Water-cooled condensers involve a heat rejection loop where condenser heat is dissipated to the environment via water. The most common type of water-cooled condensers in geothermal power plants are direct-contact and surface types. A water-cooled condenser diagram is a visual representation of the components and processes involved in cooling and condensing vaporized refrigerant using water as the cooling medium. The diagram typically includes labeled parts such as the condenser coil, water inlet and outlet, compressor, and expansion valve..
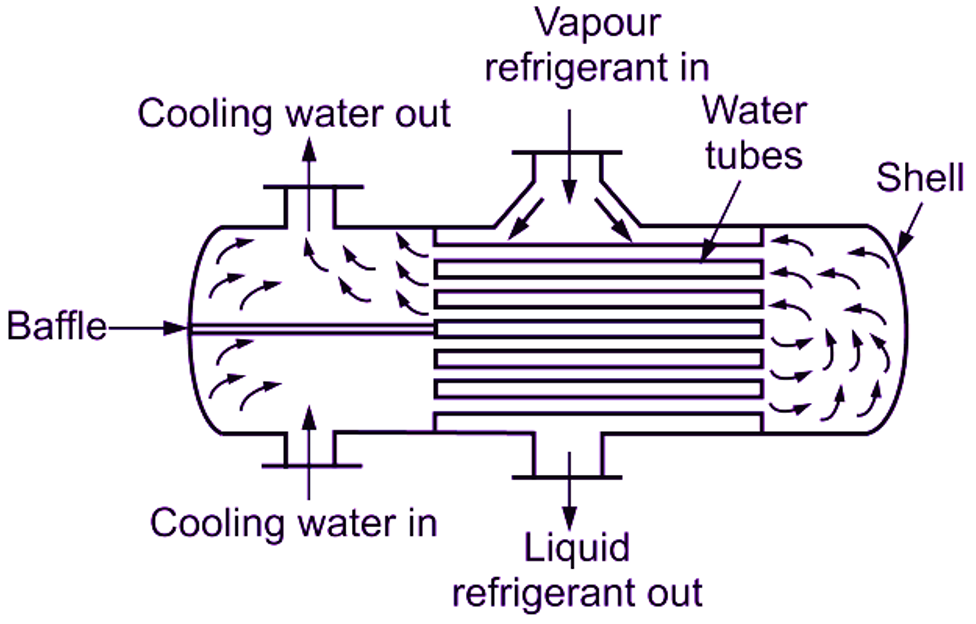
What is Shell and Tube Condenser? Working, Construction & Diagram
detailed information on water cooled condensers https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/water-cooled-condenserThe News water cooled condenser troubl. What Is a Water-Cooled Condenser? It is a technical heat exchanger used to remove heat from the refrigerant vapor and transfer it to the water running inside the tube. Water-cooling systems have seen considerable use over the years, although they are also increasing in small businesses & some residential applications. Chilled Water Schematic and Condenser water schematics. In this article we'l be covering chilled and condenser water schematics to learn how to read them, how to identify the main components and symbols as well as real world examples, additionally we'll cover the purpose of the main components and different design types. Water-cooled condenser To cool a building or process, the transferred heat must ultimately be rejected outdoors or to another system (heat recovery). The total amount of heat rejected includes the sum of the evaporator load, the compressor work, and the motor ineffi ciency. In a hermetic chiller, where the motor and compressor
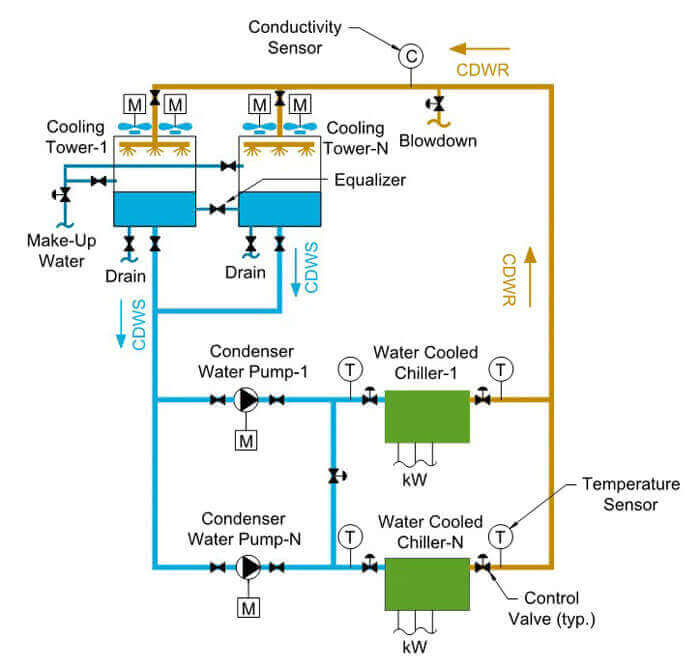
Condenser Water Pump Design Guide, How to Size and Select a Condenser
Sequence of Operation. When the operating fan(s) are operating at 50 percent speed, an additional fan shall be enabled and controlled at the same speed as the operating fans until all active cooling tower cell fans are enabled. When operating fans are running at minimum speed and the tower supply water temperature is five (5) degrees below the. Qi Fu To solve the problems of single heat source heat pump systems in severe cold regions, a dual-source hybrid heat pump unit (DSHHPU) is proposed. The mathematical models of the DSHHPU when. Figure 2 shows a typical evaporative cooler and evaporat ive condenser diagram. Figure 3 shows a typical open recirculating cooling water system; and Figure 4 shows a. does a once- through cooling water system, due to the air - and water -mixing design of the open recirculating system. These problems are associated with water-caused deposits, Condenser fouling is one of the common faults in water-cooled chillers that degrade its energy efficiency. Studies were conducted to develop fault detection and diagnostics (FDD) algorithms to.
