, you will learn how to prepare the bar bending schedule alias BBS of any trapezoidal footing. The reinforcement along x axis (taken as L) of the footing underneath = 1200 mm The reinforcement along y axis (taken as Y) of the footing underneath = 1500 mm The East (Section 5-5) and North (Section 3-3) walls are shown in cross section. The column footing and pier reinforcing bars are shown in schedules. In drawing wall elevations where footing steps occur, the detailer refers to the "Typical Stepped Footing" detail on the structural drawing and footing elevations on the plan view.

Types of Footings Used in Construction Structural Guide
MY NEW CHANNEL LINKhttps://www.youtube.com/channel/UClCahX62Od8WYQEGhcNgvhABrick Calculationhttps://youtu.be/WeG86W2r6AEBBS (Bar Bending Schedule) - Trapezoi. Trapezoidal footing is a type of footing that holds unequal loads from 2 columns when the heaviest load outside the column distance is restricted. It is utilized when the area of footing is fixed and the soils at the site are loose soil. 1. Formula for Calculating Trapezoidal Footing Volume
1. Concrete cover of Reinforcements According to IS 456-200, the minimum thickness to main reinforcement in footing should not be less than 50mm if footing is in contact with earth surface directly, and 40mm for external exposed face such as surface levelling PCC. #CommercialBuildingConstruction#FootingDesign#CivilTechnicalAbout this video :-Reinforcement Detail of Trapezoidal Footing | How to Read Civil Engineering Dr.
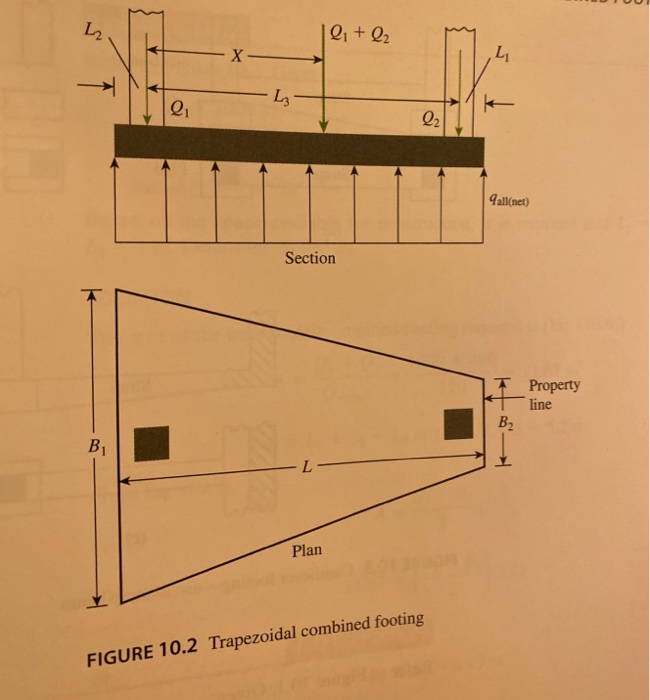
Solved 10.2 Refer to the trapezoidal combined footing in
Types of Isolated Footings Isolated footings are generally three types: Flat, Pad, Plain, or Reinforced Isolated Footing Stepped isolated Footing Sloped Isolated Footing Flat, Pad, Plain, or Reinforced Isolated Footing It is commonly square, rectangular, or circular in shape and is built separately under each column. 1. Area of footing 2. Thickness of footing 3. Reinforcement Details of footing with a satisfying moment and shear force consideration. 4. Check for development length and shearing stresses. All these things are performed on the basis of the loads on footings, safe bearing capacity (SBC) of the soil, grade of concrete and steel.