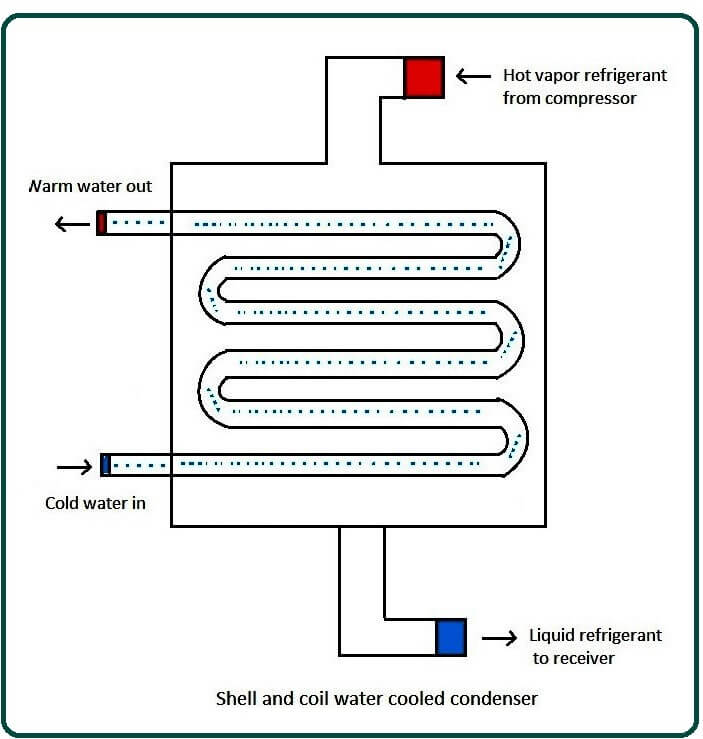
How Does a Condenser Work? Different Types of Condensers
The evaporative condenser is essentially a combination of a water-cooled condenser and an air-cooled condenser, utilizing the principle of heat rejection by the evaporation of water into an air stream traveling across the condensing coil. Water-Cooled Condensers #3: Coaxial tube-in-tube. Overview: Coaxial tube-in-tube is the third type of condenser in a water-cooled chiller. It earns its name because the tubes are coiled around the same axis. Excellent anti-fouling characteristics make these high-performance and compact heat exchangers stand out from other condenser types.
For R134a and R290/R600a, the TEWI of the system with water-cooled brazed plate heat exchanger is lower than that of the system with air-cooled condenser by 26.8% and 21%, respectively. • 12-20°F ΔT chilled water • 12-18°F ΔT condenser water CoolTools™ Chilled Water Plant Design and Specification Guide, 200011 • 15-18°F ΔT chilled water Kelly and Chan, Optimizing Chilled Water Plants, HPAC Engineering, 199912 • 18°F ΔT chilled water • 14°F ΔT condenser water 1 ANSI/ASHRAE/IES, 2016.

Surface Condenser Types Of Surface Condenser
A typical water-cooled chilled water system consists of 4 major components as below: Chiller Cooling Tower Chilled Water Pump Condenser Water Pump Each component has a lot more to talk about but, in this post, I'll give you an overview of them and explain through the chilled water system as a whole. Example 1: System Peak Diversified Load = 1000 tons. It is determined a fully redundant chiller is not required. 500 ton chillers are determined to be the best chiller selection. Provide (2) 500 ton chillers, (3) primary chilled water pumps, and (3) condenser water pumps. Example 2: System Peak Diversified Load = 1000 tons.




